By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where thyroid gland makes excessive thyroid hormones. The term thyrotoxicosis is used to describe tissue level pathology of high thyroid hormone. Though used interchangeably, these two conditions are not same. In fact thyrotoxicosis is a generalized term which includes hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid gland is located in front of your neck. The hormones produced by this small gland are essential for metabolism, bone growth, weight management, temperature balance, normal cell functions, cell growth, differentiation etc.
Excessive thyroid hormones impart excessive stimulation on the metabolism. They also exacerbate the effect of the sympathetic nervous system. As a consequence, there is speeding up of various systems of the body. Symptoms include faster heart beats, feeling of your heartbeats, tremors, anxiety and hyper-motility of digestive system, unintended weight loss and unusually low serum cholesterol.
In hyperthyroidism, the events look exactly the opposite of those in hypothyroidism including the pathogenesis and symptoms.
Read related: Hypothyroidism: Causes, Symptoms, Ayurvedic Explanation, Treatment
We cannot find any disease explained in Ayurveda which can be compared to hyperthyroidism. Understanding of hyperthyroidism in an Ayurveda language is done by inferential knowledge.
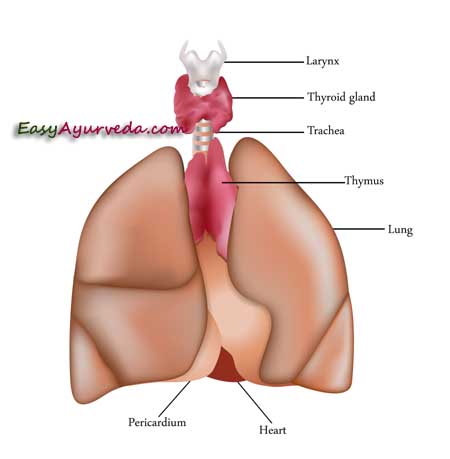
Table of Contents
Signs and Symptoms
Varies from one person to the other, sometimes symptomless. The common symptoms are –
- Weight Loss
- Heat Intolerance
- Increased appetite, often accompanied by weight loss
- Increased sweating
- Fine and brittle hairs, hair loss (especially on the outer third of the eyebrows)
- Pretibial myxedema (in Graves’ disease)
- Enlargement of Thyroid Gland as evident from swelling of the front of the neck from an enlarged thyroid gland (Goiter)
- Opthalompathy (eyes look enlarged)
Neurological symptoms
- Tremors in the hands
- Chorea
- Myopathy
- Periodic Paralysis
Cardiovascular and respiratory symptoms
- Increased Heartbeat
- Palpitations
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Shortness of breath
Musculoskeletal symptoms
- Muscle pains and weakness, especially in the upper arms and thighs
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Osteoporosis (in long term untreated hyperthyroidism)
Mental symptoms
- Emotional lability
- Panic attacks
- Loss of concentration, Memory problems
- Psychosis and Paranoia (common during thyroid storm)
- Delirium
- Anxiety
- Nervousness
- Irritability, hyperactivity
Systemic symptoms
- Sleeplessness
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Excessive urination
- Excessive thirst
- Thinning of skin
- Loss of libido
Other symptoms
- Irregular (less often) menstrual periods in women or with longer than usual cycles, amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods)
- Gynecomastia
- Feminization
- High blood sugar
Eyes Signs of Hyperthyroidism
- Dalrymple Sign or Hyperthyroid Stare – The eyelids are retracted upward more than normal
- Double Vision – is usually caused due to weakness of extra-ocular muscles of the eyes
- Lid-Lag or von Graefe’s sign – When the patient tracks an object downward with their eyes, the eyelid fail to follow the downward moving iris. The same type of upper globe exposure which is seen with lid retraction occurs but temporarily.
- Exopthalmos or Protrusion of Eyeball – It occurs specifically and uniquely in hyperthyroidism caused by Graves’ disease. Not all conditions of exopthalmos are caused by Graves’ disease. But when exopthalmos is present with hyperthyroidism, it is diagnostic of Graves’ disease. Exaptholmos may exacerbate the lid-lag and stare associated with hyperthyroidism.
