Relationship Of Doshas With Nidana Panchakas
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Nidana Panchakas are five tools of examination of a disease.
These tools help physician to know, understand and analyse various aspects of disease including its manifestation, etiological factors, pathogenesis, premonitory symptoms, symptoms and complications of a disease. All this information procured from help of these tools helps physician to plan a comprehensive treatment protocol.
Table of Contents
Nidan Panchak
Nidan Panchak – five tools of examination of a disease
Nidana Panchakas are 5 in number. They are –
- Nidana – causative / etiological factors of disease
- Purvaroopa – premonitory symptoms of disease, helps in predicting disease before it occurs
- Rupa – symptoms and signs of disease, helps in diagnosing a manifested disease
- Upashaya-Anupashaya – pacifying and aggravating factors of a disease which helps in knowing disease through application of trial and error method
- Samprapti – sequence of formation of a disease process, pathogenesis of a disease
Sanskrit verse
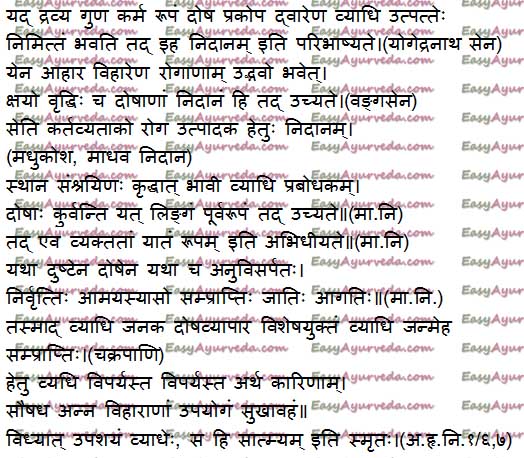
Dosha relation
Dosha relationship with Nidana Panchaka
Doshas – as related to nidan
Nidana means ‘causative factors of a disease’.
They may be caused by external factors like incompatible foods and unwholesome activities or trauma. Vitiated doshas are internal causative factors for a disease.
After one gets exposed to etiological factors of a disease, doshas inside body gets vitiated. These doshas damage tissues and cause diseases. All systemic diseases are caused by vitiated doshas. Therefore vitiated doshas are causative factors of a disease.
Below mentioned classical references establish dosha relationship with and as etiological factors of a disease.
Nidanas are those causes which vitiate doshas and in turn lead to causation of disease – Anything in form of material, substances, qualities and activities which tend to vitiate doshas and hence lead to manifestation of disease are called Nidanas.
Thus, anything which disturbs doshas and become responsible for causation of disease is called Nidan. Vitiated doshas contaminate body tissues and cause diseases.
Read – Pradhanya Samprapti – Understanding Pathogenesis Based On Dosha Strength
Nidanas are those foods and lifestyle practices / activities which cause diseases –
External etiological factors – Foods and lifestyle practices which cause diseases and also qualitative and quantitative depletion or increase of doshas are called nidanas.
Internal etiological factors – Pathological increase or decrease of doshas also causes diseases. They are also nidanas.
Nidanas are those causes which bring about a series of events in the body leading to manifestation of disease. One of most important and mandatory events is vitiation of doshas in body caused by consumed etiological factors.
Series of events are called as ‘iti kartavya’.
Read – Samprapti Vighatana – Breaking Of Pathogenesis Meaning, Importance
Below mentioned chain of events occur after body comes into contact with etiological factors.
- Etiological factors create disturbance once they come in contact with our body.
- Later they cause disturbance of doshas. One or more doshas may be disturbed.
- Vitiated doshas circulate all over body through channels.
- These doshas get lodged in weak and susceptible tissues. Later, they damage tissues and cause many diseases.
- Defence mechanism of body gets disturbed and body becomes weak.
- Over a period of time disease(s) syndrome is manifested with their characteristic signs and symptoms.
Here, we can observe that doshas act as etiological factors and give initiation to disease process. Not only that, they also help in completion of disease pathology, manifestation of symptoms and complications.
Read – Upadrava: Complications of diseases, Definition, Examples
Doshas – as related to premonitory symptoms of disease
Purvarupas are premonitory symptoms of disease.
They are formed when morbid doshas invade tissues during pathogenesis of disease. Interaction of doshas and tissues cause these symptoms which indicate ‘yet to be manifested disease’. They give clue that disease is going to be formed shortly.
Below mentioned classical references establish dosha relationship with premonitory symptoms of a disease.
‘During process of Sthana Samshraya i.e. amalgamation of vitiated doshas and susceptible tissues, vitiated doshas produce certain unclear symptoms which indicate forthcoming disease. These symptoms of yet to be manifested disease are called Purvaroopas or premonitory symptoms’.
