Celiac Disease – Causes, Symptoms, Remedies, Ayurvedic Treatment
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Celiac disease is a disease which occurs in small intestine. It is an immune reaction to eating gluten. Therefore it is an autoimmune disorder. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley and rye. It is the substance contained in these foods which makes the dough elastic and gives the bread its chewy taste.
Read – Wheat Uses, Health Benefits, Side Effects: Complete Ayurveda Details
The immune reaction damages the inner lining of small intestine and prevents it from absorbing nutrients. This is called malabsorption. Due to the intestinal damage, diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, bloating and anemia occur. This can lead to serious complications.
When malabsorption occurs in children it hampers growth and development. The symptoms mentioned above are also present.
Other names of Celiac disease –
- Celiac sprue
- Non-tropical sprue
- Gluten sensitive enteropathy
Table of Contents
Mechanism of disease occurrence
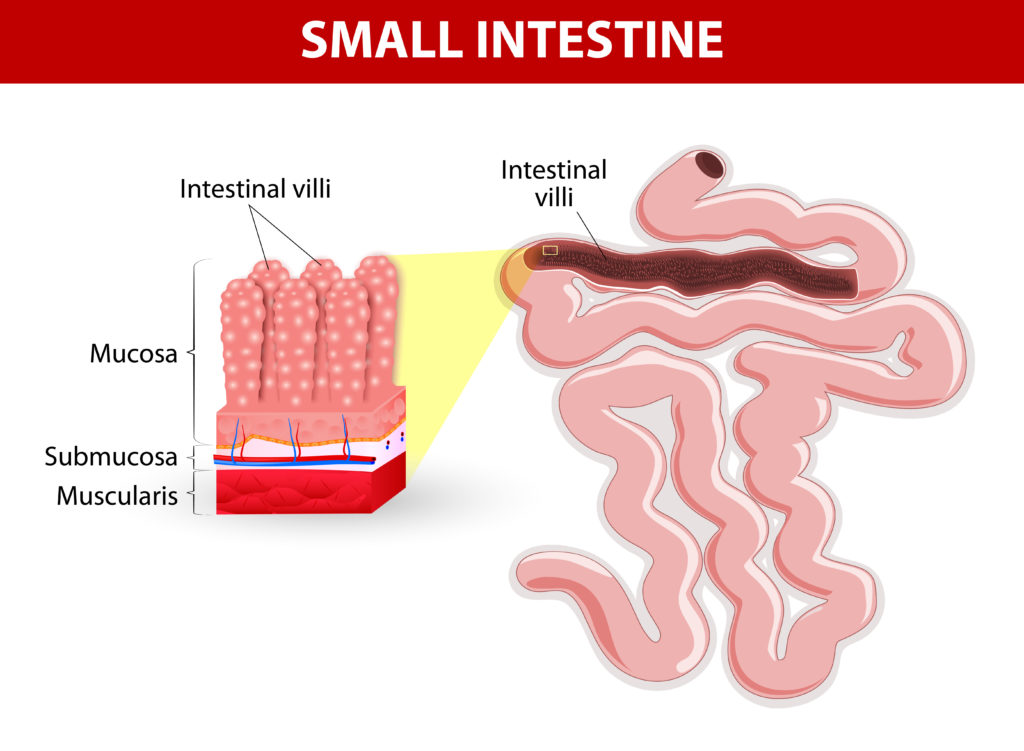
When we take gluten rich food, the body’s immune system overreacts to it. This reaction damages the small intestinal villi i.e. hair like projections in the inner layers of small intestine. Villi are those structures which absorb nutrients including vitamins, minerals etc from the food we eat. If these villi are damaged we can’t get enough nutrients immaterial of what quantity of food we consume. This immune reaction of small intestine to glutens causes celiac disease.
Read – Doshas And Ayurvedic Immunology
Causes
The exact causes for celiac disease are not known. It tends to run in families and might be linked to certain genes. If one of your close family members has it, like a parent or sibling, you have 1 in 10 chance of getting celiac disease.
