Ajagallika Meaning, Symptoms, Treatment
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Ajagallika is one of the diseases mentioned under the context of Kshudra Rogas i.e., minor diseases. The disease is said to be manifested mainly in children. Therefore, it can be considered as a special pediatric condition i.e., bala roga. Master Srikantadatta opines that this disease may also manifest in the adults but has been seen to predominantly occur in the children and hence Master Sushruta has stressed and specified the word ‘balanam’ i.e., that which occurs in the children, while explaining the ajagallika disease.
Read – Kshudra Roga: Minor Diseases: Symptoms, Ayurvedic Treatment
Dosha predominance – Kapha and Vata are predominantly vitiated in ajagallika.
Tissues involved – Rasa tissue is mainly contaminated by the doshas and hence the skin is involved in the disease. Skin is the site of manifestation of the disease.
Size and shape of the lesion – the lesion looks like mudga i.e., a grain of green gram. Prognosis – this disease is curable.
Treatises in which ajagallika has been explained –
- Sushruta Samhita
- Astanga Sangraha
- Ashtanga Hrdaya
- Bhavaprakasha
- Madhava Nidana
- Yogaratnakara
Read – Itching And Pruritus: Ayurvedic Understanding
Table of Contents
Symptoms of Ajagallika
Ajagallika is a lesion occurring due to the vitiation of kapha and vata. This disease manifests mainly in the children. The nature and features of the blister is as described below –
- Snigdhah – oily appearance
- Savarnaa – color similar to that of the surrounding skin
- Grathita – nodular
- Niruja – painless
- Mudga sannibha – size and shape of grain of green gram
Additionally, Nyaya Chandrika commentary tells that the blister will also have size and shape of masha i.e. black gram apart from resembling a green gram grain. Therefore, ajagallika blister may appear in 2 forms either like a green gram or black gram. The commentary also clarifies that the lesions are limited to the skin and muscles and do not encroach to the deeper tissues.
Read – Dhatu – 7 Body Tissues As Explained In Ayurveda
Pathogenesis
- Exposure to the etiological factors which jointly vitiate kapha and vata
- Simultaneous aggravation of kapha and vata (aggravated vata takes the association of kapha or pulls it into the skin and muscles – Nyaya Chandrika commentary)
- The aggravated doshas get lodged in the skin and muscles
- Blisters / boils / lesions resembling green gram or black gram appear which are oily, painless, and nodular and have similar color of the surrounding skin
- This condition is called as Ajagallika (manifests mainly in children)
Read – How To Balance Kapha Vata Dosha? 6 Factors To Consider
Sanskrit Verses

Treatment of Ajagallika
The treatment principles of ajagallika are based on whether the lesions are suppurated or non-suppurated. In both these conditions the principle of treatment will differ. Therefore, the physician should be able to differentiate both these conditions from the treatment perspective. This also reflects that the diagnosis of the stages of ajagallika is important for proper and comprehensive treatment to be implemented.
This also makes us understand that Ajagallika is of two types –
- Apakva – immature / non-suppurated – acute
- Pakva – mature / suppurated – chronic
Ajagallika is of two types –
- That manifesting in children
- Adult type
Ayurveda has specified that ajagallika is manifested mainly in children, the discussion of ajagallika and related treatment here is limited to the disease manifested in children. The same principles of treatment shall be implemented in ajagallika manifested in adult.
Read – Blisters: Ayuvedic Understanding, Treatment Principles
Treatment by stages (A.Hr)
- Immature blisters – bloodletting shall be done. For this jalauka avacharana i.e. leech application shall be done.
- Mature blisters – when the lesions get matured and break open, it is treated on lines of vrana chikitsa i.e. on the lines of treating ulcers / wounds.
The treatment principle of ajagallika has been explained in a similar way in Ashtanga Sangraha.
Bloodletting is done using leech application in case of immature disease. Following this the paste of the below mentioned herbs shall be applied on the lesion –
- Yavakshara – alkali of whole plant of barley
- Shukti – pearl oyster
- Saurashtrika – alum
Just by pricking the blisters of ajagallika with fresh and sharp thorns of Kantakari (Solanum xanthocarpum) plant they get matured quickly, break open and get healed.