These signs disappear after effective treatment of hyperthyroidism, when the disease and its symptoms are under control.(Read more)
Causes
Graves’ disease
Toxic thyroid adenoma
Toxic multi-nodular goiter
Thyroiditis –Inflammation of thyroid.
Excessive consumption of thyroid hormone tablets
Amiodarone – It is an anti-arrhythmic drug used in heart conditions. It is structurally similar to thyroxine. Consumption of this drug may cause under-activity or over-activity of the thyroid.
Post-Partum-Thyroiditis (PPT)
Struma Ovarii
Excess iodine consumption
Too much thyroid hormone supplements – Example- levothyroxine.
Hyper secretion of TSH (Read more)
Treatment
Thyrostatics / antithyroid drugs
Beta Blockers
Diet – Foods high in iodine should be avoided in autoimmune hyperthyroidism. Iodized salt in food will be helpful.
Read – Foods to eat and avoid in hyperthyroidism
Surgery – Thyroidectomy
Radio-iodine, which helps to burn down the thyroid tissue.
Ayurveda way of understanding
Hyperthyroidism is related with high metabolism and its consequences. Metabolism is a process by which your food is converted into energy.
The metabolism is initiated and carried out by the metabolic fire i.e. agni. This digestive fire is seated in the gut, in the stomach and intestine to be precise. The overall metabolism is represented by the balanced function of the gut fire and its sub units. While the gut fire which is a controller of other fires is called as Jatharagni, its sub-units located in the tissues are named as Dhatvagni i.e. tissue fires. The sub-units of fire present in the elements making up the body structures is called as bhutagni i.e. elemental fires. They are 5 in number and correspond with the five elements making up the body structures. The tissue and elemental fires work jointly to convert the nutrition provided by the food primarily digested by the gut fire into tissue fuels and energy required to carry out the daily activities.
Read – Understanding Agni: Concept, Definition, Functions, Types
Pachaka pitta i.e. digestive pitta is related with digestion and metabolism of food. This pitta works in synchronization with samana vata located in its proximity. It is like a fire and air combination. The buffer and support to the stomach and intestine is provided by kledaka kapha, a kapha subtype which is also responsible for moistening the food received by the stomach. The balance between these subtypes of doshas in the stomach is equally needed for proper digestion of food and hence a balanced metabolism.
Udana Vata another subtype of vata is located in the region of thyroid gland. Though its functions do not exactly correlate with functions of thyroid gland, the normal thyroid functions or effects of production of excessive and lower thyroid hormones seem to resemble with its synchronization or non-synchronization with the functions of samana vata respectively. Udana Vata tends to move up and down from its main seat i.e. chest. It moves upwards into the throat and nose and reaches the level of navel region which is also the seat of digestive fire when it moves downwards. Therefore its functional territory extends from nose through throat, chest to stomach and intestines. Therefore it has its influence on the digestive fire.
Read – Mechanism Of Avarana, Types, Importance of Vata
Samanavrita Udana
Senior Professor Dr S.N.Ojha sir has compared hyperthyroidism with a condition called Samanavrita Udana.
Samanavrita Udana is a condition in which Samana Vata when aggravated, blocksthe Udana Vata located in the region of thyroid gland. The strong Samana Vata will surround and envelope the udana vata and disturb its functions. Due to severity of samana vata, the digestive fire in the stomach too will get intense. Due to this vicious combination the kapha in the stomach will get deteriorated. The combination of severe vata and pitta with deterioration of kapha will lead to heated up environment in the stomach. This will have an influence on the fires of all the tissues and elements in the body. All these events will eventually lead to agitated metabolism.
Read – Dhatu – 7 Body Tissues As Explained In Ayurveda
This enhanced samana vata associated with the heat of digestive fire will move upwards and hit on the udana vata located in the chest and throat regions. The disturbed and agitated udana vata in an attempt to overcome the attack from samana vata will express itself in an excessive way. The thyroid gland located in the region of udana vata will produce excessive thyroid hormones. This leads to manifestation of symptoms similar to those of hyperthyroidism.
Therefore this comparison of hyperthyroidism with Samanavrita Udana seems to be logical.
Doesn’t samana vata subdue the functions of udana vata as per the rule of avarana?
