Rasa Prakarana (Parada: Section of Mercury)
In Ayurveda, mercury is called Parada or Rasa and is used for preparing medicines. Before using mercury, it is subjected to set of diligent processes called common and special methods of purification.

Table of Contents
Different meanings of Rasa word
The Word ‘Rasa’ has different meanings according to different contexts.
Rasa – as Rasa dhatu, the first among basic tisues of the body.
Rasa – Swarasa or juice extract of wet herbs.
Rasa – as taste of a substance.
Rasa Definitions
In the context of Rasashastra, Parada has been described as Rasa. The Word derviation and explanation is as follows.
(a) The one which has the capability of liquefying and eating Swarna, Loha etc Dhatus ica Rasa.
(b) रसनात् सर्वधातूनां रसः इत्यभिधीयते ।
rasanāt sarvadhātūnāṃ rasaḥ ityabhidhīyate |”
Meaning – same as above.
(c) जरारुक्मृत्युनाशाय रस्यते वा रसो मतः ।”
jarārukmṛtyunāśāya rasyate vā raso mataḥ |”
The one which is capable of relieving old age, pain and disease is called as Rasa.
(d) मम देह रसो यस्माद्र्सस्तेनायमुच्यते ।”
mama deha raso yasmādrsastenāyamucyate |”
Mythologically, Parada has been told as got its origin from the semen of Lord Shiva. Hence it is called as Rasa.
Difference between Rasa & Rasayana
| Rasa | Rasayana |
| It is specifically has the capacity to treat disease. | It has the capacity of relieveing both disease and old age complications. |
| Its preparation is done by following general process. | For the preparation of this, a special process is adopted. |
| Its administration is done for a short period of time. | Its administration is done for a long period of time. |
| It relieves the disease. | Apart from curing disease, it also maintains the health of the healthy. |
| It preserves age. | It preserves and increases age. |
| Its usage helps to treta the symptoms of the disease. | Its usage helps to improve the immunity. |
Types of Parada
1. Rasa 2. Rasendra 3. Suta 4.Parada and 5.Mishraka.
Rasa
Its explanation has been given above.
Rasendra
रसोपरसराजत्वाद् रसेन्द्र इत कीर्त्तितः ।”
rasoparasarājatvād rasendra ita kīrttitaḥ |”
Parada has been hailed as the king among all Rasas and Uparasas.
Soota
देहलोयमयीं सिद्धि सूते सूतस्ततः स्मृतः ।
dehaloyamayīṃ siddhi sūte sūtastataḥ smṛtaḥ |
Parada has the capacity of living Dehasiddhi and Lohasiddhi.
Parada
रोगपङ्काब्धिमग्नानां पारदनाच्च पारदः ।
rogapaṅkābdhimagnānāṃ pāradanācca pāradaḥ |
As similar to saving a person from drowning in loose mud, Parada saves man from disease. So the name Parada.
Mishraka
सर्वधातुगतं तेजोमिश्रितं यत्र तिष्ठति ।
sarvadhātugataṃ tejomiśritaṃ yatra tiṣṭhati |
The Aura or the shine of all the dhatus stays in Parada. So the name Mishraka. Such a Parada yields different fruits.
Galadaroopyanibham
In some places, parada is procured in free form. Such a parada, having the shine, as similar to silver is called as Galadarupyanibha – meaning similar to liquified silver.
Chapala
Parada does not stay at a single place. So the name Chapala.
Raseshwara Darshana
The followers of Maheshwara Sampradaya formed and followed a new philosophy to get themselves united with Lord Shiva, called as Raseshwara Darshana. According to them, the only way to get salvation is by achieving ‘Pindasthairya’ that jeans attaining cpmplete control over semen.. They believed that only Parada can help them in acheiving the state of Pinda sthairya. Same type of opinión has been given in Rasarnava.
There is a strong opinión that Salvation can only be achieved alter death. If that is the case, then the state of salvation can not be enjoyed by an alive person. This opinión has been substantiated in 6 Darshanas. But Rasershwara darshana tries to achieve the state of salvation while the person is alive through the process of Pinda Sthairya. Rasa Hrudaya Tantra (Bhagavad Govinda Padacharya) has also opined the same.
Read: Introduction To Rasashastra: Using Metals And Minerals To Heal
He further goes on tos ay that, due to Rasashastra, Due to practices like Pinda Sthairya etc, the body can be made to liev for a very very long time period, which helps the person to achieve salvation throguh rigorous spiritual practices for a very long period of time.
