Gingivitis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Ayurvedic Remedies
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Gingiva is the part of your gum around the base of the teeth. Inflammation of gingival is called gingivitis.
It is the common form of periodontal – gum disease. It is marked by swelling / inflammation, redness and irritation of the gums. It is a non-destructive type of periodontal disease. If not treated promptly this condition may lead to periodontitis which is a form of serious gum disease and also tooth loss.
It is mostly caused by poor oral hygiene. It occurs when a film of plaque or bacteria accumulates on the teeth.
This condition often resolves with good oral hygiene which includes brushing frequently and for longer time and flossing. An antiseptic mouthwash too might help.
Read – Sensitive Teeth – Causes, Symptoms, Ayurvedic Treatment
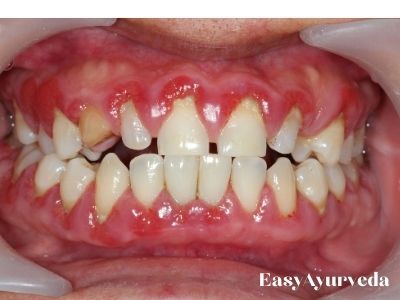
Table of Contents
Prevention and Reverse of gingivitis
- Brushing at least twice daily
- Flossing daily
- Regular dental checkups
Read – Ayurvedic Way Of Teeth Brushing And Tongue Scraping
Symptoms
In mild gingivitis the symptoms are mild and the patient may not be aware of the condition. Mild cases of gingivitis may not be associated with discomfort or noticeable symptoms.
The symptoms of gingivitis include –
- Inflamed / swollen / puffy gums
- Dark red / dusky / purple red gums
- Bleeding from the gums when one brushes or flosses
- Tenderness of gums, painful to touch
- Receding gums
- Bad breath
- Soft gums
Types
1. Dental plaque induced gingival disease – usually caused by –
- Plaque formation
- Systemic factors
- Malnutrition
- Medications
2. Non-plaque induced gingival lesions – caused by –
- Specific bacteria, virus or fungus
- Genetic factors
- Systemic conditions like allergic reactions and certain illnesses
- Wounds
- Reaction to foreign bodies such as dentures
Read – Ayurvedic Remedies and Treatment for Dental Plaque And Tartar
Causes
Poor oral hygiene and subsequent accumulation of bacterial plaques on the teeth is the most common cause of gingivitis. The plaque accumulates between and around the teeth. This plaque triggers an immune response. This in turn causes inflammation of the surrounding gum tissues. This further leads to destruction of gum tissue. If not addressed complications including loss of teeth may occur.
Pathogenesis
When the starches and sugars in the food you eat interact with the normal bacteria found in your oral cavity, plaque is formed. Plaque is an invisible sticky film that forms on the teeth. Since the plaque re-forms quickly it needs to be removed daily.
Dental plaque – is a bio-film which naturally accumulates on the teeth. It is formed by colonizing bacteria which stick around the smooth surface of a tooth. The plaque tends to cause tooth decay, gingivitis and chronic periodontitis.
Formation of tartar and calculus – This plaque when not addressed properly and neglected (not removed at proper time) stays on the teeth. This, in due course of time hardens under your gum-line i.e. base of your teeth into tartar. Tartar looks stony and is a calculus. It also collects bacteria. When tartar is formed, it becomes difficult to remove plaque. Plaque and tartar also causes irritation along the gum line apart from creating a protective shield for bacteria. They also cause inflammation at the base of the teeth. Eventually the gums bleed easily. Tartar can be removed only by a professional dentist.
Effects of untreated plaque and tartar – The gums are constantly irritated and subjected to inflammation with longer persistence of the plaque and tartar. The gums gradually become swollen and easily bleed. Dental caries / tooth decay may also result in due course of time. Untreated gingivitis advances to form periodontitis. Tooth loss may be the ultimate consequence of untreated gingivitis and periodontitis.
Read – Gum Boils – Causes, Symptoms, Ayurvedic Treatment (Danta Pupputa)
Other causes, Risk factors
- Oral negligence – poor habits of oral care
- Smoking
- Chewing tobacco
- Dry mouth
- Poor nutrition
- Vitamin C deficiency
- Ill-fitting dental restorations
- Crooked teeth difficult to brush or clean
- Viral and fungal infections
- Diabetes, leukemia, HIV / AIDS, cancer etc conditions wherein there is lowered immunity
- Old age – risk of gingivitis increases with age
- Hormone changes – related to puberty, menstrual cycle pregnancy, menopause or due to use of birth control pills
- Genetics
- Drugs – like phenytoin, some calcium channel blockers, Dilantin (anticonvulsant), some anti-angina medications etc
- Family History – if one’s parent or parents have had gingivitis, he or she would have a higher risk of developing gingivitis.
