Interrelationship Of Pelvic Organs As Explained By Sushruta
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Human body is an abode of organs. These organs are interrelated with each other and work as an integrated system. Similarly they are also related to each other through pathogenesis. This means to tell that if one organ is diseased, the other organ in its neighborhood is also afflicted.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Even functionally connected organs located at a distance are afflicted when one of them is diseased.
Example, hypertension can cause kidney disease. Diabetes can cause eye disease. Obesity can cause heart, kidney and liver disease.
Similarly treatment of one diseased organ can cure other organ related to it, either structurally or functionally.
Read – Gastro intestinal Bleeding Causes, Symptoms, Differential Diagnosis
Ayurveda, in spite of being an ancient school of medicine had a precise and comprehensive knowledge of this relationship between different organs and tissues in body.
Sushruta, known as father of surgery was also first pioneer of anatomy in Ayurveda. His section of Sushruta Samhita which deals with anatomy and embryology is considered as best as far as these topics are concerned.
Read – Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Ayurvedic Treatment, Therapies, Medicines
Sushrutha’s opinion
Interrelationship between the pelvic organs as explained by Sushruta
Like other organs in body, organs located in pelvic cavity are related to each other functionally and pathologically as explained above. Ayurveda had clear cut knowledge of such connectivity.
Sanskrit verse

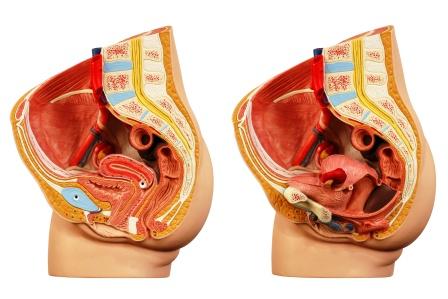
Relationship between uterus and urinary bladder
Sushruta and Vagbhata have explained anatomical relationship between uterus and urinary bladder and have said that uterus is situated behind urinary bladder.
Dalhana, commentator of Sushruta Samhita says that urinary bladder is located behind vulva and uterus is situated above urinary bladder.
Uterus and urinary bladder are included in mahasrotas i.e. great channel of body.
Dalhana’s explanation that uterus is situated above urinary bladder and Sushruta’s explanation that uterus is situated behind urinary bladder is not mutually controversial. There is no doubt that uterus is not only present behind urinary bladder, but a part of it i.e. fundus bends over upper surface of urinary bladder and hence a part of uterus is above bladder.
Read – Marma Shaareera: Definition, Composition: Vital Points of The Body
Connectivity
Connectivity between urinary bladder and other pelvic structures
We have an example for such an instance quoted in chapter dealing with treatment of urinary bladder calculi in Sushruta Samhita.
In chapter of treatment of urinary bladder stones, Sushruta and Vagbhata have cautioned to avoid injury to eight vital parts i.e.
– Mutravaha srotas – channels carrying urine
– Shukravaha srotas – channels carrying semen
– Mushka srotas / phala srotas – testes in men and ovaries in women
– Mutrapraseka – urethra
– Sevani – perineal raphe
– Yoni – entire reproductive system, vaginal canal
– Guda – anus, rectum
– Basti – urinary bladder
Read –Urinari calculi – Home Remedies, Ayurved Treatment, Diet, Recipes
Injury of one structure enlisted above creates possibility of other structure being injured because they are neighbors located very closely to each other. Injury to urinary bladder may injure reproductive system, anus, perineum, rectum, ureter and urethra, semen carrying ducts etc. and vice versa. This can happen both in case of males and females.
Urinary bladder is a vital organ predominant in ligament tissue. It is also called as Basti Marma. It is also a vital organ whose injury will take away life instantaneously. Therefore extraction of stone impacted in urinary bladder is always challenging.
This also shows that extreme precaution needs to be taken while conducting any surgery on urinary bladder. There is a possibility that neighboring organs are injured in process if caution is not taken during surgery. Therefore, Sushruta being a surgeon cautions to protect these structures while removing stones from bladder.
Read – Dysuria: Causes, Remedies, Tips, Diet, Ayurvedic Treatment
Though all of these structures cannot be strictly termed as vital organ on basis of definition and classification of marmas (vital organs), with exception of rectum and urinary bladder, we may consider them as causing marma-like effect when they get injured.
They may cause death, failure of functions, deformity etc when they get injured.
Also we should remember that term marma includes not only one structure or organ but also structures and tissues around it.
Marma is a place of amalgamation of blood vessels, muscles, tendons and ligaments, bones and joints with one of them being predominant in a given area.
Read – Importance Of Marma: Need for study
In same context anatomical location of urinary bladder in relation to uterus has been explained. After describing location of uterus behind urinary bladder, it is advised that for extracting urinary bladder stone in females, instrument should be passed directing it upwards, or else an ulcer discharging urine may be formed.
According to Dalhana, if instrument is forcibly inserted, deeper and directing it downwards instead of upwards, then, after puncturing skin and flesh, it will puncture urinary bladder, vagina and uterus located behind bladder and thus produce a wound discharging urine inside vagina.
Injury to bladder with uterus or vagina results in development of utero-vesical or vesico-vaginal fistula respectively and injury to urethra with vagina to urethra-vaginal fistula.
Besides, above mentioned structures should also be taken care of during any gynecological surgeries since injury to these structures may cause fistulas.
Read – Fistula In Ano Ayurvedic Understanding And Effective Treatment
In this context we should appreciate –
– Knowledge of Ayurvedic teachers of ancient time about anatomy of organs and their structural connectivity
– Precision in surgical knowledge and caution which they used to take while conducting surgeries
– Comprehensive knowledge about complications which could occur when structures around a particular organ are damaged while doing a surgical process and caution taken to preserve and protect these structures during surgery
– Contextual explanation of anatomical relation of organs, example, in this context relationship between uterus and urinary bladder has been explained during explanation of treatment of urinary bladder stones. If this relationship is explained anywhere else in any other context, it would be difficult to understand and remember in comparison to its explanation being found in right context.
This is among first references available about understanding of surgical anatomy i.e. to have a precise knowledge of anatomy of organs and their interrelation to conduct surgeries safely and avoiding damage to the organs and not creating complications.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Email / Skype









