Moth Bean – Uses, Medicinal Qualities, Research

By Dr Renita D’Souza
Moth bean used variedly as dry snack to spicy stew. The seeds are used traditionally to treat fever, paralysis, obesity, cough, rheumatism and liver disorders. Its roots are intoxicating in nature. It is the rich source of proteins and minerals. It is called Makushta in Ayurveda
Botanical Name – Vigna aconitifolia
Synonyms – Phaseolus aconitifolius Jacq, Phaseolus palmatus, Dolichos dissectus
Family – Leguminosae
Table of Contents
Vernacular names
Names in Different Languages
English Name – Moth bean, Mot bean, Turkish Gram, Aconite leaved kidney bean, Aconite bean
Hindi Name – Moth, Mot
Marathi Name – Matkya, Mat, Math, Matha
Bengali Name – Vanmug, Kheri
Gujarati Name – Mat
Kannada Name – Madaki, Madike, Saabara hesara kaalu, Thuruku hesaru, Tutuku hesaru
Telugu Name – Vanmudg, Kunkumapesalu, Minumulu
Tamil Name – Payaru, Tulkapayir
French – Haricot papillon
Japanese Name – Mosu biin
Thai – Matpe
German Name – Mottenbohne
Urdu – Mat, Matki
Qualities, Uses
Medicinal qualities of Moth Bean
Taste – sweet
Vipaka (taste conversion after digestion) – sweet
Graahi – absorbent in nature
Laghu – light to digest
Ruksha – dry
Krimikrth – increases worm infestation
Ruchikrth – improves taste
Causes constipation and bloating
Therapeutic uses of Moth bean (Van mudga)
Jwara – fever
Daha – burning sensation
Raktapitta – bleeding disorders
Effect on Tridoshas
Vatala – increases vata dosha
Kaphapittahara – balances kapha and pitta dosha
Culinary Uses
Culinary uses of Moth Bean
Usal – It is an Indian Spicy stew prepared mainly in the state of Maharashtra. Here sprouted moth beans are cooked to prepare spicy stew. It is usually served with other popular dish of Maharashtra called Mishal Pav.
Dalmoth – Fried moth bean is used make dry snack.
Bhujiya – It is the savory snack prepared from bean flour.
(read more)
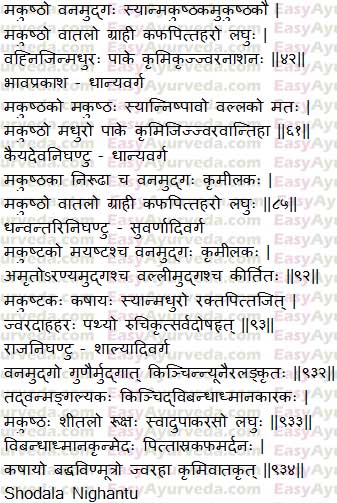
Sanskrit verse
Morphology, Nutrition
Morphology of Vigna aconitifolia
Vigna aconitifolia is a creeping annual herb. Stems grow up to 40 cm in height. Branches are hairy. Flowers are yellow in color. Seeds exists in a variety of color. Leaves are pinnately trifoliolate.
Nutritional Value of Moth bean
Vitamin B9 (Folate) 1272 µg, Iron 21.27 mg, Isoleucine 3.02 g, Magnesium 747 mg, Manganese 3.567 mg, Copper 1.348 mg, Phosphorus 958 mg, Threonine 2.23 g, Carbohydrate 120.58 g, Vitamin B1 1.102 mg

Interaction with medicines, supplements
Can this be used while taking Homeopathic medicine?
Yes. This product does not react with homeopathic medicine.
Can
this medicine be continued while taking supplements like multivitamin tablets,
Omega 3 fatty acids etc?
Yes. Generally, this product goes well with most
of the dietary supplements. However, if you are taking more than one product
per day, please consult your doctor for an opinion.
With western
medicines
Seek your
doctor’s advice if you are taking this product along with other western
(allopathic / modern) medicines. Some Ayurvedic herbs can interact with modern
medicine.
If both Ayurvedic and allopathic medicines are advised together, then it is
best to take Allopathic medicine first, wait for 30 minutes and then take the
Ayurvedic medicine.
Pharmacology, Research, Distribution
Pharmacological Activity of Moth bean
Vigna aconitifolia possess antioxidant, anti inflammatory, neurodegenerative activity.
Research
Moth bean – useful herbal medicinal plant – A review article on pharmacognostic and pharmacological activity of Vigna aconitifolia have proved that moth bean is an useful medicinal plant used to treat various diseases.
Distribution
Vigna aconitifolia is found native to India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Myanmar. It is cultivated in cultivated in the United States, Australia, Thailand and other parts of Asia.
Classification
Classical categorization
Bhavaprakasha Nighantu – Dhanya varga
Kaiyadeva Nighantu – Dhanya varga
Dhanvantari Nighantu – Suvarnadi varga
Raja Nighantu – Shalyadi varga
Shodala Nighantu – Shimbidhanya varga
Sanskrit Synonyms
Makushta, Vanamudga, Makushtaka, Mukushtaka
Read – Green Gram (Mung bean) Qualities, Uses, Remedies, Research
Scientific Classification
Kingdom – Plantae
Order – Fabales
Family – Fabaceae
Subfamily – Faboideae
Tribe – Phaseoleae
Genus – Vigna
Species – V. aconitifolia
Click to Consult Dr Renita D’Souza