Read – Teeth Eruption In Babies – Common Problems, Ayurvedic Remedies
Complications
Promptly treating gingivitis and following all the instructions given by health professionals can help in prevention of complications.
When gingivitis is not treated, it spreads to the underlining bone (periodontitis) and tissues. This condition is of serious nature and can eventually lead to tooth loss.
The complications of gingivitis include –
- Abscess / infection in gums or jaw bone
- Periodontitis – leads to loss of bone and teeth
- Recurrent gingivitis
- Trench mouth – bacterial infection leads to ulceration of gums
Chronic gingivitis is believed to be associated with some of the systemic diseases mentioned below –
- Respiratory disease
- Diabetes
- Coronary artery disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis and
- Stroke
According to some researches – the periodontitis causing bacteria possibly enters the bloodstream through the gum tissue. This could eventually affect your heart, lungs or other parts of the body.
NUG (Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis) / Trench Mouth – is a severe form of gingivitis. It causes –
- Pain in gums
- Infection in gums
- Bleeding gums
- Ulcerations of the gums
It is common in countries having poor living conditions and poor nutritional status.
Read – Spongy Gums – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Remedies
Diagnosis
Oral examination – Your dentist or oral hygienist will conduct a thorough oral examination and check for plaques and tartar or any symptoms which could help in diagnosing gingivitis.
X-ray or periodontal probing might help in checking for signs of periodontitis and also to diagnose it.
Prevention
Brushing, flossing and maintaining good oral hygiene – You should brush your teeth for at least two times in a day. Brushing should be done for at least 2 minutes once in the morning and once at night before bed. Flossing should be done at least once a day. In fact you need to brush after every meal or snack. You can cleanse away the loosened food particles and bacteria from in between your teeth when you floss before brushing your teeth. Electrical toothbrush is a good option for optimum cleansing. Your tooth brush needs to have soft or extra-soft bristles. Replace your toothbrush once in every 3 months. Use natural mouthwashes.
Regular dental visits – You should at visit your dentist for cleanings at least once or twice in a year. You will need frequent cleaning if you have risk factors. Dental diseases that are missed in visual routine dental examination can be identified on X-rays. Therefore they are essential tools of diagnosis and should be sought for annually especially if you have frequent tooth issues or gingivitis. This will help in monitoring your dental health precisely.
Good health practices – You should eat healthy foods and also manage your blood sugar levels especially if you are diabetic. These are very essential for maintaining your gum health and in turn your teeth and oral health.
Diet – Eating healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help prevent gum disease and other oral conditions.
Other measures – Keep away from smoking or chewing tobacco. Limit use of sugar.
Read – 3 Ayurvedic Home Remedies For Toothache: Garlic Paste, Mustard Oil
Treatment
Gingivitis can be successfully treated and reversed if it is diagnosed early and if treated properly and promptly.
Proper care by a dental professional / dentist followed by follow-up procedures at home carried out by the patient and his attendants form the basis of comprehensive treatment for gingivitis.
Professional care by a dentist
- Scaling – plaque and tartar are removed by professional dentists.
- Training – patients are trained about the importance of oral hygiene, about brushing and flossing effectively.
- Follow up – follow-up appointments are recommended and scheduled. Cleanings may be suggested in the follow-up visits.
- Fixing – of damaged teeth will be done which also contributes to oral hygiene.
Home care
Patients should –
- Brush their teeth at least twice daily
- Use electric toothbrush
- Floss their teeth at least once daily
- Use antiseptic mouthwash regularly to rinse their mouth
Read – How To Make Your Own Ayurvedic Tooth Powder? 7 Factors To Consider
Home remedies
Home remedies for gingivitis shall be used in earlier stages of the disease. Chronic disease needs medical opinion and interventions. Plaques should be dealt with before they become tartar or calculus. One needs to increase the frequency and duration of brushing and flossing.
Home remedies are effective to an extent and are also safe to use but it is good to take a medical advice before using them, especially if you are a pregnant, breastfeeding your child or have any other associated medical condition.