Premonitory symptoms are of two types, generalised and dosha specific premonitory symptoms.
Read – Ayurvedic Treatment Strategies To Break The Pathogenesis
Doshas – Symptom relation
Rupas are signs and symptoms of a manifested disease. This happens when amalgamation of doshas and tissues completes and when there is more damage to tissues by morbid doshas.
Below mentioned classical references establish dosha relationship with symptoms of a disease.
‘same premonitory symptoms when get clearly manifested will be called as Roopas (symptoms)’. This definition explains that roopas are transformed and matured forms of purvaroopas.
Since premonitory symptoms are caused by vitiated doshas, symptoms of disease are also caused by same doshas. This is because premonitory symptoms by themselves mature into symptoms in due course of time.
Among various types of symptoms of disease are also mentioned ‘doshaja lakshanas’ i.e. dosha specific symptoms of disease.
Read – Sannipataja Dosha Dushti – When All Three Doshas Are Imbalanced
Dosha – pathogenesis
Doshas – as related to pathogenesis of disease
Samprapti is story of disease. It explains chronology in which a disease is formed after consumption of etiological factors. It includes below mentioned events in chronological process –
Exposure to etiological factors – These etiological factors will disturb equilibrium of doshas and cause their vitiation. At same time, metabolic fire will be disturbed and ama i.e. immature nutritional juices are formed.
Vitiation of Doshas (Dosha Dushti) – is a mandatory process in initiation and progression of a disease process.
Different phases of dosha vitiation and progression towards causation of diseases – This will take place in 6 stages and are called as shat kriya kala. They are –
- Stage of accumulation of doshas in their own seats
- Stage of aggravation of doshas in their own seats
- Stage of spread of doshas to other places of body
- Lodgment of doshas in weak tissues leading to tissue damage and formation of premonitory symptoms of disease
- Extended damage of tissues by morbid doshas leading to formation of signs and symptoms of disease
- Formation of complications of disease
All above explained happenings are subsequent steps of disease formation or Samprapti.
Thus, ‘All stages from very contact of body with etiological factors to development of disease including all its stages are together called as Samprapti of disease’.
Read – Independent And Dependent Dosha Imbalance – Explanation, Example
Below mentioned classical references establish dosha relationship with symptoms of a disease.
Process in which doshas which have undergone vitiation in many forms, due to exposure to many etiological factors, travelling in different tracts, having various kinds of movements get lodged at various tissues and organs of body and produce diseases pertaining to that particular organ or tissue, after getting amalgamation with tissues and causing their contamination and subsequent damage vitiation is called as Samprapti.
‘manifestation of a disease due to different pathological activities and effects caused by doshas, involved in process of pathology is called samprapti’.
Aggravated doshas get lodged in weakened tissues vitiate them and produce deformity in them leading to disease. This is called Samprapti.
There are many components involved in a disease pathogenesis. Among them, dosha is also counted; dosha is in fact primary and most important component involved in pathogenesis. Other dosha related component are dosha gati i.e. movement of vitiated doshas in various directions of body.
Read – Role of Doshas In the Causation of Disease
Doshas – as related to upashaya-anupashaya i.e. relieving and aggravating factors of a disease
Upashaya means that which relieves dosha or disease.
Anupashaya is opposite of upashaya, it means that which aggravates dosha or disease.
Diseases and doshas can also be examined on basis of aggravating and relieving factors. When it becomes difficult to diagnose a disease or its nature, it is wise to do a trial and error method and diagnose disease. This is called Upashaya i.e. knowing disease through relieving factors and Anupashaya i.e. knowing disease by factors which do not pacify a disease, but cause its aggravation.
It is a method of examining and diagnosing diseases with concealed symptoms. Methods of examining diseases on basis of relieving and aggravating factors are of 18 types. They are not only tools of examination of a disease but also become treatment of disease. While doing trial and errors we would have administered perfect treatment for disease.
Read – Roga, Rogi Pareeksha: Examination Of Disease And Patient
In this, we administer medicines, diet or activities which are similar or antagonistic to cause of disease, disease or both.
Since diseases are caused by doshas, above said strategy i.e. trial and error method of diagnosing disease are also applicable to doshas. It is not enough that a disease is diagnosed, it is equally important that causative dosha(s) and their gradient of vitiation also should be diagnosed. Same medicines, diet or activities which are pacifying or antagonistic to the cause of disease, disease or both are also pacifying and antagonistic to causative doshas. This strategy helps in identifying dosha(s) and sub-types of doshas involved in causation of disease.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Email / Skype










