Madhava Nidana Chapter 36 Shotha Nidanam
This article explains Madava nidana 36th chapter “Shotha Nidanam”. Causes, pathology and symptoms of Shotha are explained in this chapter.
Read – Acharya Madhavakara: His Work ‘Madhava Nidana’, Legacy, Amazing Facts
Table of Contents
Shotha Samprapti, Bheda
Pathogenesis and types of Shotha
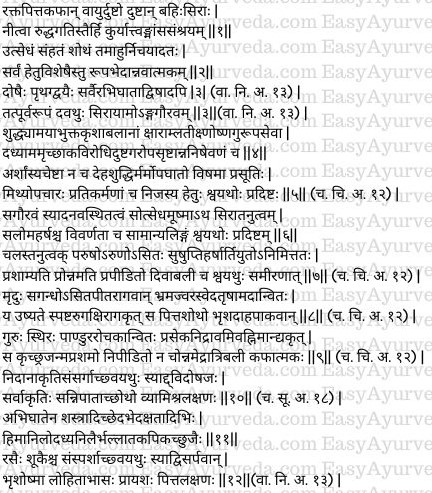
Vaata undergoing increase due to its own etiological factors pushes the vitiated rakta (blood), pitta and kapha into the superficial veins. Therein (inside the veins) the vata gets obstructed by the same blood, pitta and kapha. These three doshas along with the vitiated blood gets accumulated between the skin and muscles and cause swelling. This swelling is called as Shotha.
Types of Shotha – All shothas are of one type seeing that they all present with swelling. But due to different causative factors and symptoms (caused due to different causative factors), shotha is classified into nine types. They are – one each from each dosha (vataja, pittaja and kaphaja), one each from combination of two doshas (vata-pittaja, vata-kaphaja and pitta-kaphaja), one type from the combination of all three doshas (tridoshaja, sannipataja), one from injury (abhighataja) and one from the effect of poisons (vishaja). (1-2)
Read – Shotha: Causes, Types, Treatment, Medicines
Shotha Purvarupa
Premonitory symptoms of Shotha
Premonitory symptoms of shotha are mild burning sensation of the skin (eyes, nose, etc.), appearance of venous network (engorgement of veins) and feeling of heaviness of the body parts. (3)
Shotha Nidana
General etiological factors of Shotha
Causes for Nija Shotha (Shotha caused by doshas) –
- Excessive administration of foods which are alkaline, sour, strong / deep penetrating, hot (heat producing) or heavy foods (difficult to digest foods), to those who have got emaciated due to (excessive or improper) administration of purificatory therapies (panchakarma therapies like emesis, purgation etc), long standing diseases (fever etc), not eating food / lack of food (starvation) or foods of low quality (and nutrition) and to the weakened persons will cause shotha (by causing aggravation of doshas).
- Excessive consumption of curds, uncooked foods, mud, leafy vegetables, mutually incompatible (having opposite qualities and nature) foods, spoilt (contaminated) foods, and gara visha (combination of poisons or foods poisoned by such poisons)
- Haemorrhoids
- Absence of physical activities
- Not administering purificatory measures (panchakarma treatments) in spite of their requirement
- Damage to the marmas (vital organs and tissues) by aggravated doshas (disorders of marmas caused by aggravated doshas)
- Abnormal delivery in women (miscarriage, abortion)
- Improper administration of purificatory therapies (4-5)
Read – Charaka – Shotha Chikitsa 12th Chapter
Shotha Samanya Lakshana
General Symptoms of Shotha
The general symptoms of shotha are – swelling associated with feeling of heaviness, inconsistency i.e., increasing or decreasing frequently, warmth, thinning of the veins, horripilation (hairs standing on ends), and discolouration. (6)
Vataja Shotha
The symptoms of vataja shotha (oedema caused due to increase of vata) are –
- the skin over the oedema is movable, thin, rough, golden yellow / brown (reddish brown) or black in colour,
- loss of sensation or feeling of pins and needles, horripilations / hyperesthesia,
- oedema subsides temporarily without any apparent cause
- pits on pressure and when the pressure is released the pit fills up quickly
- the swelling increases during daytime (7)
Read – Ayurvedic Treatment For Pedal Edema: Principles, Panchakarma, Limitations
Pittaja Shotha
The symptoms of pittaja shotha (oedema caused due to increase of pitta) are –
- the swelling (skin over the swelling) is soft
- swelling emits peculiar type of smell
- is black, yellow or red in colour
- the patient has giddiness, fever, excessive sweating and thirst, intoxication
