Green Pea (Matar) Medicinal Qualities, Uses, Research

By Dr Renita D’Souza
Botanical Name – Pisum sativum
Synonyms – Pisum vulgare Jundz, Pisum arvense L, Lathyrus oleraceus Lam, Pisum biflorum Raf, Pisum elatius M.Bieb, Pisum humile Boiss. & Noe
Family – Leguminosae
Table of Contents
Introduction
Green peas are nutritious vegetable. They are good source of protein and fiber. They are rich in nutrients that are useful in lowering the risk of cancer. In Ayurveda, peas (kalaya) are included under vata increasing diet, hence it is not recommended in Vata diseases like low back pain, neck pain etc. They are used in the form of soup in diarrhea.

Names in Different Languages
Sanskrit Name – Kalaya
English Name – Field pea, Garden pea
Hindi Name – Matar, Mattar
Bengali Name – Mattar, Mator
Marathi Name – Vataane, Vatana, Mattar, Watane
Gujarati Name – Matana, Vatana
Kannada Name – Batani, Bataani
Tulu Name – Batani
Konkani Name – Batani
Telugu Name – Gundusaa, Pachabatthani, Bataneelu
Tamil Name – Patani
Punjabi Name – Kabli Chole, Mattar
Kashmiri Name – Kara
Medicinal Qualities
Medicinal Qualities of Peas
Taste – Sweet
Vipaka (taste conversion after digestion) – sweet
Ruksha – dry in nature
Virya (potency) – cold
Laghu – light to digest
Sangrahi – absorbent in nature
Uses
Therapeutic uses of peas
Dahapaha – relieves burning sensation
Ruchi prada – improves taste
Pushti prada – improves physical strength
According to Bhojana Kutuhalam twelfth chapter, the leaf of kalaya acts relieves constipation, light to digest, bitter in taste and alleviates all the three doshas.
Effect on Tridosha
It balances kapha and pitta dosha
Increases vata
Nutritional value
Nutritional Value of Green peas
Green Peas are rich source of fiber, protein, vitamin A, vitamin B6, vitamin C, vitamin K, phosphorus, magnesium, copper, iron, zinc and lutein.
Pharmacological activity of Peas
Pisum sativum possess antibacterial, anti-diabetic, anti-fungal, anti-inflammatory, anti-hypercholesterolemia, antioxidant and anticancer activities.

Chemical Components
Pisum sativum possess alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, isoflavones, phenols, phytosterols, phytic acid, protease inhibitors, saponins and tannins
Research
Anti-cancer activity – A review article proved that Pisum sativum possess Anti-cancer activity.
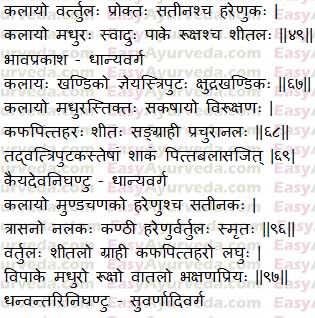
Sanskrit Verse