In Raseshwara Darshana, the Parada and Abraka have been considered as Veerya of Lord Shiva and Godess Gouri respectively. When Parada combines with the Abhraka, it gains special power to keep the body healthy and disease-free for a long period of time.
There is a quotation is Raseshwara Darshana, saying – Mahesha, Someshwara, Govinda Bhagavat Pada, Govinda Nayaka, Charpati, Kapila, Vayli etc RasaShastra experts Belice in Rasavada.
According to Raseshwara darshana, there are mainly two ways of attaining salvation. One is by controlling Vayu and the other is by controlling Rasa. Here rasa jeans Parada, because Parada is considered as the rasa of Lord Shiva. So, Parada can hmake the person attain tour types of Purusharthas i.e Drama, Artha, kama and Moksha, according to Raseshwara Darshana. Adinatha (Mahadeva) is the founder of Raseshwara Darshana. Yogis like Chandrasena, Gorakshanatha, Nityanatha and kapali etc are known as Practitioners and experts of Raseshwara Darshana.
Read: Rasashastra Itihasa (History of Rasashastra)
Benefits of Parada
- The collective good results of performing many Ashwamedha Yaagas, Donation of Cows, thousands of Gold coins and visitting to all the saced places, can bachieved simple by the Vision of Parada.
- The collective good result of offering Pooja ot all the Lingas present in the three worlds can be achieved by doing Pooja of the Linga, prepared by Parada.
- Consumption of parada relieves a person of all the bad deeds of his past births.
- The bad deds of yester births get deleted by offering Pooja to the Linga prepared with Pisti of Parada and Gandhaka.
- One who does even a small bit of Parada Jarana with Abhraka gains the good results of Ashwamedha Yaaga.
- Consumption, Touch, Meditation, Donation & Processing of Parada – BY perofrming these five rituals, all the bad deeds get deleted.
- One who does Parada Shodhana Marana etc procedurees, gains the good deeds of Tulabhara, Ashwmedha etc.
- One who meditates upon the Fact – “Being Rasasiddha, I will erradícate all the poverty and disease” the person Hill get rid of even the greatest sin of Brama Hatya.
- Adding the Grasa (bolus) of Abhraka into Parada is known as Naivedya. By doing this, one Hill get the good results of peforming a Homa.
- If a person dies, having Parada in his stomach, then all his bad deeds Hill be eradicated, and he gains the ultmate position in the outer World.
Parada is the only capable thing that can bring stability to the body. During the time of massive global disaster, the Praana of all the living beings gets united with the God, similarly, all the medicines of plant origin get merged with Naga (Lead), Naga merges with Vanga (Tin), Vanga merges with Tamra (copper), Tamra with Rajata (Silver), Rajata with Swarna (Gold), and Swarna merges with Parada. Hence Parada only can achieve longevity. Peoplle gain nector by uniting with Lord, similarly, by giving Grasa of Abhraka to Parada, Parada unites with Swarna ec Lohas and makes it nector.
The success of Rasabandha lies in the peroformer thinking in the beginning that he will eradicate all the poverty and disease from this world by attaining rasasiddhi (expertise in rasa processes).
The principle of Raseshwara Darshana is – Parada does Loha siddh i(converision of lower metals into higher metals), similarly Parada also does Deha Siddhi. i.e. conversion of the body into a disease free status. To know whether the Parada has gained the power of making the body disease-free is known by testing it with Loha (metals). The Siddha rasa (processed Parada) which can convert lower metals into higher metals, can convert the body into a long living, disease – free body. Hence, the Parada testing is first done on metals.
Parada
Synonyms
Rasa, Rasendra, rasaraja, Maharasa, Soota, Sootaraja, Parada, Chapala, Mukunda, Shivabeeja, Khechara, jaitra, Rudrateja, Raashihemanidhi, Divyarassa, Mrutyunashana, Rasaayana, Rasottama, Ananta, Amara, Galadaroupyanibha, Dehaja etc.
Introduction
Parada is the only liquid metal, shining white in colour, instable, heavy.
Specific gravity – 13.6
Boiling point – 3570 C
Vapourizes at 3600 C
Solidying point – -390 C At this temperatura, it is malleable and ductile.
Availability
Mercury is available mainly in Spain and Italy. It is alos found in other places like Russia, France, ran, Brazil, Hungary, Germany, North & South America, Yuogoslavia, Australia, California, Africa, Portuguese, Romania, japan China etc. In some parts of India, mercury is found in ore form.
Forms
- Native mercury – procured from the mines in liquid form. Native mercury is found in mines of California called Sonema and rattle snake.