You need to immediately see your doctor or dentist if the symptoms are severe including extreme pain or bleeding and also if your gingivitis is not improving with natural / home remedies.
It is very important that you practice doing good oral care to begin with. Home remedies will not be effective if you are not taking care of your teeth and gums.
The above said preventive measures too are effective home remedies. These measures should be practiced thoroughly before trying home remedies.
Read – Mouth Ulcers Ayurvedic Treatment, Medicines, Remedies, Tips
Effective home remedies
Salt Water Rinsing – Salt is very frequently a natural disinfectant. Salt water rinse, according to studies heals inflamed gums in gingivitis. It reduces pain, bacteria and bad breath and also helps in removing food particles stuck in between the teeth and gums. You need to swish the lukewarm salt water solution prepared by adding half to ¾ teaspoon of salt to a glass of lukewarm water for at least 30 seconds and spit it out. Repeat this for 2-3 times in a day.
Mouth Wash – Mouth washes may be tried if there is no relief from symptoms in spite of using salt water rinse. Over-the-counter mouthwashes are available but homemade ones are good enough to try.
1. Lemongrass oil mouthwash – Dilute a cup of water with 2-3 drops of lemongrass essential oil. Swish the solution for 30 seconds in your mouth and spit it out. Repeat it for 2-3 times in a day.
2. Aloe Vera Mouthwash – Swish undiluted and organic, pure Aloe Vera juice in your mouth for 30 seconds.
3. Tea Tree Oil Mouthwash – use it same as lemongrass oil mouthwash. You may also add a drop of this oil to your toothpaste every time you brush your teeth. Don’t use this oil in high concentrations.
4. Sage Mouthwash – Studies showed that this mouthwash significantly lowers the number of bacteria that cause dental plaque. 2 tablespoons of fresh sage or 1 teaspoon of dried sage should be added to 1 cup / 2 cups of boiled water. Leave it for 5-10 minutes, strain and allow the water to cool. Rinse your mouth for 2-3 times in a day. Sage has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. It heals swollen gums and helps in treating the infection of gums.
5. Guava Leaf Mouthwash – Add 4-5 crushed tender leaves of guava to 1 cup of boiling water. Simmer it for about 10-15 minutes. Cool the solution and add little salt to it. Swish the lukewarm mouthwash in your mouth for up to 30 seconds and spit the solution. Repeat it for 2-3 times in a day. Guava leaves are good for oral hygiene. The guava leaf mouthwash, according to studies, is good for controlling plaques owing to its antibacterial and antimicrobial properties. It may reduce pain and gum inflammation and causes freshness of breath.
Read – How To Make Facepack, Mouth Wash, Body Lotion From Curd
Oil Pulling – It is a technique which involves swishing oil in your mouth for 20-30 minutes. This is found to reduce bacteria, eliminate toxins and improve oral health. This is a popular concept in Ayurveda for thousands of years and is getting popular among the Western population in recent years.
1. Coconut oil pulling – Swish 1-2 teaspoons of coconut oil in your mouth for 20-30 minutes and spit it later. Following this, rinse your mouth with water and spit this out. Later drink a full glass of water and brush your teeth. This oil contains lauric acid. It has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Studies have shown this oil reduce plaque and symptoms of gingivitis after regular oil pulling.
2. Arimedadi Ayurveda oil pulling – Swish 1-2 teaspoons of this oil around your mouth for 20-30 minutes. Don’t allow the oil to touch the back of your throat. Spit the oil after swishing and rinse your mouth with water, spit that water too. Later drink a full glass of water. Brush your teeth. Oil pulling with this oil has shown to inhibit the growth of plaque and improve symptoms of gingivitis. It strengthens your teeth and gums, reduces swelling and heals pain and mouth ulcers.
Read – How To Do Oil Pulling In Genuine Ayurvedic Way?
Topical treatment / application – Topical cream or gel might help if mouthwashes are not helping in easing the symptoms of gingivitis.
1. Clove – Mince about 1 teaspoon of cloves. Now dip a damp cotton ball into the minced cloves and gently rub this ball onto your gums. Allow the cloves sit on your gums for about a minute. Swish water to collect all of the cloves and spit the clove water out. Studies show that cloves, owing to its antiviral and antioxidant properties prevent plaque and reduce inflammation. Cloves help in relieving pain. Cloves shall not be used for longer periods or in large quantities.
