Comparative Study Between Avascular Necrosis And Vatarakta
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Avascular Necrosis abbreviated as AVN is a condition in which there is damage and death of bone tissue due to lack of blood supply. This causes collapse of the bone. It is a painful condition.
From an Ayurveda viewpoint we can try to compare many conditions to AVN so as to facilitate it to be treated through effective Ayurveda interventions.
Vatarakta which is often compared to gout is also considered in the comparative study with AVN. But as I said it is traditionally compared to gout and gout is a different entity from AVN. If I put Vatarakta across into the discussion alongside AVN it will be unconventional. Some Ayurveda physicians are also in the opinion of treating AVN on the lines of Vatarakta treatment principles especially when AVN presents with AVN-like symptoms. And when AVN presents with Vatarakta-like symptoms it is seen that the treatment given on the lines of Vatarakta gets successful.
Read – Vatarakta: Causes, Pathogenesis, Types, Treatment
Table of Contents
AVN and Vatarakta
Vatarakta is a disease caused by a pathological combination of vitiated vata and vitiated blood. Aggravation of vata and blood tissue may occur independently, both these entities getting vitiated by their respective etiological factors. They may also get aggravated due to common etiological factors aggravating both vata and blood. In the process of pathogenesis both vata and blood are also capable of aggravating and contaminating each other.
Read – Charaka Samhita Vatarakta Chikitsa 29th Chapter
From perspective of etiological factors
Destruction of bones is caused by vitiated vata because bones and vata share residence and resident relationship. This takes place through two pathways –
- Depletion of tissues aggravates Vata. Depletion of blood tissue leading to loss of blood circulation to the bones leading to death of bones will aggravate vata.
2. Aggravation of vata causes depletion of tissues. Here the aggravated vata destroys and causes death of bone tissue. This vata also destroys the blood tissue and contaminates the channels carrying blood and bones.
Etiological factors which cause aggravation of vata and blood together or independently cause vatarakta. This disease too afflicts the bones and joints just like AVN does.
Among the etiological factors of vatarakta, trauma and contaminated blood are mentioned. Trauma is also said to be the main causative factor for AVN in modern medicine.
Riding horses and camels, travelling in excess, swimming and jumping are said to be the causes of vatarakta. Riding animals can be compared to riding two wheeler vehicles in excess from the modern day point of view. This and excessive travelling may lead to road traffic accidents and trauma so does excessive jumping and swimming.
We need to figure out if other etiological factors mentioned as causal for vatarakta contribute towards pathogenesis of AVN.
Read – Different Causes For Vata Dosha Imbalance, Increase
From perspective of location of the disease
AVN is localized in the bones and joints. Vatarakta is also said to be located in all joints of the body.
From the perspective of premonitory symptoms
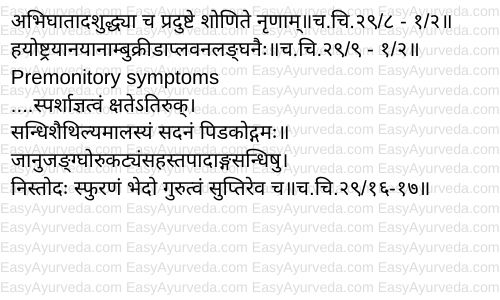
There are no premonitory symptoms mentioned for AVN. Ayurveda has mentioned premonitory symptoms of vatarakta. This helps in early identification of the disease. Below mentioned premonitory symptoms of the disease are similar to the manifested symptoms of AVN –
– Loss of sensation
– Severe pain at the region of injury / trauma
– Looseness of the joints – this explains the collapse of the dead bones and the joint which involves them due to lack of blood tissue
– Pricking pain, pulsating pain, breaking pain, heaviness and numbness in the knee, leg, hip joint, pelvic joints, shoulder joints and joints of hands and feet
Read – Understanding Blood Functions, Vitiation And Treatment As Per Ayurveda
From the perspective of symptoms of the disease
1. Symptoms of Ubhayashraya Vatarakta
AVN occurs in bones and joints of the body. Vatarakta too occurs in the same regions of the body. Vatarakta manifests in one of the below mentioned forms –
– Uttana – Superficial – occurs in skin and muscles
– Gambhira – Deep – occurs in deeper tissues of the body
– Ubhayashraya – Bi-way – occurs both in superficial as well as deeper tissues
The symptoms of bi-way vatarakta resemble the symptoms of AVN. They are –
– Cutting pain in the bones, joints and bone marrow is caused by vata repeatedly
– Crookedness of the bones and joints
– Limp and lameness
2. Symptoms of Vata predominant Vatarakta
– Shula – pain
– Sphurana – pulsations
– Toda – pricking / throbbing pain
– Dhamani anguli sandhinam sankocha – constriction of arteries (main cause of AVN), fingers / toes and joints (joints of fingers)
– Ati ruk – severe pain in bones and joints
– Kunchana stambhane – stiffness of the joints leading to difficulty in moving the joints / loss of flexibility
Read – Rakta Pradoshaja Rogas – When Blood Is Vitiated By Doshas
From the perspective of prognosis
Getting crippled / lameness is one of the signs of bad prognosis of vatarakta. Even in AVN when the joints and bones collapse especially on both sides the person becomes lame and this points towards bad prognosis of the disease.
From the perspective of treatment
Treatments of vatarakta are found to be effective in relieving the symptoms of AVN and halt the progression of disease. The treatment principles which work in AVN are –
– Snehana – administration of medicated fats for internal and external treatments
– Virechana – mild purgatives of unctuous or non-unctuous variety shall be used to cleanse the gut, flush the morbid doshas and toxins, to combat vata and improve circulation to the ailing joints and bones
– Vasti – Repeated administration of decoction and oil enemas
– Parisheka – showering the affected joints with decoctions prepared with disease modifying herbs which do not cause burning sensation
– Abhyanga – massage with disease modifying herbal oils
– Pradeha – anointment with pastes which cure vatarakta, relieves pain and improves circulation
– Avidahi anna sneha – foods and fats (oils and ghee) prepared with herbs which are non-corrosive in nature, modify the disease and do not cause burning sensation
Sanskrit Verses


Principles of treating vata predominant vatarakta
In vata predominant vatarakta, ghee, oil, muscle fat and bone marrow are administered in different modes – for oral consumption, massage and enema and hot / warm poultices should be judiciously administered.
To finish with –
Symptoms resembling AVN are mentioned among the causes (trauma), premonitory symptoms and symptoms of vata predominant vatarakta. Symptoms of the disease manifesting both at superficial and deeper levels are almost similar to those of AVN. The ‘treatment principles of vatarakta’ when applied in the ‘treatment of AVN’ yields good results. Therefore Vatarakta can be compared with modern explanations of Avascular Necrosis vis-à-vis AVN.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)










2 comments
sumanayur
very useful information. Thank you dr Hebber
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Thanks to Dr Raghuram 🙂