Vrshamuladi Lepa – paste of vrshamula, roots of Adhatoda vasica and vishala – Citrullus colocynthis shall be applied over the ajagallika lesion. If the blister is hard, preparations of alkalies shall be applied or poured on them and break them open.
Modern correlation
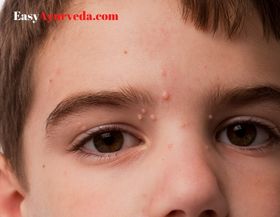
Ajagallika is correlated to a disease of the modern time named Molluscum Contagiosum. The shape and size of the lesion resembling that of green gram shall be correlated to the pearly papules of molluscum contagiosum with characteristic central umbilication.
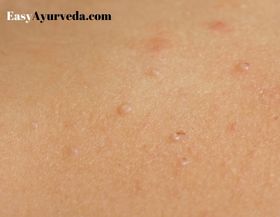
Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a type of viral skin infection. The causative agent (virus) also carries the same name as that of the disease. It is common in children but can affect adults also, mainly in those who have weakened immune systems. This disease is considered as a sexually transmitted disease when genitals are involved in adults having normal immune system.
Characteristic features
The disease is characterized by raised bumps presenting on the upper layers of the skin. Usually it is painless. Most often they go away without being treated. They also do not leave scars when they get resolved. The virus may last for varying lengths of time (different in different individuals). The lesions may also remain for varying periods of time ranging from 2 months to 4 years. In those having weak or compromised immune system, this condition may become difficult to treat or may cause severe effects or complications.
Read – Immunity In Ayurveda: Concept, Diet, Herbs, Medicines, Exercise
How does the disease transmit?
- Direct skin contact with a person having this virus (person-to-person)
- Touching any object contaminated by the virus
The infection of molluscum contagiosum would spread to surrounding skin if the lesions are scratched or injured.
Causes
This disease is caused when one acquires M. contagiosum virus, a type of poxvirus. Active lesions of the patients can transmit the virus. The transmission can also happen from the skin of one part of the body to the skin of other parts of the body of the same person.
Transmission of Molluscum Contagiosum
M. contagiosum virus may pass from one person to the other in many ways. Skin contact with infected person may occur by
- touching the lesions of an infected person,
- among children while playing,
- due to sexual contact in adults
- during contact sports
Surface contact – one can contact the virus by touching the surfaces which the infected person had touched, like contaminated clothing, toys etc.
Sharing – sharing the sports equipment used by the infected person. Example, football helmets, wrestling mats, baseball gloves etc
Internal spread – once you have contacted the virus the infection might spread throughout the body. Similarly the infection / virus may spread from one part of the body to another. This happens by touching other part of the body after touching, scratching, rubbing or shaving (over a bump).
Other points of interest –
- Transmission is found to take place more in wet environments.
- The virus would not spread to other person if the lesions are not active / not visible.
According to experts it is likely that swimmers transmit this virus through many things like shared towels, equipments, or skin contact. So it might be common condition in swimmers.
Read – Concept Of Immunosuppression In Ayurveda
Symptoms
The symptoms may be seen sometimes between 2-7 weeks after one acquires the molluscum contagiosum virus. A small group of painless bumps may appear at first. The appearance of bumps may vary. They may occur as a single bump or a patch comprising of as many as 20 or more bumps.
The characteristic appearance of bumps in molluscum contagiosum –
- Size – small, 2-5 millimeters in diameter/ size varies from that of the head of a pin to that of an eraser on the pencil top
- Texture – Shiny / smooth
- Color – white, pink or flesh colored
- Shape – firm, raised, dome or round shaped with a pit / dimple / indentation in the middle (elevated on the sides and depressed at the center)
- Content – waxy material filling the central core
- Location – anywhere, except on palms or soles, specifically found on the face, neck, abdomen, arms, armpits, hands, legs or torso in children and over inner thigh, genitals (if the infection is sexually transmitted) and abdomen in adults
- Changes – bumps may become red, inflamed or itchy
Complications
- Disseminated secondary eczema
- Impetigo
- Conjunctivitis
- Widespread and larger than usual molluscum contagious most often manifested on the face (mainly in those with compromised immunity)
- Sudden scarring with pitted appearance (may be caused by surgery also)
- Immune response to infection – the bumps and skin around the lesions may become red and inflamed.
