Jalavetasa (Salix tetrasperma) Remedies, Dose, Side Effects, Research
By Dr Renita D’Souza Jalavetasa (Salix tetrasperma) is an Ayurvedic herb used traditionally to treat fever, diarrhea, dysentery, rheumatic arthritis, diabetes, skin diseases, bleeding disorders, piles, epilepsy, swellings, urinary calculi, wound, cough, cold, ear pain etc. The dried leaves have beneficial effects over the functions of the heart and nervous system.
Botanical Name – Salix tetrasperma Family – Salicaceae
Table of Contents
Home remedies
Traditional Remedies of Jalavetasa (Salix tetrasperma)
- In Manipur, the new flowers are used to prepare delicious dishes. Flowers are lightly boiled and mixed with smashed potatoes.
- Bark of Salix tetrasperma is the best antipyretic agent. Bark decoction is used to bring down high body temperature.
- Leaf juice is used to treat bloody diarrhea (rakta Atisara), splenomegaly, hepatomegaly and jaundice.
- Leaves are dried, powdered and used along with sugar to treat rheumatic arthritis, swellings, epilepsy, venereal diseases, bladder stone and piles
- In painful menstruation, sap of the stem is used orally.
- Jalavetasa moola( roots) are used to treat diabetes, cough and cold.
- Decoction of roots and leaves are used to treat whooping cough in children.
- Dried leaves possess cardio tonic and neurotonic activity.
- Leaf and root paste is applied externally to heal wounds, warts, sores, scorpion stings and bug bites.
- In ear pain leaf juice is used as ear drops.
- Hot water extract of the plant is used in the vaginal canal to induce abortion and used rectally to treat sores in the rectum.
- Leaves are also made use in rheumatism and piles.
- In Hepatitis, decoction of dried roots is used.
- The tribes of Keonjhar district of Orissa drink the bark paste properly suspended in water to treat diabetes mellitus.
- Its non medicinal uses includes making traditional utensils, basket, ornaments, as roofing material, furniture, fuel wood, fodder etc
Qualities, indications, dose
Medicinal Qualities of Jalavetasa
Rasa (taste) – Kashaya (astringent)
Virya (potency) – Shita (cold)
Guna (quality) – Ruksha (dry)
Karma – Sangrahi (absorbent)
Rakshogna (protects from evil spirits and psychological ailments)
Vrana shodana – cleanses the wound
Indications of Jalavetas
Kusta – skin diseases Raktapitta – bleeding diseases
Effect on Tridoshas
Increases Vata dosha Balances Kapha dosha
Dose Juice – 25 – 50 ml Arka (distillate) – 50 – 100 ml Bark powder – 5 – 10 grams
part used, morphology
Part used
Bark, Leaves, Roots, Flowers, Stem sap
Morphology of Salix tetrasperma
Salix tetrasperma is a medium sized tree grown along riverbanks. Leaves simple, alternate, ovate – lanceolate, 5 – 10 cm long with minute toothed margin. Flowers uni-sexual in axillary catkins, minutely silky-villous, male yellowish and female greenish. Capsules are 4 mm long, stipulate, in groups of 3 – 4. Seeds 1-4, oblong, with long deciduous hairs. Bark is rough with deep vertical fissures.
Sanskrit verse
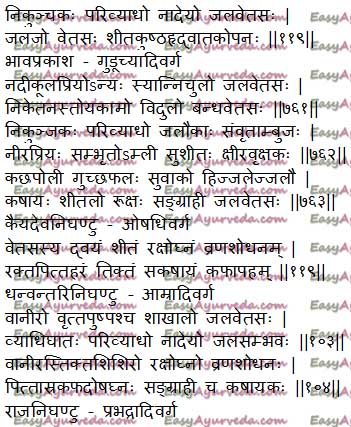
Distribution, pharmacology, chemistry
Distribution
Salix tetrasperma is found in south and southeastern Asia, India, Pakistan, Nepal, Laos and Thailand.
Pharmacological activity of Salix tetrasperma
Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Cytotoxic, Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Antipyretic, CNS activities, Laxative and Diuretic activity.
Chemical Compounds of Salix tetrasperma Catechol, salicin and its derivatives, flavonoid and phenolic acid derivative
Side effects, research, category
Side Effects of Jalvetas
No recorded side effects. In high doses and prolonged usage can cause stomach irritation, nausea and constipation. Seek medical advice for its usage in pregnancy and lactation
Research
1. In a review article the plant Salix tetrasperma is studied for its ethnobotanical uses, phytochemistry and biological activities. The present study has concluded that plants contain phytochemicals such as phenolic compounds, flavonoids, saponins, sterols etc. Study also reported that plants exhibit bioactivities such as antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activity. Also indicated that the plant is ethnobotanically important and used in various medicinal and non-medicinal purposes.(A)
2. Antimicrobial Activity – A research study conducted to evaluate antimicrobial activity of leaf extract of Salix tetrasperma have studied the plant for various bio-activities and concluded that, the leaf of Salix tetrasperma is suitable to include as a ingredient in herbal formulation and can be used to treat bacterial infections and manage seed-borne fungal diseases of plants.
3. Hypoglycemic Activity – The present research study conducted to evaluate hypoglycemic activity of the barks of Salix tetrasperma Roxburg have proved that all the extracts of Salix tetrasperma barks have hypoglycemic activity as it lowers blood glucose level in both normal and diabetic rats. Hence justified the use of bark in treating diabetes as suggested in the folklore remedies.
Classical Categorisation of Indian willow
Bhavaprakasha Nighantu – Guduchyadi Varga Kaiyadeva Nighantu – Aushadi Varga Dhanvantari Nighantu – Aamraadi Varga Raja Nighantu – Prabhadraadi Varga
Scientific Classification
Kingdom: Plantae
Clade: Angiosperms
Order: Malpighiales
Family: Salicaceae
Genus: Salix
Species: S. tetrasperma
Interaction with medicines, supplements
Can this be used while taking Homeopathic medicine?
Yes. This product does not react with homeopathic medicine.
Can this medicine be continued while taking supplements like multivitamin tablets, Omega 3 fatty acids etc?
Yes. Generally, this product goes well with most dietary supplements. However, if you are taking more than one product per day, please consult your doctor for an opinion.
With western
medicines
Seek your
doctor’s advice if you are taking this product along with other western
(allopathic / modern) medicines. Some Ayurvedic herbs can interact with modern
medicine.
If both Ayurvedic and allopathic medicines are advised together, then it is
best to take Allopathic medicine first, wait for 30 minutes and then take the
Ayurvedic medicine.
Vernacular names, synonyms
Vernacular Names
English Name – Indian willow
Hindi Name – Bod, Vet, Jalmala
Kannada Name – Baiche mara, Neeruvanji
Marati Name – Walunj, bithsa
Bengali Name – Panijama
Telugu Name – Etipaala
Tamil Name – Atrupalai
Punjabi Name – Bisa
Malayalam Name – arali, attupala, nirunni, vetasa
Manipuri Name – Ooyum
Sanskrit Synonyms
Nikucha, Parivyadha Nadeya Nichula, Vidula Bandavetasa Vanjula, Deergapatra Jalakama, Vrintapushpa, Gandapushpa
Click to Consult Dr Renita D’Souza










