Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis
Article by Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) & Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
PID or Pelvic Inflammatory Disease is a condition wherein inflammation (swelling) following infection occurs in the pelvic region and pelvic organs, mainly reproductive organs in women.
PID is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system. The condition includes infection of uterus (Womb), fallopian tubes (uterine tubes or tubes which convey eggs from the ovary to the uterus) and ovaries. It also includes infection of the inner side of the pelvis.
Table of Contents
Symptoms
Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Evident symptoms may sometimes be absent in PID. Many times there are severe symptoms. Thus there is variability in symptoms and severity.
- Pain in the lower part of the tummy / belly (lower abdominal pain)
- Vaginal discharges, New discharges or different type of discharges
- Fever
- Burning urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Irregular menstruation
- Cervical motion tenderness
- Uterine Tenderness
- Adnexal tenderness
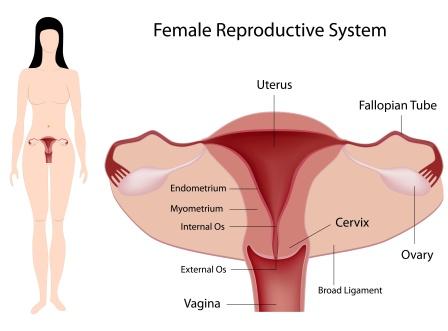
Causes of PID
PID is caused by bacterial infections. In about 75-90 % cases PID is associated with infections caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis. According to available data, PID is caused by many bacteria (poly-microbial). Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrheae are usually the main causes among the lot. When these infections are not treated comprehensively, they lead to manifestation of PID.
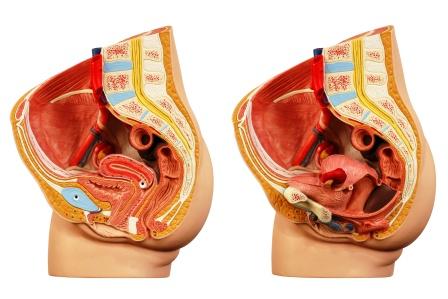
Bacteria spread from the vagina and cervix. The pathogens ascend from the vagina to the pelvic cavity through the infundibulum. Disturbance of naturally occurring vaginal microbiota along with bacterial vaginosis enhances the risk for development of PID. Anaerobes and facultative bacteria were also seen to be present in the upper part of the genital tract in nearly 2/3 of PID patients.
Complications of PID
Complications of PID occur when the condition is improperly treated or when it is not addressed at proper time. Infection causes scarring. Scarring of reproductive system leading to one or the more complications like –
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Infertility
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Complications of pregnancy
- Cancer
- Endometritis
- Salpingitis
- Tubo-Ovarian abscess
- Pelvic peritonitis
- Peri-appendicitis
- Peri-Hepatitis
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (Formation of scar tissue on the outer surface of liver)
Risk Factors
Multiple sexual partners
Drug use
Vaginal douching
Diagnosis and Examination
Diagnosis of PID is mainly done on the basis of signs and symptoms which are typical of this condition.
Finding of pus involving fallopian tubes during surgery confirms the diagnosis of PID
Ultrasound too helps in diagnosis of this condition
PID should be suspected and considered when a women of childbearing age presents with lower abdominal pain
On pelvic examination – cervical motion, uterine or adnexal tenderness will be experienced
Muco-purulent cervicitis or Urethritis may be seen
Laparoscopy – is helpful in severe conditions
Intra-abdominal bacteria sampling and culturing or tissue biopsy – will be done as and when needed in severe conditions
Imaging – USG (Ultrasonography), CT (Computed tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Imaging) are good tools for diagnosis of PID
Blood tests – Blood tests in PID helps in identifying the presence of infection. ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), CRP (C – reactive protein) and Chlamydial and Gonococcal DNA probes are useful.
Sensitive tests to identify specific pathogens – NAATs (Nucleic acid amplification tests), DFA (Direct Fluorescein Tests) and ELISA (Enzyme linked immune-sorbent assays)
Definitive criteria – Histo-pathological evidence of endometritis, thickened fallopian tubes or laparoscopic findings. Gram stain or smear help in definitive identification of rare, atypical and serious organisms.
