Pterygium – Arma Eye Disorder – Symptoms, Ayurveda Treatment
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Ayurveda explains pterygium as arma. It is a disorder requiring surgical intervention. Arma is one of the diseases of the sclera of the eye (netra shukla gata roga).
Read – Netra Shuklagata Rogas – Disorders Affecting Scler
Table of Contents
Classification
Classification based on location – Arjuna is a Netra Shuklagata Roga i.e. disease occurring in the sclera part of the eye.
Classification based on Predominant Dosha – Arma is of five types. Dosha involvement in each condition differs.
- Prastari arma – is caused by predominant vitiation of all three doshas
- Shukla arma – is caused by predominant vitiation of kapha dosha
- Adhimamsa arma – is caused by predominant vitiation of all three doshas
- Snayu arma – is caused by predominant vitiation of all three doshas
- Lohita arma – is caused by predominant vitiation of blood
Read – Classification of Eye Diseases As Per Ayurveda

Classification based on prognosis – Arma is a Sadhya roga i.e. curable disease.
Classification based on predominant treatment / surgical process– It is Chedana Sadhya Vyadhis i.e. diseases which can be cured by excision method. Therefore, excision is the treatment of choice in Arma eye disorder.
Read – Eye Diseases Causes, Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Treatment, Herbs
Arma – definition
Arma Definition, Meaning, Pathogenesis
Arma is an eye disorder where a growth / swelling of the conjunctiva covers the white part of the eye over the cornea. It is often wedge / triangular shaped and looks like extending from the black of the eye to the outer angle of the eye or otherwise. Signs and symptoms differ according to its types. Arma is is a curable condition.
Read – Ayurveda Eye Treatment Types, Methods – Ashtanga Hrudaya Sutrasthana 23
Signs and Symptoms of Arma
Below mentioned are the signs and symptoms of arma eye disorder as per its sub-types.
| Type of Arma | Predominant features (signs and symptoms) | Meaning |
| Prastari Arma | Prathitam iha arma shuklabhage vistirnam tanu rudhiraprabham sanilam | A thin, spreading, predominantly red and little blue colored, linear swelling occurs over the white of the eye |
| Shukla Arma | Shuklakhyam mrudu kathayanti shukla bhage sashwetam samamiha varddhate chirena | A soft, white and even, slowly spreading linear swelling occurs over the white of the eye |
| Lohita Arma | Yat mamsam prachayam upaiti shuklabhage padhmaabham tad upadishanti lohita arma | A fleshy linear swelling occurs in the fleshy part of the eye and resembles a red lotus in colour |
| Adhimamsa Arma | Vistirnam mrdu bahalam yakrut prakasham shyavam vaa tad adhimamsaja arma vidhyat | A widespread, smooth, thick, dark linear swelling which resembles Liver in colour |
| Snayu Arma | Shukle yat pishitam upaiti vruddhim etat snayu arma iti abhipathitam kharam prpandu | A rough and pale colored swelling occurs in the fleshy part of the white of the eye |
Read – Computer Vision Syndrome: Causes, Ayurvedic Remedies, Tips
Modern correlation
Arma is compared to an eye disorder called Pterygium explained in the modern texts.
Pterygium is an eye disorder which occurs in the white portion i.e. sclera of the eye. It is growth of conjunctiva covering the sclera over the cornea. It is also called as Surfer’s Eye. There is a growth of pink fleshy tissue on the conjunctiva and has a triangular shape.
Read – Alaji Eye Disorder Definition, Location, Symptoms, Treatment
It is said to be caused due to excessive exposure to UV light, spending lot of time in sun and wind, warm conditions and exposure to smoke, sand, pollen and wind. Avoiding these causes helps in prevention of pterygium. It presents with swelling of conjunctiva, redness, burning sensation, irritation, itching of eye and blurring of vision. Surgical intervention will be needed when pterygium interferes with vision.