- Compound form
- Native calomel – it appears similar to diamond. Available in Idria and Almaden. Only a little amount of Mercury is available in this form.
- Cinnabar – It is the main ore of mercury. Its characters have been described as follows:
Japakusuma Sankahsa – Colour similar to the flower of Japa. It is also called as hamsapada Hingula. It is found in hard stone form or in powder form.
Darada yakrutakara Hingula (Hepatic cinnabar) – here, the mercury is mixed with Shilajatu.
Read more about Hingula bhasma here
Meta Cinnabar – It is black in colour.
- Coral ore – It has the colour of coral (Pravala). It is mainly available in India, and Italy. It is a mixture of Hingula, shilajatu and Phosphate of lime.
- Red oxide of mercury (Giri Sindhoora) – it is red in colour, powder in form.
- Sulphide form – Available in Hungary, Algeria, etc countries. Here the ore will be a mixture of Iron, copper, zinc etc..
- Arteficial form – Prepared using different techniques of Rasashastra like Kajjali, Parpati, Rasapanka, Raasindhoora, Pottali, bhasma etc.
Apart from the above-mentioned forms, Parada is also available in many other forms and ores also.
Types of Parada
According to Rasaratna Samucchaya – Rasa, Rasendra, Parada, Soota and Mishraka are the five types.
Doshas of Parada
There are mainly three types of Doshas of Parada.
- Naisargika Doshas (natural)
- Yougika Doshas (artificial)
- Aupadhika Dhoshas.(due to exposure into many atmospheric factors)
- Naisargika Doshas (natural) – Parada beign a metal, is found in free and compound form in the mines. It has the natural capability to dissolve other metals and compounds. Hence, the other metals and minerals present in the mines tend to react with Parada leading to Naisargika Dosha.
- Yougika Dosha (artificial) – In the market, many other metals like naga, Vanga etc are admixed with Parada to gain extra commercial benefits, elading to yougika Dosha of Parada.
- Aupadhika Dosha – It occurs due to exposure of Parada to many metals, water, etc atmospheric factors.
The overall Doshas and their effects have been explained in the following flow chart –
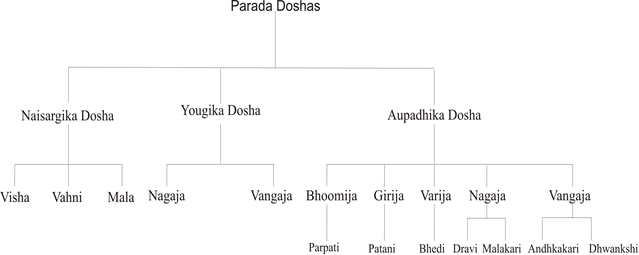
In these Doshas,
Visha Dosha causes Death
Vahni Dosha causes burning sensation (Santapa)
Mala Dosha causes Unconsciousness
Nagaja and Vangaja Doshas cause Jadya (lethargy), Adhmana (bloating) and Kushta (skin diseases).
Features of a good quality Parada
The inside colour should be bluish, and externally it should be bright as smilar to the brightness of the mid day sun, such a Parada is of very good quality.
Features of a bad quality Parada
Parada having greyish to whitish colour, visible foreign particles floating over its surface, having mixture of colours, such a Parada should not be used for therapeutic purposes.
Movement of Parada
Parada has five types of movements. Through these movements, loss of Parada occurs during its shodhana etc processes. Hence the knowledge about its types of movement is very important, in order to check these movements.
The five types are –
1. Jalagati 2. Hamsagati 3. Malagati 4. Dhoomagati 5. Jeevagati
1. Jalagati – The loss of Parada occurring during its washing, is attributed to jalagati.
2. Hamsagati – The loss occurring while transferring Parada from one vessel to the other, while triturating, etc is attributed to its Hamsagati.
3. Malagati – Parada is subjected to various Patana etc processes in order to remove its mala (impurities). The loss occurring during such processes is attributed to Malagati.
4. Dhoomagati – During processes like Jarana etc, Parada evaporates due to heat and such a loss is attributed to Dhoomagati.
5. Jeevagati – The life moves out of body without being noticed by anybody. In the same manner, loss of Parada occurs, which is called as Jeevagati.
In the above Gatis, the first four are visible and can be avoided by taking necessary precautions. The Jeeevagati can not be stopped by anybody, except the desire of the Lord Ishwara.