The initial mechanism of samanavrita udana no doubt occurs following the rule of avarana. The aggravated and more powerful samana vata surrounds and blocks the udana and tries to subdue it. Later the subdued udana vata fights back and tries to overcome the obstruction caused to it by samana vata and over expresses. Over expression of udana too takes place when the block of disease initiating samana vata gets cleared away from the region of samana vata.
Read – Types Of Doshas And Their Functions
Pittavrita Udana
Pittavrita Udana is a condition in which the aggravated pitta envelopes udana vata and disturbs its functions. Thyroid gland is located in the region of udana vata as already said. When pitta influences udana vata, initially the udana vata as per the rule of avarana is blocked and subdued. Later due to over provocation of udana vata with or without the presence of pitta around it will cause stimulate the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormones. This marks the picture of hyperthyroidism. The seat of udana is also the primary seat of kapha. Due to influence of pitta and vata there is deterioration of kapha. Increased vata and pitta associated with decreased kapha marks the events leading to exaggerated metabolism as happens in hyperthyroidism.
Read – Pitta Increase Symptoms – Pitta Vriddhi Lakshana
Pitta Vriddhi
Hyperthyroidism may be understood on the basis of ‘pathological increase in pitta’ in the body. This happens due to increase in pitta and the fiery components located in it, pitta being triggered by the severely aggravated samana vata. Since this combination increases the heat to abnormal proportions in the stomach, there is also a relative imbalance of kapha. Kapha decreases in the stomach. This further gives scope for further aggravation of vata and pitta. The overall impact of these events will be an abnormal increase in metabolism.
Read – How To Balance Pitta Dosha? Line Of Treatment
Kapha Kshaya
Kapha and Vata act as opposite forces. When there is vata increase there will definitely be kapha decrease. Kapha has similar equation with pitta. When there is pitta increase there will be kapha decrease. In hyperthyroidism since there is increase in both vata and pitta, the lethal combination will cause excessive deterioration of kapha in the stomach. The kapha being a water body and cool element will provide a buffer and protect the stomach from the severe aggravation of vata and pitta. But when there is kapha decrease it will further fuel aggravation of vata and pitta. This will further provoke the metabolism.
Read – Kapha Increase Symptoms – Kapha Vruddhi Lakshana
Note
Though pitta increase and kapha decrease cannot be strictly compared to hyperthyroidism it is needed for understanding the pathogenesis of hyperthyroidism. The relative imbalance of Tridoshas will happen in the pathogenesis of hyperthyroidism and these should be brought to balance.
Teekshnagni
Teekshnagni is a disorder of digestive fire in which it becomes abnormally severe. When the digestive fire is influenced by high pitta and fueled by increased vata it becomes severe. This is a key event in the pathogenesis of hyperthyroidism. To treat the disease by its root this intensity of pitta and vata should be controlled at the earliest. This will bring calm down disease process, symptoms get reduced, pathogenesis will stop and bring the metabolic process to control.
Bhasmaka Roga
Bhasmaka Roga is a disease in which the food is burnt down instead of getting digested. When we are cooking food just as more fuel burns and chars the food instead of cooking it severe fire in the stomach too does the same. The food is supposed to get burnt and charred. When the food gets charred less nutritive juices are formed and the body tissues are deprived of nutrition. The tissues are damaged; there is severe depletion of energy and thinning of body with loss of fat and muscles. We can see that some patients of hyperthyroidism lose weight. Again when it comes to intervention balance of pitta and vata in the gut is the key.
