Bodhaka Kapha – Location, Functions, Imbalance, Disorders, Treatment
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Bodhaka means to know or ‘that which helps one to know’. In this context, the type of kapha which helps one to know and recognize tastes of different kinds of food is called bodhaka kapha.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Other meanings of bodhaka (all denoting taste of substances consumed once they come into the contact of tongue) –
- To inform
- To reveal
- To enlighten
- To awaken
- To arouse
- To denote
- To indicate
Read – Sub Types Of Kapha – Importance, Salient Features
Subtype of kapha which informs, reveal, awaken, arouse or denote the tastes present in different types of substances is called bodhaka kapha. Once the food substances are kept in mouth, they come in contact with tongue and bodhaka kapha located in it. The ‘taste denoting kapha’ further helps in recognizing the taste of food which has come in contact with tongue and also to discriminate and relish different types of food.
Read – Six Tastes Of Ayurveda: Qualities, Benefits, Therapeutic Action (Shad Rasa)
Bodhaka Pitta is one of the five sub-types of kapha.
Sanskrit sloka

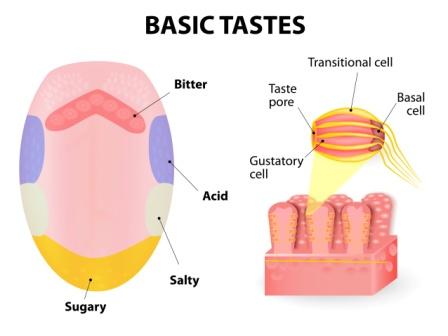
Location
Seat of Bodhaka Kapha
- Jihwa i.e. tongue (A.Hr.Su.12), Jihwendriya (Sushruta)
- Jihwamula i.e. root of tongue (Su.Su.21)
- Kantha i.e. throat
Bodhaka kapha being located in tongue and throat helps in perception of different tastes. It helps tongue or rasanendriya (sense organ of taste perception) to perceive tastes of foods, liquids and substances coming into its contact immediately after they are kept in mouth.
Read – Ayurvedic Tongue Examinations Explained In Vaidya Sara Sangraha
Functions
Functions of Bodhaka Kapha
Perception of taste –
Helps in perception of taste by tongue.
Recognition and distinguishing between different tastes –
Bodhaka kapha helps in recognition and discrimination of different tastes. For this to happen, the substances kept in mouth should dissolve in bodhaka kapha produced in mouth and located in tongue.
When food substances are kept in mouth, they come into contact with tongue. As a response, the tongue produces bodhak kapha. It is also produced by tongue as a response to sight of tasty, favorite foods.
Read –
Bodhaka kapha allows dissolution of food substances in it. Once dissolved, the food come in contact with taste buds. When this happens, one can perceive different tastes. If secretions of salivary glands produced in mouth help in taste perception, they can be collectively considered as bodhaga kapham.
Keeps mouth moist –
Keeps mouth wet all time and lubricates tongue, buccal cavity, gums and throat.
Read – Dry Mouth Causes, Ayurvedic Treatment, Remedies, Tips, Diet
Helps in maintenance of voice –
For a good quality voice to be produced, mouth and throat should be lubricated always. We would have experience of not being able to speak properly when mouth and throat gets dried. This is due to absence of bodhak kaph and generally happens when one is undergoing stressful moments or has consumed some foods which cause dryness in throat and mouth.
Bodhaka kapha thus helps in manifestation and modulation of voice.
Read – 6 Quick Natural Remedies To Improve Singing Voice
Pathology
Pathology related to Bodhaka Kapha imbalance
When bodhak kaf gets imbalanced there is loss of perception of taste. One could neither appreciate taste of consumed food nor could differentiate between different tastes.
When it gets decreased, it causes dryness of mouth and throat. It causes hoarseness of voice and thirst.
Deficiency in bodhaka kafa along with decreased samana vata and pachaka pitta may lead to tastelessness and anorexia.
Different tastes are manifested in mouth when doshas are imbalanced in body. Example, when vata is vitiated the taste in mouth becomes bitter, when pitta is vitiated taste is sour or salty and when kapha is vitiated taste will be sweet.
Read – Bitter Taste – Qualities, Health Benefits, Side Effects
Dosha vitiation will also change the configuration of bodhaka kapha. At the same time bodhaka kapha helps in identifying the vitiated dosha by causing abnormal tastes in tongue. Such pathological manifestations of bodhaka kapha leading to abnormal tastes in tongue can happen in various diseases.
Excessive production of bodhaka kapha will lead to excessive salivation, water brash, nausea and vomiting.
Modern correlation
Probable Modern Correlation
It may be compared to salivary juices secreted by salivary glands.
Salivary glands comprise of parotid glands, submaxillary and submandibular glands and sublingual glands. Parotid glands are situated in mastoid process, a projection of bone just below the ear.
Secretion of these glands is conveyed to mouth through the ducts of Stenson. Secretions are predominantly serous in nature.
Sub-maxillary glands secretion is mixed type, it comprises of secretions of serous and mucus types. Ducts of Wharton carry these secretions to the floor of mouth.
Read – Benefits And Usage of Water As per Ayurveda: Complete Compilation
Sub-lingual glands are situated near dorsum of tongue. They convey secretions through Ducts of Rivinus. The secretions of these glands are predominantly mucus in nature.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Email / Skype









