Puyalasa – Definition and meaning, location, symptoms, treatment
Article by Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Puyalasa is a Netra Sandhi Gata Roga i.e. one of the 9 diseases affecting the junction areas of eye.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Pooyalasa – Quick look about the disease
Location – Kaneenika Sandhi – Inner Canthus (meeting point of eye lids on the inner side of the eye)
Classification based on Predominant Dosha – Pooyalasa is a Raktaja Netra Roga – caused by vitiated blood
Classification based on prognosis – It is a curable disease
Classification based on predominant treatment / surgical process used in combating the disease – Pooyalasa is a Vyadhya Netra Roga i.e. curable by administration of vyadhana i.e. puncturing or pricking
Related reading – Netra Sandhi Gata Rogas
Definition, meaning
Puyalasa, definition and meaning
Puyalasa is a suppurating swelling (protuberance, growth) occurring in the inner angle of the eye, the meeting place of the two eyelids near the nose (kaneenika sandhi).
Puyalasa is a swelling (protuberance, growth) which occurs in the kaneenika sandhi or outer canthus (junction between upper and lower eyelids on the inner side of the eyes.
First a swelling (shopha) occurs in the kaneenika sandhi. Later, this swelling will undergo suppuration. Following suppuration of the inner angle of the eye, there is discharge of thick, viscous, foul smelling pus. This is called as Puyalasa.
Vagbhata tells that this swelling (protuberance, growth) after suppuration and discharge of pus goes on to form sukshma vranas (small ulcers) in the kaneenika sandhi. He also mentions the presence of pain in the affected area.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Pooyalasa
Pakvah Shophah Kaneena Sandhau – suppurating swelling (protuberance, growth) in the inner canthus (meeting place of the eyelids on the inner side of the eye.|
Sandra puti puya srava – discharge of thick, viscous, foul smelling pus from the inner angle of the eye
Sukshma Vrana (Vagbhata) – small ulcers in the inner canthus of the eye
Vedana – pain in the region of the swelling (inner canthus)
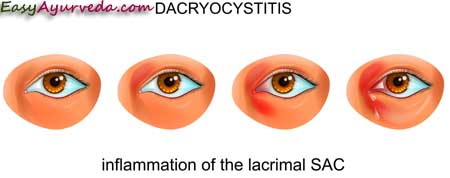
Modern correlation
Pooyalasa can be compared to acute or chronic dacryocystitis or lachrymal abscess.
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac (tear bag), secondary to obstruction of the naso-lacrimal duct at the junction of lacrimal sac. The term derives from the Greek words dakryon (tear), cysta (sac) and itis (inflammation) i.e. inflammation of the tear sac. It causes pain, redness and swelling over the inner aspect of the lower eyelid and epiphora.
Treatment
Treatment of Pooyalasa
Raktamokshana and Upanaha –
Rakta Mokshana (bloodletting) and Upanaha (herbal poultices) are the treatments of choice for Pooyalasa.
Internal and external cleansing:
Apart from the above said key strategies, all the treatments advised for treating and curing akshipaka (suppuration of the eye), including
antah shuddhi (internal cleansing treatments – mainly virechana or purgation) and
bahi shuddhi (external cleansing measures)
Kasisadi Anjana 1 (collyrium) – Kasisa (purified), Saindhava Lavana (rock salt) and Ardraka (ginger) are grinded properly in honey. The resultant mixture (paste) is used as collyrium and applied to the eyes of the patient suffering from Puyalasa.
Kasisadi Anjana 2 – To the same ingredients mentioned above, add purified ash or powder of tamra (copper) and ayasa or loha (iron). Use this as anjana (collyrium) in Puyalasa.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu) – Email / Skype