Dosha predominance in hyperthyroidism
| Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism | Dosha predominance |
| Fatigue | Vata, Kapha |
| Weight loss | Vata, Pitta |
| Heat intolerance | Pitta, Vata |
| Increased appetite | Vata, Pitta |
| Fine and brittle hairs, hair loss | Vata, Pitta |
| Increased sweating | Vata, Pitta |
| Enlargement of thyroid gland / goiter | Vata, Kapha |
| Opthalmopathy, stare, weakening of extraocular muscles, lid lag | Vata |
| Tremors | Vata |
| Chorea | Vata |
| Myopathy | Vata, Kapha |
| Periodic paralysis | Vata |
| Increased heartbeat | Vata |
| Palpitations | Vata |
| Abnormal heart rhythms / atrial fibrillation | Vata / Kapha |
| Shortness of breath | Vata, Kapha |
| Muscular pain and weakness | Vata |
| Weakness | Vata |
| Fatigue | Vata |
| Osteoporosis | Vata |
| Emotional lability | Vata |
| Panic attacks | Vata |
| Loss of concentration, memory issues | Vata |
| Delirium | Vata |
| Anxiety | Vata |
| Nervousness | Vata |
| Irritability, hyperactivity | Vata |
| Sleeplessness | Vata |
| Diarrhea | Vata, Pitta |
| Vomiting | Vata |
| Excessive urination | Vata |
| Excessive thirst | Vata, Pitta |
| Thinning of skin | Vata |
| Loss of libido | Vata |
| Irregular menstrual periods, amenorrhea | Vata |
| High blood sugar | Vata, Kapha |
| Symptoms of thyroid storm | Vata, Pitta |
Read – Srotas: Body Channels and Duct systems – Easy Explanation
Srotas and dhatus involved
Symptoms and diseases pertaining to many tissues, channels and organs are seen in this disease.
Rasa dhatu and Rasavaha Srotas
Heart is the root of channels carrying rasa tissue. Excessive stimulation of thyroid gland and excessive production of thyroid hormones causes some of the serious complications of hyperthyroidism involving the heart. The symptoms include
- disorders of heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation which can cause stroke
- high cardiac output and left ventricular hypertrophy in the early stages and biventricular dilatation and congestive heart failure in the later stages
- ventricular dilation, persistent tachycardia and eventual chronic heart failure that can result into fatal events
When hyperthyroidism is associated with these events the involvement of rasa carrying channels should be considered.
In hyperthyroidism we get to see irregular menstrual periods and amenorrhea. Menstrual blood is the sub-tissues of rasa tissue.
Mamsa dhatu and Mamsavaha Srotas
Galaganda which is often compared to goiter is a symptom caused due to contamination of channels carrying muscle tissue. Thyrotoxic Myopathy (TM) is a neuromuscular disorder caused due to excessive production of thyroxine. It is also known as hyperthyroid myopathy. This causes weakness of muscles and also breakdown of muscle tissue.
Meda dhatu and Medovaha Srotas
Loss of weight is mentioned as one of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism. When thyroid hormones are elevated, the net effect is fat loss. There is net reduction of hepatic triglycerides due to fatty acid metabolism occurring at a higher rate than fatty acid synthesis. Increased thyroid hormone levels stimulate fat mobilization, leading to increased concentration of fatty acids in plasma. They also increase oxidation of fatty acids in many tissues.
Asthi dhatu and Asthivaha Srotas
Hyperthyroidism is associated with accelerated bone remodeling, reduced bone density, osteoporosis and an increase in fracture rate. Bone damages are necessarily associated with vata imbalance.
Read – Signs Of Person Having Enriched Bones (Asthi Sara Purusha Lakshanas)
Majja dhatu and Majjavaha Srotas
Majja means bone marrow. The other meaning of majja is brain. Bones and joints are the roots of bone marrow carrying channels in the body. The bone related deformities have been explained in the above said context. Tremors, chorea, myopathy and periodic paralysis are some of the neurological symptoms recorded in hyperthyroidism.
Shukra dhatu and Shukravaha Srotas
Excessive thyroid hormones caused as an effect of hyperthyroidism can affect fertility by disrupting the menstrual cycle, causing reduction in sperm count and increasing the risk of early term miscarriage. This also interferes with ovulation in women. (read more)
Pureeshavaha Srotas
Frequent bowel movements, diarrhea and malabsorption with steatorrhea are commonly seen in patients of hyperthyroidism since the overactive thyroid speeds up bodily systems.
Swedavaha Srotas
There will be rise in temperature when the thyroid gland makes more hormones. As a consequence of this, the patient becomes extra sensitive to heat and also sweats a lot.