Necessity for Parada Shodhana
Read more about Shoshana procedure here
It is very necessary to remove the kanchuka Doshas of Parada. Because, though Parada is similar to nector, it exhibits poisonous effects due to the presence of these Doshas. Hence purification of Parada is very essential.
Parada Shodhana (Purification of Parada)
रसेश्वरं समसुधा रजसा मर्दयेत् त्र्यहम् ।
ततो द्विगुणवस्त्रान्तर्गालितं खल्वके न्यसेत् ॥
रसोनं निस्तुषं तुल्यं तदर्धं लवणं हरेत् ।
तत्कल्के मर्दयेत्सूतं यावदायाति कृष्णताम् ।
कृष्णं कल्कं परित्याज्यं तथा प्रक्शाल्य युक्तित: ।
एवमेकेन वारेण रसेन्द्रशुद्दिमाप्नुयात् ॥ – रसतरंगिणी
raseśvaraṃ samasudhā rajasā mardayet tryaham |
tato dviguṇavastrāntargālitaṃ khalvake nyaset ||
rasonaṃ nistuṣaṃ tulyaṃ tadardhaṃ lavaṇaṃ haret |
tatkalke mardayetsūtaṃ yāvadāyāti kṛṣṇatām |
kṛṣṇaṃ kalkaṃ parityājyaṃ tathā prakśālya yuktita: |
evamekena vāreṇa rasendraśuddimāpnuyāt || – rasataraṃgiṇī
Parada Shodhana –
- First Parada is mixed with lime powder and triturated for three days, filtered. Then it is mixed with equal quantity of dehsuked garlic and half part of Saindhava and triturated till the bolus turns to black colour. Then it is washed with hot water and collected. In this manner, Parada gets purified by doing it only one time.
- Parada is triturated with Kumari swarasa, Chitraka moola, Raktasarshapa, Brihati and triphala Kashaya for three days. Then it is washed and collected.
- Parada is triturated with Tambula patra swarasa, Adraka swarasa, Yavakshara, Swarjika kshara and tankana kshara for three days, washed. Thus it gets purified.
Parada Samskara
The processes followed to improve the quality of Parada is known as Samskara.
There are three main purposes of Samskara –
- Beeja Dosha Nivrutti – Removal of intrinsic defect
- Guna Vruddhi – Improve quality
- Angapoorti – making it a complete medicine.
Because of Shodhana, the impurities are removed, due to samksara, the drug gains special qualities.
Number of Parada samskara –
Some say it is 18 and some say 19.
18 types of Parada samskara
स्वेदनमर्दनमूर्च्छोत्थापनपातननिरोधनियमाश्च ।
दीपनं गगनग्रासप्रमाणमथ चारण विधानम् च ॥
गर्भद्रुतिबाह्यद्रुतिजारणरसरागसारणं चैव ।
क्रामण वेधो भक्षणंमष्टादशधेति रसकर्म ॥ (र ह्र् त २\१२)
svedanamardanamūrcchotthāpanapātananirodhaniyamāśca |
dīpanaṃ gaganagrāsapramāṇamatha cāraṇa vidhānam ca ||
garbhadrutibāhyadrutijāraṇarasarāgasāraṇaṃ caiva |
krāmaṇa vedho bhakṣaṇaṃmaṣṭādaśadheti rasakarma || (ra hr ta 2\12)
18 Samskaras of Parada are –
1. Swedana 2. Mardana 3. Murchana 4. Utthapana 5. Patana 6. Rodhana
7. Niyamana 8. Deepana 9. Graasamana 10. Chaarana 11. Garbhadruti 12. Bahyadruti 13. Jarana 14. Ranjana 15. Sarana 16. Kramana 17. Vedha 18. Bhakshana.
Eight types of Parada Samskara
स्वेदनं मर्दनञ्चैव मूर्च्छनोत्थापने तथा ।
पातनत्रितयञ्चाथ बोधनं सुनियामनम् ॥
सुप्रदीपनमित्यष्टौ प्रोक्ताः सर्वोपयोगिनः ।
svedanaṃ mardanañcaiva mūrcchanotthāpane tathā |
pātanatritayañcātha bodhanaṃ suniyāmanam ||
supradīpanamityaṣṭau proktāḥ sarvopayoginaḥ |
1. Svedana
2. Mardana
3. Moorcana
4. Utthapana
5. Trividha pathana
6. Bodhana
7. Nitamana
8. Deepana
Among the above 18, the first 8 are called as Ashta Samskaras of Parada. For the purpose of Rasayana, the parada which has undergone these 8 Samskaras should be used.