It is usually caused by a –
- combination of eating foods with gluten and genetic defect
- gastro-intestinal infections
- gut bacteria
- infant feeding practices
- the disease becomes active after surgery, viral infections, emotional stress, pregnancy and childbirth
- being a Caucasian
- those having diseases like Addison’s disease, Down syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis, Turner syndrome and Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Symptoms
If you have celiac disease and accidentally eat something with gluten in it you may have the below mentioned symptoms –
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Pain in the abdomen
- Gaseous distension and bloating
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Poop which is pale, smells bad or floats (steatorrhea)
Other symptoms not related to disturbances of digestive system / small intestine –
- Anemia, usually from iron deficiency
- Osteoporosis or osteomalacia
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Skin itching / blisters on the skin – dermatitis herpetiformis
- Nervous symptoms – Tingling and numbness in the hands and feet, problems related to balance of the body and cognitive impairment
- Mouth ulcers
- Hyposplenism – less functioning of spleen
Symptoms in children – Children with celiac disease present with nausea, vomiting, chronic diarrhea, swollen belly, constipation, gas in abdomen and pale and foul smelling stools. Inability to absorb nutrients might result in failure to thrive, especially in infants, damage to tooth enamel, anemia, irritability, delayed puberty, short stature, weight loss and neurological symptoms like seizures, lack of muscle coordination, crankiness or mood changes, headaches, learning disabilities and ADHD i.e. attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. (read more)
Right time to see the doctor
- When you have diarrhea or digestive discomfort for more than 2 weeks
- If your child is pale, irritable or if his or her growth is slow
- If the child has potbelly and foul smelling stools which are bulky
- See a doctor if there is family history
- If you have a risk factor for celiac disease, along with family history, like type 1 diabetes
Risk Factors
- Family history of celiac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Down syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Addison’s disease
- Lymphocytic or collagenous colitis
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
(read more)
Complications
The below mentioned complications may appear if celiac disease is not promptly treated –
- Malnutrition – as intestine cannot absorb essential nutrients
- Anemia and weight loss – due to malnutrition
- Bone weakening – rickets in children and osteopenia or osteoporosis in adults occur due to malabsorption of vitamin D and calcium
- Reproductive issues – Infertility and miscarriage may occur due to mal-absorption of calcium and vitamin D
- Lactose intolerance – consumption of lactose-rich dairy products will cause diarrhea and abdominal pain due to damage to your small intestine
- Cancer – there is an increased risk of developing many forms of cancer, mainly small bowel cancer and intestinal lymphoma if the celiac disease patients do not give up gluten-rich foods
- Problems related to nervous system – seizures and peripheral neuropathy are common
- Slow growth and short stature in children – due to malabsorption
- Pancreatic disease
Other manifestations–
1. Nonresponsive celiac disease
This condition occurs due to contamination of food by gluten. Some people do not respond to gluten free diet. People suffering from this variant of celiac disease have bacterial overgrowth in their intestine, poor functioning of pancreas, irritable bowel syndrome, microscopic colitis, difficulty in digesting sugar in dairy products sugar / sucrose or fructose and refractory celiac disease.
2. Refractory celiac disease
In some cases of celiac diseases, the intestinal injuries do not respond to gluten-free diet. This condition is called as refractory celiac disease. People may not be relieved from the signs and symptoms after following a gluten free diet for 6-12 months. In this case one should seek the help of doctor to rule out other conditions.
Diagnosis
Celiac disease can be diagnosed with the help of two blood tests –
- Serology testing – to look for antibodies in your blood, the elevation of which gives clue to an immune reaction to gluten
- Genetic testing for human leucocyte antigens (to rule out celiac disease)
One of the below mentioned tests may be indicated if the above mentioned tests suggest presence of celiac disease –
- Endoscopy – which enables viewing of small intestine and to take a sample (biopsy) to analyze for damage to villi
- Capsule endoscopy – the camera in the capsule which you are given to swallow takes many pictures of your intestine and transmit then to a recorder
Skin samples – if dermatitis herpetiformis is suspected, a skin tissue sample is taken for analysis (skin biopsy)
Read – Charaka Grahani Dosha Chikitsa 15th Chapter
Prevention
Actually celiac disease cannot be prevented. Its flare-ups may be avoided by following gluten-free diet.
Home Remedies
Celiac disease can be dangerous since it presents with so many disturbing systemic symptoms. It is not good to try any home remedies for celiac disease. But the best home remedies are taking gluten free foods. Below mentioned can be considered as home remedies for celiac disease –
- Go gluten free
- Be careful about hidden glutens, read labels
- Purchase gluten free products
- Specify and speak out that you prefer gluten free when you are dining outside or traveling as in planes
- Keep away the foods which you are not sure about
Read – Some home remedies to try after accidentally ingesting gluten rich foods
- Ginger – relieves nausea, treats gastritis, aids digestion, good for stomach and intestines
- Turmeric – is a potent anti-inflammatory agent, heals the gut quickly
- Herbal infusions – of ginger, peppermint, chamomile
- Activated charcoal – absorbs ingested poisons, helps reduce bloating and gas
- Drink plenty of water – helps homeostasis in the body, flushes toxins
- Fast – gives a break to the digestive system, allows quick healing process,
- Digestive Enzymes – provide relief from bloating and gas, known to speed up gluten elimination process, good to relieve constipation
- Marshmallow root – aids digestion, repairs gut lining, reduces inflammation and gas
- Omega-3 – anti-inflammatory, aids absorption
- Apple cider vinegar – good remedy for many stomach ailments, is enzyme rich and aids digestion, relieves constipation and inflammation, encourages growth of good bacteria
- Probiotics – restores gut bacteria
- L-Glutamine – is a nutrient, aids your intestines to repair and build, cures diarrhea
Read – Turmeric Curcuma longa Benefits, Usage, Dose, Side Effects
Treatment and Diet
The one and the only way to manage celiac disease are to follow a stringent lifelong gluten-free diet. Even a small amount of gluten in foods is dangerous. Wheat, barley, malt and rye are commonly known food inclusions rich in gluten. The others are bulgur, durum, graham flour, semolina and triticale.