2. Turmeric gel – First brush your teeth. Apply the and rinse your mouth thoroughly. Now apply turmeric gel to your gums and let the gel sit there for 10 minutes. Swish water around your mouth so as to collect all of the gel in the mouth and spit the water. Repeat this at least twice a day. Studies suggest that turmeric gel prevents plaque and gingivitis probably owing to its anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric also has antimicrobial and anti-fungal properties. It helps in checking the bleeding and reduces redness of the gums.
Sanskrit Verses


Ayurveda Understanding of Gingivitis
In Ayurveda the oral and dental diseases are described under mukhagata vyadhis or mukharogas.
A few diseases mentioned in dantamulagata rogas i.e. diseases and afflictions of gums and alveolar processes resemble the description of gingivitis closely.
The symptoms mentioned in gingivitis are scattered along the below mentioned diseases explained in Ayurveda –
- Dantaveshta
- Saushira
- Paridara
- Upakusha
- Danta Vaidarbha
All these conditions appear to be one or the other stage of gingivitis.
Read – Home Remedy For Gum Swelling And Bleeding Gums

Danta Veshta
This disease occurs due to vitiated blood and is characterized by bleeding and discharge of pus from the gums along with loosening and shaking of teeth.
Saushira
This condition is caused due to vitiated kapha and vata. It presents with the below mentioned symptoms –
- Dantamula shotha – swelling / inflammation of the gums
- Ruja – pain in the gums and root of the teeth
- Lala srava – excessive salivation
- Kandu – itching
- Danta mamsa prashatana – falling of gums
Treatment of Saushira
- Rakta nirharana – bloodletting
- Lodhradi Lepa – application of paste of Lodhra – Symplocos racemosa, Musta – Cyperus rotundus and Rasanjana – extract of Berberis aristata along with honey
- Kshiri vriksha kashaya gandusha – gargle / mouth wash with decoction prepared from the bark of latex yielding trees
- Nasya – errhine / nasal medication with ghee prepared with Triphala (Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellirica and Emblica officinalis), licorice, Utpala – Water lily and Padmaka – Prunus cerasoides
Paridara
This condition is caused by vitiated pitta, blood and kapha.
Symptoms include –
- Dantamamsani shiryante – the gums get detached and fall off
- Ati asrk srava – excessive bleeding from the gums
Treatment
- Vamana – therapeutic emesis
- Virechana – therapeutic purgation
- Nasya – errhine / nasal medication / head purging
- Treatment explained in Shitada disease
Read – Bleeding Gums – Ayurvedic Treatment, Home Remedies
Upakusha
This condition is caused by vitiated pitta and rakta (blood).
Symptoms –
- Veshta daha – Burning sensation around the gums
- Veshta Paka – Suppuration around the gums
- Chala Danta – Loosening and shaking of teeth
- Atyarditah prasravanti – bleeds on pressure
- Mandavedana – mild pain
- Adhmayante srute rakte – the gums get swollen up again after bleeding
- Putim – foul smell
Treatment
1. Shodhana – therapeutic emesis and purgation
2. Shirovirechana – head cleansing / errhines
3. Raktasravana – bloodletting should be done after scrubbing the gums with Kashtaudumbara – Ficus racemosa and Gojihva patra – Onosma bracteatum
4. Pratisarana – gums should be rubbed with one of the below mentioned combinations
- Trikatu – Pippali, Pepper and Ginger, Rock salt and Honey
- Pippali – Piper longum, Mustard, Ginger and Vetasa phala – Salix caprea
5. Kavala dharana – gargle should be done by using
- Decoctions prepared with the herbs mentioned in pratisarana (both formulations)
- Ghee prepared with Kakolyadi Gana group of herbs
6. Nasya – nasal medication / drops with ghee prepared with Kakolyadi Gana group of herbs
Danta Vaidarbha
It is an abhighataja vyadhi – disease of the gums caused by trauma. In this condition redness and swelling occur due to friction / injury to the base of the teeth (gums) and the teeth start shaking.
Treatment –
- Shastra karma – the contaminated muscle (gum) at the root of the teeth should be surgically removed.
- Kshara Karma – after the removal of contaminated gum as said above, using instrument, that site should be applied with alkali.
- Shita upachara – following the above said measures, cold measures like gargles, mouth wash etc should be given to the patient.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)