Quantity of Parada to be taken for Samskara:
स्वेदनमर्दनमूर्च्छोत्थापनपातननिरोधनियमाश्च ।
दीपनं गगनग्रासप्रमाणमथ चारण विधानम् च ॥
गर्भद्रुतिबाह्यद्रुतिजारणरसरागसारणं चैव ।
क्रामण वेधो भक्षणंमष्टादशधेति रसकर्म ॥ (र ह्र् त २\१२)
svedanamardanamūrcchotthāpanapātananirodhaniyamāśca |
dīpanaṃ gaganagrāsapramāṇamatha cāraṇa vidhānam ca ||
garbhadrutibāhyadrutijāraṇarasarāgasāraṇaṃ caiva |
krāmaṇa vedho bhakṣaṇaṃmaṣṭādaśadheti rasakarma || (ra hr ta 2\12)
According to rasa Ratna Samucchaya, 2000 Pala, 1000 Pala, 100 pala, 28 Pala, 10 pala or een ½ Pala of Parada can be taken for the purpose of Samskaras.
According to Rasatarangini, 100 Pala, 50 Pala, 25 Pala, 10 Pala or 1 Pala of Parada can be taken.
spherical.
| Jalukakara | Valayakara | Gutikakara |
| 8 Angula | Till 16 years | For childrenÉå |
| 10 Angula | Till 32 years | For Young people |
| 12 Angula) | Till 50 years | For Older people |
Parada Bandha
Parada or mercury, even after purification, cannot be administered internally because of its chanchalya (quickness) and durgrahatva (difficulty in absorbing). To overcome this, the mercury should be in bound form and this is called “Bandha”.
According to Rasaranta Samucchaya –
येन येन हि चाञ्चल्यं दुर्ग्रहत्वं च नश्यति ।
रसराजस्य संप्रोक्तो बन्धनार्थो हि वार्त्तिकैः ॥ (र.र.स.११/६०)
yena yena hi cāñcalyaṃ durgrahatvaṃ ca naśyati |
rasarājasya saṃprokto bandhanārtho hi vārttikaiḥ || (ra.ra.sa.11/60)
The procedures that are capable of relieving hypermobility and ‘difficult to grab’ qualities of Parada are called as Bandhas.
Types of Bandha –
हठारोटौ तथाऽऽभासः क्रियाहीनश्च पिष्टिका ।
क्षारः खोटश्च पोटश्च कल्कबन्धश्च कज्जलिः ॥
सजीवश्चैव निर्जीवो निर्बीजश्च सबीजकः ।
शृंखला द्रुतिबन्धौ च बालकश्च कुमारकः ॥
तरुणश्च तथा वृद्धौ मूर्त्तिबद्धस्ततथाऽपरः ।
जलबन्धोऽग्निबन्धश्च सुसंस्कृतकृताभिधः ॥
महाबन्धाभिधश्चेति पञ्चविंशतिरीरिताः । (र.र.स.११/६१-६३)
haṭhāroṭau tathā”bhāsaḥ kriyāhīnaśca piṣṭikā |
kṣāraḥ khoṭaśca poṭaśca kalkabandhaśca kajjaliḥ ||
sajīvaścaiva nirjīvo nirbījaśca sabījakaḥ |
śṛṃkhalā drutibandhau ca bālakaśca kumārakaḥ ||
taruṇaśca tathā vṛddhau mūrttibaddhastatathā’paraḥ |
jalabandho’gnibandhaśca susaṃskṛtakṛtābhidhaḥ ||
mahābandhābhidhaśceti pañcaviṃśatirīritāḥ | (ra.ra.sa.11/61-63)
There are 25 bandhas. Viz –
1. Hata Bandha 2. Arota Bandha 3. Abhasa Bandha
4. Kriyaheena Bandha 5. Pishtika Bandha 6. Kshara Bandha
7. Khota Bandha 8. Pota Bandha 9. kalka Bandha
10. kajjali Bandha 11. Sajeeva Bandha 12. Nirjeeva Bandha
13. Nirbeeja Bandha 14. Sabeeja Bandha 15. Shrunkhala Bandha
16. Druti Bandha 17. Baalaka Bandha 18. Kumara Bandha
19. Taruna Bandha 20. Vruddha Bandha 21. Moorti Bandha
22. Jala Bandha 23. Agni Bandha 24. Susamskruta Bandha
25. Maha Bandha
These 25 types of bandas are explained in Rasaratna samucchaya.
Some others add Jaluka as 26th type of Bandha.