Read – Trachoma – Causes, Symptoms, Prognosis, Treatment, Remedies
Treatment of Arma eye disorder
Arma eye disorder can be treated by excision method.
Pterygium – Causes, Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Prevention, Treatment
Pterygium is an eye disorder. It occurs in the white portion of the eye (sclera) over the cornea. Cornea is a transparent structure placed in front of the black of the eye and meets the white portion at its circular border i.e. sclera-corneal junction. It is also called as Surfer’s Eye.
Read – Stye – Causes, Symptoms, Remedies, Treatment
Pterygium is marked by the growth of pink fleshy tissue on the conjunctiva. It looks like a wedge shaped growth / triangular growth running from the sclera-corneal junction to the angle of the eye or otherwise. The growth can progress or stop after a particular point of time. It can be seen in one or both the eyes. When it occurs in both eyes it is called bilateral pterygium.
Pterygium is a noncancerous growth. Usually it doesn’t cause any problems and also doesn’t need any intervention. When this comes into the way of one’s vision, it needs to be removed.
Read – Blepharitis: Inflamed Eyelids Ayurvedic Treatment, Remedies
Sometimes before pterygium occurs, a yellowish patch or bump called pinguecula may be noticed over the conjunctiva which gets red when irritated.
It is usually said to occur in people aged between 20 and 40 years of age, but have also been seen in other age groups.
Read – Chalazion – Causes, Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Treatment
Word Derivative
The word Pterygium is derived from a Greek word ‘Pterygos’ which means ‘wing’. Pterygium appears like a winged lesion / swelling in the conjunctiva covering the limbus, more frequently on the nasal side rather than on the temporal side.
Causes of Pterygium
The exact causes of pterygium are not known yet. An increased incidence is noted in latitudes nearer the equator and in those who are exposed to UV light. There is slight higher incidence in males than females.
Exposure to UV light – It is said that it might be caused due to excessive exposure of the eye to ultraviolet light which subsequently causes these growths in the conjunctiva.
Impact of living conditions and environment – Living in warm conditions may predispose to manifestation of this condition. Similarly spending lot of time outdoors in sunny or windy environments also has similar impact. It can occur in anyone who lives in a sunny place.
Exposure to certain elements – Excessive and regular exposure to pollen, sand, smoke and wind are also said to cause pterygium.
Read – Eye Diseases Causes, Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Treatment, Herbs
Pathology of Pterygium
Pterygium in the conjunctiva is characterised by elastotic degeneration of collagen and fibro-vascular proliferation.
Pterygium has three parts. Head of pterygium is an advancing portion. It is connected to the body of the pterygium by a neck. Stocker’s line is a line of iron deposition seen adjacent to the head of pterygium.
Research suggests that a genetic predisposition due to an expression of vimentin which indicates cellular migration by keratoblasts embryological development, which are the cells that give rise to the layers of cornea.
Read – Netra Shuklagata Rogas – Disorders Affecting Sclera
Parts of pterygium
- Head / apex – raised and highly vascular
- Body – fleshy elevated portion, has tortuous vessels
- Superior edge – upper edge of the triangular portion
- Inferior edge – lower edge of the triangular portion
- Hood – fibrous non-vascular portion
- Stocker’s line – brownish line composed of iron deposits
- Fuchs’ Patches – minute gray blemishes that disperse near the head
Read – Computer Vision Syndrome: Causes, Ayurvedic Remedies, Tips
Symptoms of Pterygium
Painful and disturbing symptoms are not common in pterygium. This condition doesn’t cause symptoms always. Even when the symptoms are present they are of mild intensity.
