Madhava Nidana Chapter 30 Mutrakrichra Nidanam
This article explains Madava nidana 30th chapter “Mutrakrichra Nidanam”. Causes, pathology and symptoms of Mutrakrichra are explained in this chapter.
Read – Acharya Madhavakara: His Work ‘Madhava Nidana’, Legacy, Amazing Facts

Table of Contents
Nidana
Etiological Factors
Excessive indulgence in exercise, medicines which are penetrating in nature (heat producing), dry foods and alcoholic drinks, riding regularly on the backs of animals like horses which basically run fast (or riding any other vehicles with fast pace regularly), regular and excessive consumption of flesh of animals and birds living in the marshy places, eating food in excess and indigestion of foods are the etiological factors of mutra krchra.
Read – Dysuria: Causes, Remedies, Tips, Diet, Ayurvedic Treatment
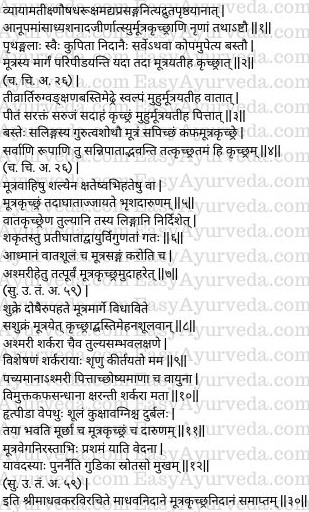
Mutrakrichra Samprapti
Pathogenesis – The above-mentioned etiological factors aggravate one or all doshas and cause 8 kinds of mutrakrchra. The vata and other doshas aggravated by their respective etiological factors reach the urinary bladder (urinary tract) either singly or collectively and get lodged therein. These doshas cause constriction, pressure or irritation of the urinary passages. As an effect, the person will find difficulty in voiding the urine. This condition marked by ‘difficulty in urination’ is called Mutrakrchra. This is of 8 types. (1-2)
Types
8 types of Mutrakrchra are –
- Vataja Mutrakrchra
- Pittaja Mutrakrchra
- Kaphaja Mutrakrchra
- Sannipataja Mutrakrchra
- Shalyabhighataja Mutrakrchra (caused due to injury caused by foreign object)
- Purishaja / Shakrdvighataja Mutrakrchra (caused by forcibly holding the urge for defecation)
- Shukraja Mutrakrchra (dysuria caused by impaction of urinary passages by semen)
- Ashmarijanya Mutrakrchra (dysuria caused by urinary stones)
Read – Urinary calculi – Home Remedies, Ayurvedic Treatment, Diet, Recipes
Vataja Mutrakruchra
In this type, severe pain in the groins, urinary bladder and penis, scanty and frequent urination are the symptoms.
Pittaja Mutrakrichra
In this type of dysuria the patient will pass urine which is yellow in colour and mixed with blood. The patient will experience pain and burning sensation along with difficulty in passing the urine.
Kaphaja Mutrakrichra
In this condition the patient will have heaviness and swelling in the region of the urinary bladder and penis. The urine will be thick and viscid (sticky, slimy).
Tridoshaja Mutrakrichra
Sannipataja Mutrakrchra – In this condition all the above-mentioned symptoms in the individual doshaja types of mutrakrchra (vataja, pittaja, kaphaja) are found together and in severe form. (3-4)
Read – Urethritis Causes, Symptoms, Ayurvedic Treatment
Shalya abhighataja Mutrakrichra
This condition occurs due to the injury caused by the foreign bodies inside the urinary tract or due to external injury. The difficulty in urination is of a severe form and will have symptoms similar to those of vataja type of mutrakrchra. (5)
Shakrd Vighataja Mutrakruchra
Due to the obstruction to the movement of the faeces as caused by habitual suppression of the urge for defecation will cause vata aggravation. This vata will move in an abnormal route (upward direction against its normal downward course) and produces distension of abdomen, colic of vataja type and difficulty in urination. (6)
Read – Different Causes For Vata Dosha Imbalance, Increase
Ashmarijanya Mutrakrichra
If mutrakrchra (dysuria) is caused due to asmari (urinary calculi) it is called Ashmarijanya Mutrakrchra. Here calculus is the cause and difficulty in urination is the effect.
Shukraja Mutrakruchra
When the semen which has been displaced from its place (and has not been ejaculated) gets vitiated and obstructed by the aggravated doshas in the urinary passages it leads to difficulty in micturation. Since this condition is caused by the obstruction of semen it is called shukraja (shukra = semen) mutrakrchra. In this condition the urine mixed with semen is eliminated with great difficulty. It is also associated with pain in the region of the urinary bladder and penis. (7-8)
Read – Mutra sharkara – gravel in urine – Ayurvedic understanding and treatment
Difference between Asmari and Sarkara
Asmari (calculii) and sarkara (gravel) are similar in their causes and symptoms. But there is a difference in both these conditions.
Sarkara – The asmari (calculus) undergoing processing by pitta, dried by vata (dehydration of asmari by vāta) and losing the property of cohesion (or sticking together) of kapha, broken into tiny particles and passed out is called as sharkara (gravel).
Symptoms of dysuria (mutrakrchra) caused by ashmari or sarkara – pain in the region of the heart, shivering (tremors), pain in the abdomen (epigastrium), weakness of the digestive fire (poor digestive capacity), loss of consciousness (fainting) and great difficulty in urination are the symptoms caused by calculi or gravel.
Pain of the urinary tract subsides after the gravel gets eliminated along with the force of urination. The relief will be only until the urinary passage is impacted / obstructed by yet another gravel or stone. This means to tell that the symptoms recur (dysuria) when a new gravel or stone passes into the urinary tract and causes obstruction therein. (9-12)
Thus ends the chapter on Asmarī Nidanam in Madhava Nidana text written by Acharya Madhavakara.