- will have peculiar type of burning sensation in the affected part, clear pain,
- redness of the eyes
- there will be severe burning sensation and quick suppuration of the swelling (8)
Kaphaja Shotha
The symptoms of Kaphaja shotha (oedema caused due to increase of pitta) are –
- the swelling is heavy and immovable (fixed) and pale
- the patient has loss of taste, excessive salivation, excessive sleep, poor digestion (weakness of digestive fire or capacity)
- the swelling manifests and subsides slowly
- the swelling pits on pressure and doesn’t fill up quickly after the pressure is released
- the swelling is profound (increases) during night time (9)
Dwidoshaja, Tridoshaja Shotha
Swelling caused by two and three doshas
In dvidosaja shotha there will be presence of combined etiological factors and symptoms of two dosas. On the other hand, in sannipataja shotha the symptoms of all the three doshas are collectively present together. (10)
Read – Shothahara Gana Of Charaka – Anti Inflammatory Group Of Herbs
Abhighataja Shotha
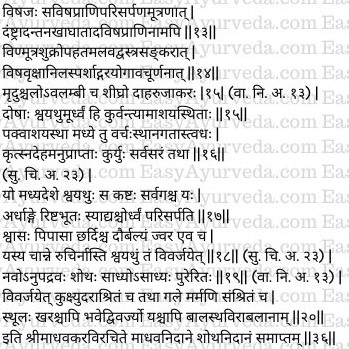
Assault by weapons causing cutting, breaking or tearing of the parts, assault by snow (frost), breeze, or winds coming from sea (cyclone); contact with fumes or oil of bhallaataka (marking nut) and fine thorns of the pod of kapikacchu (Mucuna pruriens), irritating juices of herbs, etc., bring about an oedema which spreads quickly all around. This condition is associated with severe burning sensation, redness and other symptoms of pitta increase. (11-12)
Vishaja Shotha
Poisonous animals crawling or urinating on the body, stinging, biting with teeth, scratching with nails by non-poisonous animals, contact with faeces, urine, or semen of poisonous animals or coverings / contact with contaminated cloth, contact with poisonous trees, air (gases) and sprinkling or application of artificial poisonous materials also produce oedema. The skin over she swollen part is soft, movable, moves (spreads) quickly in downward direction (to the lower parts of the body) and is associated with burning sensation and pain which manifests quickly. (13-14)
Seat of doshas and shotha
Doșas residing in the stomach produce oedema in the upper part of the body. Doshas residing in the colon (large intestine) produces oedema / swelling in the trunk. The doshas residing in the rectum produce oedema in the lower parts of the body. The doshas which are spread out in the entire body produces swelling / oedema in the entire body (all parts of the body). (15-16)
Read – Types Of Doshas And Their Functions
Symptoms of incurability of Shotha
Oedema manifesting in the trunk and that which has spread to involve the entire body (all parts of the body) is difficult to cure.
Oedema / swelling occurring in half of the body and also spreads to involve the upper parts of the body are considered to be equal to arista (ominous signs which indicate that the person is going to die shortly) i.e., it is incurable.
The patients in whom the oedema / swelling is associated with dyspnoea (difficulty in respiration), thirst, vomiting, debility, fever and lack of desire in food should be refused treatment i.e., such a condition of shotha is incurable.
Oedema caused by its own complications which begins in the feet in men should be considered as fatal. Likewise, the swelling which begins in the face and spreads downwards in women should be considered as fatal in women. When the swelling begins in the genitals is considered as fatal in both men and women.
Oedema of recent onset which is not associated with complications is curable and the other type of oedema (explained above) are said to be incurable.
Oedema occurring in the abdominal cavity, abdomen, and neck and located in the vital organs is considered incurable. Similarly, the oedema occurring in children, old aged people and weak (women) people is incurable and hence should not be treated. (17-20)
Thus ends the chapter on Shotha Nidanam in Madhava Nidana text written by Acharya Madhavakara.