Common symptoms of pterygium are –
- Swelling of conjunctiva
- Redness of the eye
- Burning sensation
- Irritation
- Itching in the eyes
- Blurred vision
- Loss of vision (if the pterygium grows large and covers the cornea)
- Feel of a foreign object in the eye, especially when the swelling is large
Read – Watery Eyes: Causes, Ayurvedic Treatment, Remedies
Complications of Pterygium
Corneal scarring – Severe and progressive, untreated pterygium may cause severe scarring of cornea and may intervene with the vision. This is however a rare condition. If scarring occurs on the cornea, it should be treated as early as possible. Otherwise it may lead to loss of vision. Minor cases shall be treated by administering eye drops or ointment to treat the inflammation. Surgical removal of pterygium is the option in advanced and severe cases. Presence of pterygium makes it impossible to wear contact lenses.
Read – Arjuna, Pishtaka Eye Disorders – Definition, Symptoms, Treatment
Other complications –
- Corneal perforation
- Sclera melt
- Non-healing epithelial defect
- Strabismus
- Recurrence
Diagnosis of Pterygium
- Inspection of eye – The swelling of pterygium is typical. The doctor can diagnose the condition just by looking at it, sometimes as a part of general physical examination.
- Slit lamp examination – Allows seeing the eye with the help of magnification and bright lighting.
- Visual acuity test – by asking the patient to read letters on an eye chart.
- Corneal topography – used to measure curvature changes in cornea.
- Photo documentation – pictures are taken to track the growth rate of pterygium.
Read – Anatomy of Eye: Netra Rachana: Ayurveda Perspective
Prognosis
Usually Pterygium is said to have a good prognosis. It can be treated easily. Surgery is preferred when it interferes with the vision. Recurrence rate can be as low as 1/1000. Complications are uncommon.
Prevention of Pterygium
- Avoiding exposure to the environmental factors like pollen, smoke etc
- Use of sunglasses and hat to shield the eyes from sunlight, wind and dust will help in prevention. Wraparound styles are the best in providing shield against light, wind and dust. Hats with brims shall be preferred. Use of sunglasses also protects the eyes from ultraviolet rays. It should be worn every day, including overcast conditions. One should choose shades which 99-100% of both ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation.
- One can use these glasses while driving cars too. Protective films may be used on the side windows of the cars. This protects the eye while one is driving.
- A person already suffering from pterygium should avoid getting exposed to wind, dust, pollen, smoke and sunlight. This will prevent growth of pterygium or slow its growth. The same measures may be followed to prevent recurrence following the treatment / removal of pterygium.
- Surfers and other athletes participating in water sports should wear eye protection that blocks 100% of the UV rays from the water. The snow sports athletes also should use the same measure.
- One should use artificial tears to keep the eyes moist, especially in dry climates.
Read – Alochaka Pitta – Location, Functions, Imbalance, Disorders, Treatment
Pterygium in Ayurveda
In Ayurveda, an eye disorder named Arma has been explained in the context of the Shuklagata Rogas i.e. diseases of the eye afflicting the sclera i.e. white of the eye. By description, this condition appears closer to pterygium and hence can be compared with it. Even in Arma, there is a swelling or elevated lesion which occurs on the sclera / conjunctiva and is said to be treatable by excision method. Arma is said to be of five types whereas the modern texts have not described any types of pterygium. Ayurvedic enumeration is based on various types of presentation and dosha involvement in each of the armas, though the shape and appearance of the swelling is the same in all types of arma.
Treatment of Pterygium
Usually pterygium does not require any treatment unless it interferes with one’s vision or it causes severe discomfort.
The doctor may prescribe eye drops or ointments containing corticosteroids to combat pterygium causing irritation or redness. These would reduce inflammation associated with pterygium.
Read – Shuktika Eye Disorder – Definition, Symptoms, Treatment
Surgery
Surgery is indicated in stubborn, spreading and growing pterygium, especially if it doesn’t respond to eye drops and ointments. Surgery will be an option when the pterygium encroaches over the cornea causing loss of vision or a condition called as astigmatism which causes blurring vision. Surgery is also an option to remove pterygium for cosmetic reasons.