Chronic dyspeptic symptoms like fullness and pain in epigastric region, eructation, nausea and vomiting are seen in hyperthyroidism. Large goiter can impart pressure on the thyroid gland making swallowing difficult. Aversion to food and vomiting which may be the effects of pressure on food pipe are explained among the symptoms of contamination of channels carrying food. The patient also will have increased appetite.
This term includes two systems i.e. respiratory and cardiovascular system and the pathways of nutrition. Heart is one of the roots of these channels, just like in the channels carrying rasa tissue i.e. the nutritive fluid. Various kinds of breathing disorders, screaming, perplexing and bending of body and giddiness – caused due to lack of nutrition and oxygenation have been mentioned among the symptoms caused by contamination of prana carrying channels. The respiratory symptoms associated in hyperthyroidism are increase in respiratory drive and dyspnea on exertion. The involvement of heart has been highlighted in the explanation of channels carrying rasa tissue.
Note – The symptoms of destruction of tissues and contamination of tissue carrying channels mentioned above comprise mostly of those of aggravation of vata and pitta.
Manovaha Srotas
Emotional liability, panic attacks, loss of concentration and memory issues, delirium, anxiety, nervousness, irritability, hyperactivity and sleeplessness are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism which reflect contamination of channels carrying mind.
Treatment in Ayurveda
Treating Samanavrita Udana
In Avaranas the stronger and aggravated vata should be treated first. The vata causing obstruction i.e. avaraka is said to be associated with ama. In Samanavrita Udana, the samana vata which is causing obstruction of udana and hampering its functions should be treated first. In this instance since the digestive fire is severe due to aggravation of samana vata the association of ama may be less because the heat itself wards off the ama. On the other hand we need to see any abnormal behavior of the digestive fire and see if pitta associated with samana vata is associated with ama or the samana vata itself is associated with ama and treat that condition. Following this, samana vata is addressed.
Read – How To Balance Vata Dosha? Line Of Treatment And Reasoning
Following this, interventions should be planned to control the udana vata functions.
The combined interventions for controlling samana vata and udana vata and bringing them to a state of balance include vata pacifying foods and medicines, unctuous purgation, medicated enemas, intake of medicated fats prepared with vata alleviating herbs and use of Rasayanas – tissue rejuvenating formulations. Since there is tissue damage balya i.e. strengthening medicines and brimhana i.e. bulk promoting medicines should be thought of in the treatment strategy. This will enhance the tissue strength and immunity.
Read – Immunity In Ayurveda: Concept, Diet, Herbs, Medicines, Exercise
Treating Pittavrita Udana
Initially the aggressive pitta should be addressed.
If pitta is associated with ama – the ama dissolving medicines and foods should be given.
If pitta is not associated with ama or if ama has been digested by medicines – pitta alleviating herbs, diet and purgation to expel excessive pitta should be administered.
Once pitta has been treated and taken into control, the udana vata should be addressed. Vata alleviating measures along with unctuous purgation and enema are the best choices for treating vata. Other treatments are similar to treating vata in samanavrita udana.
Read – Basti Chikitsa: Benefits, Routes, Types, Indications, Equipment
Other strategies of treatment
- Treating excessive accumulation of pitta
- Treating kapha decrease
- Treating teekshnagni
- Treating Bhasmaka Roga
- Karshya Chikitsa – treatment for emaciation and tissue repair
Other inclusions
- Balya – strengthening medicines and diet
- Brimhana – bulk promoting medicines and diet
- Rasayana – immunity modulating and rejuvenation therapy
- Shirodhara and Sarvangadhara with oils medicated with vata and pitta alleviating herbs
- Snigdha Virechana – unctuous purgation recipes
- Vasti – oil, ghee and medicated milk enemas
- Nasya – nasal drops with oils processed with vata alleviating herbs
Also –
Treatment as per symptoms of the disease – Hyperthyroidism should be treated according to the predominant symptom or disease presenting along with symptoms of the disease and biological values of increased thyroid hormones and reduced TSH.
Treatment in accordance to related tissues and channels – For this the related disturbance of tissue and channels related with the transportation and distribution of those tissues should be treated promptly.
Treating on lines of Galaganda – When goiter is present it should be treated on the lines of galaganda treatment.