Interaction with medicines, supplements
Can this be used while taking Homeopathic medicine?
Yes. This product does not react with homeopathic medicine.
Can
this medicine be continued while taking supplements like multivitamin tablets,
Omega 3 fatty acids etc?
Yes. Generally, this product goes well with most
of the dietary supplements. However, if you are taking more than one product
per day, please consult your doctor for an opinion.
With western
medicines
Seek your
doctor’s advice if you are taking this product along with other western
(allopathic / modern) medicines. Some Ayurvedic herbs can interact with modern
medicine.
If both Ayurvedic and allopathic medicines are advised together, then it is
best to take Allopathic medicine first, wait for 30 minutes and then take the
Ayurvedic medicine.
Morphology
Pisum sativum is a herbaceous annual plant growing up to 2-3 meter long. Leaves are pinnately compound and alternately arranged. Flowers whitish purple. Fruits are pods which are 3-10 cm long. Seeds are green, smooth and round in shape.
Distribution
Pisum sativum is commonly grown vegetable in the world. In India it is widely cultivated in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Madhya Pradesh.
Ayurvedic medicines with Pea as Ingredient
Hiowna – used to treat general fatigue and stress
Anu Tail – used as nasal drops in the treatment of diseases of sense organs, hair fall, premature graying of hair, headache, Strengthens voice etc.
Classical Formulations
(Ref – Ch.Chi 28)
Baladi Taila – used in asthma, fever, cough, vomiting, epilepsy etc
Amrtadya Taila – used in insanity, epilepsy, depression etc
Madhvarista (Ref – Ch.Chi 15) – cures hear diseases, anemia, sprue, skin diseases, piles, edema etc
Synonyms, Categorization
Sanskrit Synonyms
Kalaya, Varthula, Harenu, Sathina, Mundachanaka
Classical Categorization
Dhanvantari Nighantu – Suvarnaadi varga
Kaiyadeva Nighantu – Dhanya varga
Bhavaprakasha Nighantu – Dhanya varga
Raja Nighantu – Shalyaadi varga
Shodala Nighantu – Shimbidhanya varga
Scientific classification
Domain – Eukaryota
Kingdom – Plantae
Phylum – Spermatophyta
Subphylum – Angiospermae
Class – Dicotyledonae
Order – Fabales
Family – Fabaceae
Genus – Pisum
Species – Pisum sativum
Controversy
Some authors opine that kalaya is peanut and harenu is green peas. Peanut increases Vata and Pitta and promotes healthy Kapha Dosha.
Peas, edible-podded, raw
Harenu in Sanskrit
हरेणुको हिमो रूक्षः ग्राही समधुरो लघुः |६७| (Kayyadeva nighantu)
Pea pod is also sweet in flavour.
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha increasing
Peas, edible-podded, boiled, drained, without salt
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (as boiled and drained peas is slightly more light)
Peas, edible-podded, frozen, unprepared
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha increasing
Peas, edible-podded, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (as boiled and drained peas is slightly more light)
Peas, green, raw
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha increasing
Peas, green, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (as it is lighter)
Peas, green, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt
Taste – sweet, slightly salty
Properties – light, dry
Potency – not very cold (peas is cold in potency, salt is hot in potency)
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta nourishing (peas is Pitta balancing, salt is Pittakara)
Kapha nourishing (as it is lighter)
Peas, green, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (as it is lighter)
Peas, green, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt
Taste – sweet, slightly salty
Properties – light, dry
Potency – not very cold (peas is cold in potency, salt is hot in potency)
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta nourishing (peas is Pitta balancing, salt is Pittakara)
Kapha nourishing (as it is lighter)
Peas, green, canned, regular pack, solids and liquids
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (canning involves boiling in water, so it becomes lighter than raw form)
Peas, green (includes baby and lesuer types), canned, drained solids, unprepared
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (canning involves boiling in water, so it becomes lighter than raw form)
Peas, green, canned, seasoned, solids and liquids
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata nourishing (seasoning with spices make it more Vata balancing; hence does not increase Vata but nourishes it)
Pitta neutral (spices increase Pitta)
Kapha nourishing (canning involves boiling in water, so it becomes lighter than raw form; seasoning with spices also make it more Kaphahara)
Peas, green, canned, drained solids, rinsed in tap water
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (canning involves boiling in water, so it becomes lighter than raw form)
Peas, green, frozen, unprepared
(Includes foods for USDA’s Food Distribution Program)
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha increasing
Peas, mature seeds, sprouted, raw
Taste – sweet
Properties – heavy (virooda dhanya is heavy), unctuous
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta balancing
Kapha increasing (more Kapha increasing than unsprouted peas)
Peas and carrots, canned, regular pack, solids and liquids
Canned peas – Vata increasing, Pitta
balancing, Kapha nourishing
Canned carrot – Vata balancing, Pitta nourishing, kapha balancing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta balancing
kapha balancing
Peas and carrots, frozen, unprepared
Frozen peas – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha increasing
Frozen carrot – Vata balancing, Pitta nourishing, kapha balancing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta balancing
Kapha neutral
Peas and carrots, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
Frozen cooked peas – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha nourishing
Frozen cooked carrots – Vata balancing, Pitta nourishing, Kapha balancing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta balancing
Kapha balancing
Peas and carrots, canned, no salt added, solids and liquids
Canned peas – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha nourishing
Canned carrot – Vata balancing, Pitta nourishing, kapha balancing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta balancing
kapha balancing
Peas and carrots, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt
Frozen cooked peas – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha nourishing
Frozen cooked carrots – Vata balancing, Pitta nourishing, Kapha balancing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta nourishing (peas and carrots frozen cooked is Pitta balancing, but salt is Pitta increasing)
Kapha balancing
Peas and onions, canned, solids and liquids
Peas canned – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha nourishing
Onions canned – Vata balancing, Pitta neutral, Kapha nourishing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing
Peas and onions, frozen, unprepared
Frozen unprepared peas – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha increasing
Frozen unprepared onions – Vata balancing, Pitta neutral, Kapha increasing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta balancing
Kapha increasing
Peas and onions, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
Frozen cooked peas – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha nourishing
Frozen cooked onions – Vata balancing, Pitta neutral, Kapha nourishing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing
Peas and onions, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt
Frozen cooked peas – Vata increasing, Pitta balancing, Kapha nourishing
Frozen cooked carrots – Vata balancing, Pitta nourishing, Kapha balancing
Effect on Doshas
Vata neutral
Pitta nourishing (peas and onion frozen cooked is Pitta balancing, salt is Pitta increasing)
Kapha balancing
Peas, green, canned, no salt added, solids and liquids
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (canning involves boiling in water, so it becomes lighter than raw form)
Peas, green, canned, no salt added, drained solids
Taste – sweet
Properties – light, dry
Potency – cold
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata increasing (grahi)
Pitta balancing
Kapha nourishing (canning involves boiling in water, so it becomes lighter than raw form)
Click to Consult Dr Renita D’Souza











2 comments
Jesse
Dear sir/madam,
I read on many places that peanuts increase pitta. This page says “Peanut increases Vata and Pitta and promotes healthy Kapha Dosha”. What is it about peauts that is heating? Could you please elaborate on that?
Thanks in advance.
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
We will address this question when we write about peanuts.