Read – Barley (Hordeum vulgare) – Qualities, Uses, Remedies, Research
Gluten is also found hidden in some foods medications and non-food products in small quantities. Some of them are –
- Modified food starch
- Food preservatives and stabilizers
- Vitamin, mineral, herbal and nutritional supplements
- Communion wafers
- Toothpaste and mouthwash
- Lipstick, envelope and stamp glue
- Prescription and over the counter medications etc
Read – Effect of Stress, Anxiety on Stomach And Intestines: Remedies
Vitamin and mineral supplements – In case of presence of anemia or nutritional deficiencies of severe scale, the doctor may recommend supplements which include Vitamin B-12, D & K, zinc, iron, folate and copper.
Follow up care – This is very important. Periodic tests in consultation with your doctor will help in evaluating the response of your intestines to the gluten-free diet. In most conditions, the gluten-free diet will heal the intestines and the symptoms of the disease come down. It is quicker in children wherein healing takes place usually in 3-6 months. In adults it might take several years for cure to get established.
Medicines for intestinal inflammation – Steroids may be prescribed for controlling severe inflammation. They also promote healing. Azathioprine or Budesonide might also be used. Dapsone might be prescribed if you have dermatitis herpetiformis.
Read – Ayurveda Ulcerative Colitis Diet Tips, Home Remedies
Role of dietician – Your doctor may refer you to an expert dietician or you may ask for the same so as to help you identify the gluten rich foods and keep them away.
Importance of reading labels – You need to read labels especially of packaged foods to know if they are gluten free or otherwise. Avoid taking packed foods unless they are labeled as ‘gluten free’ or have no gluten containing ingredients. The gluten containing ingredients include emulsifiers and stabilizers. Check labels of the below mentioned –
- Cereals
- Pasta
- Baked goods
- Soups
- Salad dressings and sauces
- Gravies
- Candies
- Imitation meats
- Seafood
- Seasoned snack foods like tortilla and potato chips
- Rice mixes
- Beers and vinegars
- Self basting poultry
- Processed luncheon meats
- Oats – pure oats are not harmful, but oats can be contaminated by wheat during growing and processing.
Foods allowed in gluten-free diet –
- Fruits and nuts
- Lentils
- Eggs
- Rice & wild rice
- Gluten free flours of rice, soy, corn, potato
- Corn, cornmeal, lentils
- Vegetables and potatoes
- Most dairy products
- Fresh meats, fish and poultry (not breaded, batter-coated or marinated)
- Amaranth and buckwheat
- Tapioca, quinoa, pure corn tortillas
- Wine and distilled liquors, ciders and spirits
Interesting facts
Most people never know that they have celiac disease. According to researchers as few as 20% people with this disease are diagnosed promptly.
The damage to your intestine is very slow. The symptoms are so varied that it might take many years to get a diagnosis.
Celiac disease is not the same as food allergy. They also present with different symptoms and should not be confused with each other.
Not everyone with celiac disease will have hallmark symptoms mentioned above. Some people do not notice any problems. This will make diagnosis difficult.
Read – Bad Food Combinations And Solution As Per Ayurveda
In August 2013, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) published a new standard definition for the term ‘gluten free’ on food labels. In order to be labeled as ‘gluten free’, ‘no gluten’, ‘free of gluten’ or ‘without gluten’, a food must contain less than 20 parts of gluten per million. Manufacturers of products have 1 year from the publication of this regulation to bring all food labels in compliance.
The prevalence of celiac disease isn’t known. It is estimated to affect about 1 in 3000 people. Many cases go undiagnosed because the symptoms are mild or absent. It is primarily found to affect whites of northwestern Europeans. It rarely affects African-Americans, Asians or Jews. The ratio of men to women suffering from celiac disease is 1:2.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Skype