Laparoscopic identification – helpful in diagnosing tubal disease
Gynecological ultrasound – tubo-ovarian complex is seen (it is edematous dilated pelvic structure)
Differential Diagnosis
Appendicitis – It is the inflammation of the appendix. It presents with sever right lower abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting and decreased appetite
Ectopic pregnancy – It occurs when an embryo implants somewhere other than the uterus, such as in one of the fallopian or uterine tubes. Symptoms include lower abdominal and pelvic pain, lack of menstrual period and vaginal bleeding.
Ruptured ovarian cysts – A ruptured cyst is a common phenomenon with no symptoms to symptoms mimicking an acute abdomen presenting with lower abdominal pain and pelvic pain.
Ovarian torsion – is a significant cause of acute lower abdominal pain in women. It is usually associated with reduced venous return from the ovary as a result of stromal edema, internal hemorrhage, hyper-stimulation or a mass. Nausea and Vomiting are associated with lower abdominal pain.
Endometriosis – It is a condition in which the layer of tissue which normally covers the inside layers of uterus, grows outside uterus. It may grow in pelvic organs such as ovaries or fallopian tubes. The main symptom is lower abdominal and pelvic pain associated with menstrual period. Menstrual irregularities are also seen.
Gastroenteritis – is an intestinal infection marked by abdominal pain and cramps, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and fever.
Peritonitis – is the inflammation of the peritoneum, the thin layer of tissue that covers the inside of the abdomen (tummy). This layer covers the abdominal cavity and abdominal organs. Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and diarrhea.
Bacterial vaginosis – is a type of vaginal inflammation caused by the overgrowth of bacteria naturally found in the vagina. Symptoms include abnormal vaginal discharges, itching, odor and abdominal discomfort or pain.
Recurrence of PID
There is a good chance for PID to recur in presence of below mentioned conditions –
- When there is previous history of infection
- Recent sexual contact
- Recent onset of menses
- When the Intra-uterine-device (IUD) is in place
- If the partner has a sexually transmitted disease or infection
Treatment of PID
In PID, if treatment is not done or delayed, the infection spreads and causes lot of complications. Treatment is often started even before infection is confirmed.
Antibiotics – are the main choice of treatment since infection is involved. It depends of the infectious agent. The patient is advised to seek further medical attention if the improvement is not seen within 2-3 days of starting antibiotics.
Hospitalization – may be needed in severe cases and if the complications have developed.
Treating sexual partners – Treatment of sexual partners for possible sexually transmitted infections will come in handy in treatment and prevention of PID
Par-enteral and oral therapies – are effective in PID of mild to moderate severity
Prognosis
Early identification is important – In many cases, the effects of the infection may be permanent in spite of PID infection being cured. Therefore early identification of the condition forms the key for good prognosis.
arly identification is important – In many cases, the effects of the infection may be permanent in spite of PID infection being cured. Therefore early identification of the condition forms the key for good prognosis.
Total cure – The treatment of PID should be focused towards comprehensive cure. This helps in preventing the damage to the reproductive system. If scar tissue forms following PID, it leads to tubal blockage, risk of not getting pregnant and chronic pelvic pain or abdominal pain.
Recurrence – Another infection leading to PID may occur after post pelvic operation, immediately after childbirth (postpartum), miscarriage or abortion.
Epidemiology
In 2008 – About 106 million cases of Chlamydia and 106 million cases of gonorrhea occurred. The number of these cases resulting in PID is not clear.
PID approximately affects about 1.5 percent of young women yearly
PID affects about 1 million people yearly in USA
Rates are highest with teenagers and first time mothers
PID causes infertility in over 100,000 women in the US every year
Dalkon shield (type of intrauterine device) led to increased rates of PID in 1970s. IUDs currently used are not said to be associated with this problem after the first month.
Just Before Finishing
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease is a common ailment among women folks. This condition and most complications related to it happen on the backdrop of infection and most times due to unsafe sexual practices. Keeping informed of this condition and its causes helps in prevention of the disease, which in all terms is better than cure. This article aims at educating people about the basics of this disease.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)