Excision along with adjunctive therapies such as radiotherapy, mitomycin and 5FU is the preferable surgical intervention in pterygium. Conjunctival flap / graft is said to be the gold standard of care and is said to be associated with less recurrence and minimal complications.
Read – Sushruta’s 8 Types Of Surgical Procedures – Astavidha Shastra Karma
Conjunctival auto-grafting and amniotic membrane transplantation are other effective methods.
In some cases, pterygium can recur following surgical removal. Surgery may cause dryness and irritation of eyes. In such cases, the doctor can prescribe medications to provide relief from symptoms and also to reduce the risk of re-growth of pterygium.
Post operative care with intensive topical steroids may be needed. Follow up should be regularly done, at least for one year after surgery, especially if recurrence is seen. Most recurrences are seen in the first year following surgery.
Read – Methods Of Surgical Training Elaborated In Ayurveda
Excision in Pterygium – Ayurveda perspective
Pterygium is compared to a condition called Arma explained in Ayurveda texts. Like pterygium, arma too is said to be curable by excision method. Even in the absence of modern day sophistications, Ayurveda surgeons had conducted surgeries on delicate parts of the body like eyes.
Arma Chedana – excision
Method of Chedana / excision in treating Arma eye disorder
The method of excising the arma is similar for all the five types of armas. The method is as described below.
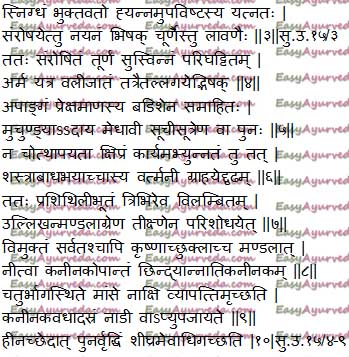
Preoperative measures
Snigdha Ahara – Before conducting the operation on arma, the patient should be fed with fatty food. There is also an opinion that snigdha ahara means medicated fats (ghee) should be given for oral consumption on the previous night and on the day of excision, the patient is made to eat food, before surgery.
Experts also opine that the body of the patient shall be cleansed by administering purifying treatments i.e. emesis and purgation and also nasal purge before conducting excision on arma. After purification, the patient shall be fed with fatty food, followed by excision of arma. Following unctuous food, the patient should be made to sit comfortably on a comfortable seating.
Read – Unctuousness Quality – Snigdha Meaning, Action On Doshas, Therapeutic Uses
Lavana Churna Anjana / Avachurnana – Later, the physician should apply finely ground salt powder into the eye in the form of collyrium to cause irritation of arma. This will also loosen the swelling of arma and prepare it to get excised. Alternatively, the salt powder can be sprinkled into the eye. The effects of sprinkling / dusting are same as application.
Read – Saindhava Lavana Rock Salt Benefits, Ayurveda Usage, Side Effects
Operative procedure
Swedana – Sudation should be given to the lump of arma which has been softened and made loose (bulged) by administering salt powder. (read here)
Parighattana – After sudation, the arma should be mobilized by touching or rubbing it repeatedly.
Chedana – Excision of Arma
The arma is loosened up by administration of salt powder, sudation and by mobilizing it. Due to these procedures, folds / wrinkles appear on the swelling of arma.
Exactly at the place where wrinkles are formed on the arma, the badisha yantra i.e. hook should be applied.
The patient is instructed to see towards outer canthus / outer angle of the eye. The physician conducting excision should sit exactly in front of the patient. The physician should now hold the swollen arma with muchundi i.e. forceps and elevate it. Alternatively, a needle in which a thread is inserted is pierced beneath the arma and the swelling is lifted up.
Read – Shastra – Surgical Instruments Of Ayurveda: Astang Hriday Sutrasthana 26
Importance of handling the swelling gently – The physician should not hurry in elevating the swelling; in fact he should do it gently and slowly. If he hurries the procedure, he may rupture the swelling in a premature way and create complications.