Treating on lines of karshya roga – Weight loss and destruction of tissues and enhanced metabolism should be taken care of and promptly addressed with vata alleviating medicines and diet and also the medicines, therapies and foods advised to treat emaciation / consumption. The treatment strategies of vishamagni i.e. erratic digestive fire influenced by vata, kshaya i.e. tissue destruction and rajayakshma i.e. tuberculosis / phthisis can also be included in treating hyperthyroidism associated with severe emaciation and weight loss.
Vasti Chikitsa – Vasti – enema with oil or milk / decoction prepared with vata alleviating herbs should be administered in chronic and stubborn cases or in presence of symptoms of multiple system involvement. This is because enema is the best treatment for morbid vata.
Read – Decrease Of Tissues – Dhatu Kshaya – Reasoning, Symptoms
Some useful formulations to treat hyperthyroidism
- Tiktaks Ghrita
- Sukumara Ghrta
- Gandharvahastadi Eranda Tailam
- Nimbamritadi Eranda Tailam
- Kalyanaka Ghrta
- Brahmi Ghrta
- Sarasvata Ghrta
- Shatavari Ghrta
- Yashtimadhu Ksheerapaka
- Ashvagandha Ksheerapaka
- Ksheerabala Taila
- Bala siddha kshira
- Rasnadi Ghrta
- Chyavanaprasha
- Ashwagandha Rasayana
- Amalaki Churna
- Amalaki Rasayana
- Kanchanara Guggulu
- Kamadugha Rasa
- Pravala Bhasma
- Pravala Panchamruta
- Sutashekara Ras
- Makaradhwaj
- Dashamularishta
- Saraswatharishta
Important herbs in treatment of hyperthyroidism
1. Ashwagandha – Withania somnifera – for weight loss, to control mind symptoms, to induce sleep, to enhance strength and promote bulk, rejuvenator, for tiredness and fatigue
2. Sariva – Hemidesmus indicus – as coolant, to reduce inflammation of thyroid gland and pitta
3. Chandana – Santalum album – as coolant, to reduce inflammation of thyroid gland and pitta
4. Ushira – Vetiveria zizanioidis – same as chandana
5. Amalaki – Emblica officinalis – as rejuvenator, to calm the tridoshas and balance them, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-pitta
6. Guduchi – Tinospora cordifolia – as rasayana, to balance vata and pitta
7. Kutaja – Holarrhena antidysenterica and Bilwa – Aegle marmelos – to control increased bowel movements, to treat diarrhea associated with hyperthyroidism,
8. Yashtimadhu – Glyzyrrhiza glabra – to combat pitta and vata in the gut
9. Eranda – Ricinus communis, Rasna – Pluchea lanceolata – to combat vata and nervous symptoms
10. Brahmi – Bacopa monnieri, Jatamansi – Nardostachys jatamansi and Shankhapushpi – Convolvulus pluricaulis – for nervous symptoms and to calm the mind
11. Shalaparni – Desmodium gangeticum and Prishniparni – Uraria picta – milk processed with these two herbs or with chatushparni (mentioned herbs with mudgaparni and mashaparni) for cardiac conditions
12. Bala – Sida cordifolia, Nagabala – Grewia hirsute, Shatavari – Asparagus racemosus, Ashwagandha – Withania somnifera and Tulsi – Ocimum sanctum – for enhancing immunity
13. Kanchanara – Bauhinia variegata – for goiter associated with hyperthyroidism
Yoga for Hyperthyroidism
- Bhujangasana – cobra pose
- Sethubandhasana – bridge pose
- Matsyasana – fish pose
- Shirshasana – headstand pose
- Sarvangasana – shoulder standing pose
- Marjari Asana – cat-cow stretch
- Surya Namaskara – Sun salute
- Balasana – Child’s pose
- Shavasana – corpse pose
- Pranayama – Nadi shodhana, Bhramari or Sheetali Pranayama
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Skype










2 comments
Pedro
Thanks for sharing all those information, however The section: important herbs in treatment of HYPOthyroidism, is it a typo and you meant HYPER? Or the herbs listed are for HYPO and not HYPER?
Thanks
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Its hyper. Thanks for pointing it out. Now corrected.