Madhava Nidana Chapter 57 Karna Roga Nidanam
This article explains Madava nidana 57th chapter “Karna Roga Nidanam”. Causes, pathology and symptoms of Karna Roga are explained in this chapter. Karna Roga means diseases of ear.
Table of Contents
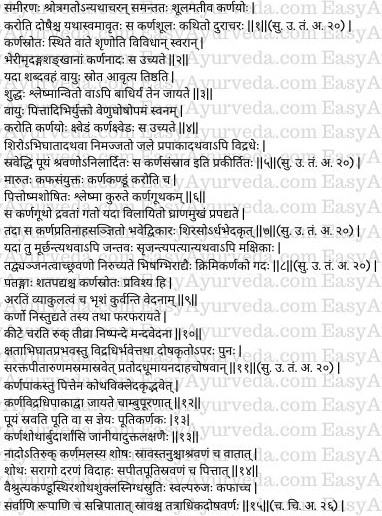
Karnasula
Vata which has been enveloped by the doshas (pitta and kapha) which have undergone abnormal increase due to their own etiological factors (etiological factors causing aggravation of pitta and kapha respectively) and has moved in upward direction (abnormal movement for vata) on reaching (and getting lodged in) the ears and produces pain in the ears. This condition is called Karnasula and is difficult to treat. (1)
Read – Ear Discharge – Causes, Symptoms, Ayurvedic Treatment, Remedies

Karnanada
When aggravated vata gets lodged in the canals of the ears the patient would hear many kinds of abnormal sounds similar to those produced by kettle drum, cymbal or conch etc. This condition is known as Karnanada. (2)
Badhirya
When vata either alone or in association with kapha (vata enveloped by kapha) blocks the passages of sound, the patient develops deafness. This is known as Bādhirya. (3)
Karna Ksveda
A condition in which increased vata in association with pitta and other dosha (kapha) produces constant sound in the ear resembling the sound produced by a bamboo (when air is blown in hollow bamboo shoot) or flute. This is known as Karna Ksveda. (4)
Read – Tinnitus Causes, Ayurvedic Treatment, Herbs, Lifestyle Tips
Karnasrava
Injury to the head, drowning in water (remaining underwater for long time) or ripening of an abscess in the ears causes discharge of pus from the ears. This is associated with pains and other symptoms of vata increase. This condition is known as Karnasrava. (5)
Karnakandu
Vata in association with kapha produces Karnakandu (itching inside the ears).
Karnaguthaka
Kapha getting dried (and solidified) by the heat of pitta produces Karṇaguthaka (hardness of the wax). (6)
Karnapratinaha
The condition in which this wax of the ears (explained above in karnaguthaka) gets liquefied (becoming watery), and reaches the nose and mouth (and gets discharged from there) is called Karnapratinaha. The patient also suffers from a headache in one half of the head. (7)
Krimikarnaka
When insects or small worms forming (entering) in the ears (due to decaying of muscles and blood), or flies producing their larva inside the ears (in the decomposed or putrefied muscles of the ears), the physicians call this disease having symptoms similar to krimiroga (worm infestation disease) as krimikarnaka. (8)
If winged insects, centipedes or other insects have entered into the canals of the ears, they produce restlessness, a sense of fear or worry and severe pain. If these insects are alive and move around in the canals of the ear, they will produce pricking pain, sounds of movement of insects (movement of insects is felt), and severe pain. The pain will be mild if the insects are not moving inside the ear canals (if insects are dead). (9-10)
Read – Krimighna Gana: Parasites Relieving Herbs: Review, Benefits, Formulations
Karna Vidradhi
One type of abscess develops due to injury or trauma to (inside) the ear and the other type develops due to aggravation of doshas inside the ear. This will cause discharge of fluids (pus) of red, yellow or crimson colour accompanied with pricking pain, feeling of hot fumes (smoke) being eliminated from the ears, burning sensation and feeling of sucking like pain. This disease is called as Karna Vidradhi. (11)
Karnapaka
Due to aggravation of pitta or due to ripening of ear abscess or due to water entering the ears a disease called karnapaka is produced. It causes putrefaction and foul discharges from the ears. (12)
Putikarnaka
A condition in which very foul-smelling pus is discharged from the ears is called Putikarnaka.
Karnasotha, Karnarbuda, Karnarsha
The symptoms of karnasotha, karnarbuda and karnarsha are similar to sotha (swelling, oedema), arbuda (tumour) and arsha (piles) which occur elsewhere in the body. (13)
Read – Tested Remedies For Eye, Ear, Nose, Throat Problems: Ramdas Pai
Based on dosha predominance
Karnarogas based on dosha predominance
Vataja Karnaroga – In the ear diseases caused due to predominant aggravation of vata, there will be noise in the ears, severe pain, drying (and hardening) of the dirt in the ears, less discharges (discharge of thin fluids), and loss of hearing (deafness).
Pittaja Karnaroga – In the ear diseases caused due to predominant aggravation of pitta, there will be reddish swelling, tearing / blasting pain, burning sensation, and yellowish offensive discharges from the ears.
Kaphaja Karnaroga – In the ear diseases caused due to predominant aggravation of kapha, there will be hearing of abnormal sounds, itching in the ears, hard and immobile (fixed) swelling, white and unctuous discharges and mild pain.
Sannipataja Karnaroga – In the ear diseases caused due to simultaneous aggravation of all the three doshas there will be symptoms of all the three doshas and the discharges will have the colour of the predominantly aggravated dosha. (14-15)
Read – Oral, Ear And Head Therapy – Ashtanga Hrudaya Sutrasthana 22
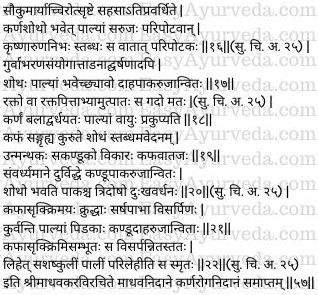
Paripotaka
Due to the delicate / tender nature (of the child) if the hole punctured on the earlobe (as a part of childhood rituals) is left unattended for a long time and in later period if one tries to dilate the orifice all of a sudden, it would cause serious swelling along with pain in the ear (earlobe) which will have black or crimson colour. This hard swelling caused by increased vata is known as Paripotaka. (16)
Utpata
Wearing of excessively heavy ornaments in the ears, blow (injury) or friction on the ears leads to the manifestation of swelling, black or red in colour, caused by aggravation of blood and pitta together, associated with burning sensation, suppuration and pain. This condition is known as Utpata. (17)
Unmanthaka
By forcibly attempting to pierce the pinna of the ears and trying to enhance the orifice, vata gets aggravated in the ears (earlobe). This vata getting associated with kapha produces stiff (hard) swelling without pain. This condition is called by the name Unmanthaka. It is caused by increased kapha and vata together and is associated with itching. (18-19)
Read – Itching And Pruritus: Ayurvedic Understanding
Dukhavardhana
When the pinna of the ear is pierced at the wrong place and when that orifice becomes bigger, it leads to the development of swelling and ripening accompanied with itching, suppuration and pain. This condition is called Dukhavardhana and is caused by increase of all the three doshas together. (20)
Parilehina
Increase of kapha and blood and presence of bacteria together produce pustules on the pinna of the ear, of the size of mustard seeds, spreading in nature, accompanied with itching, burning sensation, pain causing a disease called as Parilehi. This disease caused by increased kapha, blood and worms (bacteria) will spread all through the ears and eat off (destroy) the entire pinna and lobes. (21-22)
Thus ends the chapter on Karna Roga Nidanam in Madhava Nidana text written by Acharya Madhavakara.