Read – Types Of Swelling – Ayurveda Diagnosis Charak Samhita Sutrasthan-18
Importance of positioning the eye before excision – The physician should keep both the eyelids open and positioned properly so that it is convenient to conduct the surgery. Or else there is always a danger of damaging or cutting the eyelids in the process. When the eyelids are not held properly in position, it becomes difficult to operate on the arma. The swelling which has loosened and separated from the eyeball should be held using three hooks and elevated properly.
Excision of swelling using scalpel – Following this, the physician should cut / excise the arma using Mandalagra shastra i.e. round headed scalpel. When the arma gets detached and separated from the white and black of the eye and elsewhere on the eyeball, it should be gradually pulled towards the inner canthus / angle of the eye and excised completely while protecting the angle of the eye from getting damaged.
Read – Dacryocystitis Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Ayurveda Home Remedies
Importance of sub-total excision – While excising arma, the physician should be careful and allow one fourth of the fleshy part of it to remain on the eyeball, i.e. it should not be excised in totality. By doing so, he will not cause any damage to the eye or vision or create any new complications. Accidentally if the physician not taking caution excises the inner canthus along with the swelling of arma, it causes bleeding and formation of sinus tract in the eye. If less proportion of arma is excised, the remnants of arma will grow back into full size.

Post-operative care
Pratisarana – application of medicated powders over the excised wound of arma
After complete excision of arma, powder of alkali of barley, ginger, black pepper, long pepper and salt should be applied on the wound formed after excision. After applying the above said powder, the wise physician should give sudation to the eye, should place a cotton swab or cloth over it and tie a bandage.
Read – Kshara: Properties, Types, Preparation Method As per Sushruta
He should consider the dosha, season, strength of the patient and time of administration of medicines while doing the bandaging. After considering these factors he should wisely apply fats as and when needed and as beneficial to the condition over the wound and treat it on the line of management of ulcers and wounds.
Example, in involvement of vata or kapha, he should apply oil and in involvement of pitta, he should apply ghee. After three days, he should remove the bandage. After that he should warm his hands by rubbing them. With his warm hands, the physician should apply heat to the afflicted eye. Later he should administer cleansing and healing treatments.
Read – Oil, Ghee And Honey – Best Remedies To Balance Doshas
Management of pain associated with excision of arma
Aschottana, eye drops – If there is pain in the eye caused due to excision of arma, the physician should administer eye drops using milk prepared with paste and decoction of Pongamia pinnata, Gooseberry and liquorice after having added honey to the compound. This should be done twice daily. Pralepa, anointment – Along with the above said eye drops; paste of liquorice, stamens of lotus flower and Bermuda grass ground in milk and added with ghee is applied over the afflicted eye.
Read – Ayurveda Eye Treatment Types, Methods – Ashtanga Hrudaya Sutrasthana 23
Use of Lekhananjana
If some part of arma which had to be excised out has been left out, it needs to be destroyed by application of scraping collyrium. This collyrium scraps off the remnant part.
Read – Anjana – Collyrium Types, Method, Uses, Side Effects, Contra Indications
Shukra Chikitsa
Arma which is small, has white colour resembling the colour of curds or blue or red in colour and is thin should be treated on lines of treating shukra disease i.e. inflammation of cornea (black of the eye) / keratitis.
Management of Charma Arma (arma resembling skin)
The arma which is stout / thick resembling skin (leather) and is enveloped by thick and excessive fleshy fibres and that which encroaches over the cornea should necessarily be excised.
Signs of properly excised arma
Below mentioned are the signs of properly excised arma –
- Vishuddha varnam – eye gets its normal colour
- Aklishtam kriyasu akshi – eye gets effortlessly involved in its activities / functions including closing, opening, seeing etc
- Gata klamam – the tiredness of the eyes goes away
- Anupadravam – the eye will not get afflicted by any complications
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Email / Skype