- Infection of bumps occur if they are scratched
- If the lesions occur on the eyelids, conjunctivitis can develop.
Risk factors
Anyone can contact the infection of this virus and can suffer from the disease. But the below mentioned are more likely to acquire the virus more than the others and hence are the risk factors of the disease –
- Children between 1-10 years age group
- Those living in tropical climates
- Those having atopic dermatitis
- Having weak immune systems
- Those participating in contact sports
Read – Atopic Dermatitis – Charmadala Kushta: Case Study
Diagnosis
Physical examination – the doctor will diagnose molluscum contagiosum after examining distinct characteristics and appearance as explained above.
For confirmation, skin biopsy may be advised. This is because molluscum contagiosum should be differentially diagnosed with skin cancer, warts and chickenpox.
Prevention
One should avoid touching the skin of another person who has been infected with molluscum contagiosum. This is the best way to prevent getting infected.
How to prevent spreading the infection?
If you are infected with molluscum contagiosum you may follow the below mentioned measures to prevent spreading the infection to others –
- Make a regular practice of washing hand with warm water and soap. Also instruct the children to hand wash regularly and train them with proper hand washing techniques.
- Do not share personal items like towels, clothing, soaps, hair brushes etc with others.
- Avoid sharing other’s sport equipment or yours with others.
- One should avoid touching the lesions / bumps on his / her own body or those of infected person. Shaving over the infected areas can also spread the virus.
- Regularly clean the bumps and keep them covered.
- One should alert the others not to touch him or his materials if he / she are infected with M. contagiosum.
- Those having lesions in the genital area should avoid sexual contact until they are completely treated and the lesions have totally disappeared.
- While swimming one shall cover the lesions with a water-tight bandage.
Treatment
Most times the lesions of molluscum contagiosum will go away without treatment. Treatment might not be required at all if the person has a healthy immune system. Since the lesions are too contagious the doctors would advise them to be removed before they disappear on their own. Combinations of treatments usually work which include a methodical mixture of scraping, cryotherapy and application of medicines that causes blisters which lift off the bumps.
Read – Itching, Pruritus: Causes, Mechanism, Diagnosis, Treatment, Research
Right time to see the doctor
- Lesions are larger than normal, located on face and neck
- Having atopic dermatitis
- Received treatment that reduces immunity
- Acquired a health problem that reduces immunity
- Having low immunity
- Having concerns about spreading the virus to others
Medicinal treatments
One or more of the below mentioned therapies might be effective for those suffering from molluscum contagiosum –
- Cryotherapy – freezing the lesions / bumps with liquid nitrogen
- Curettage – piercing and scraping off the lesions / bump
- Laser therapy
- Topical therapy – application of creams or chemicals
Medicines
- Creams containing iodine and salicylic acid / potassium hydroxide
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Cantharidin application
- Imiquimod (T cell modifier)
Pregnant women, women planning pregnancy and those breastfeeding shall take caution before taking these medicines. They should let their doctor to know their status. For HIV patients contracting molluscum contagiosum, ART (Antiretroviral Therapy) is the most effective treatment.
Prognosis
The disease resolves all by itself in those having good immunity. It generally takes about 6-12 months for the resolution to take place without scarring. In many people it would take few months or years before the bumps of molluscum contagiosum disappears. In those with compromised immunity or having problems related to immune system the infection may become more persistent and can also last longer.
The infection or virus no longer stays in the body once the lesions fade out. During this period one will not spread the virus to others or to one’s own parts. The bumps will reappear if one gets infected once again. One can get infected once again in spite of having got infected once, more so if the immunity tapers in the coming days.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Skype









