Importance Of Soul In Perception Of Knowledge: Atma Jnana
By Vd.A.Rangaprasad Bhat
Table of Contents
Introduction
Knowledge of the soul helps in providing relief from somatic and psychosomatic symptoms of chronic diseases, by means of
1. Atma Vivechana – analysis of Gunas of soul of the patient followed by
2. Counselling
3. with appropriate advises of satva Avajaya (self command through autosuggestion) modalities by the vaidya.
Sanskrit verse

Atma Jnana meaning
The Atma is the principle factor responsible for the origin of different structures, such as –
Manas – mind,
Chetana – consciousness,
IndriyAni – sense organs
prANApAnou – Prana, Apana Vayus,
DhAraNam – supports the body and its organs .
Arunadatta says –
Akriti – Appearance or shape of the body
Svara – voice, tone of the speech
Varna – Character of the person
and the knowledge of various implications of the
kAma (desire),
krodha (anger),
lobha (contextually it may be desire / strong desire / impatience),
bhaya (contextually it may be fear / phobia / apprehension),
harSHa (happy / joy / thrilling),
dharmasheelata (morally or ethically – excellent natured),
Smrti (memory / mindfulness / awareness),
buddhi (intelligence / knowledge / intuition / reasoning),
IcchA (willingness / desire),
dveSHa (hatred) / enmity / repugnance),
Prayatna (effort / attempt / endeavour) ,
AhankAra (egotism / self pride / self-consciouness / arrogance),
Sukha (pleasant / joy / happiness / delightfulness),
Duhkha (unpleasant / grief / misery / sorrow / painful / sad / uneasiness) and
Ayu (Life as in life span)
are collectively referred as AtmajnAna.
Arunadatta in his Sarvanga Sundari commentary, explains the link between atma and mind by stating – Atma is the factor responsible for the cause and effect principle in creating the life principle in both intelligent and non intelligent species (Avadata and anavadAta) like animals, reptiles etc.
Mind is Atmaja. Mind originates from Soul.
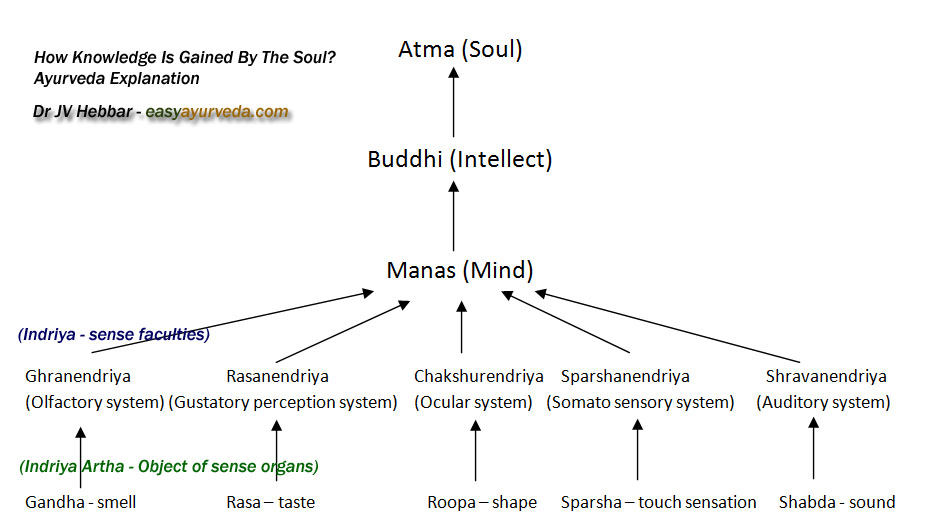
Atma Buddhi Manas Indriya Artha axis
There are five sense organs – tongue, eyes, ear, skin and nose. They perceive the object knowledge and pass it on to mind. Mind connects sense organs with intellect.
Intellect processes the incoming knowledge and the processed knowledge is stored in Soul.

Superiority of Atma
The Role of Atma and its superiority in cognition through the satva – indriya – artha axis:-
Satva (mind) is inflicted with Rajas and tamas in the human body. Human body is formed of five basic elements – earth, water, air, ether and fire.
Atma is
Avidya – unperceivable,
AkshayAdi – eternal and
Avaleena – stays inside body
When soul is not in contact with Satva (mind) and sense organs, knowledge will not be gained. Soul will be in Mukta (immune / let free) stage.
Example, when the sensory organ eye do not see an object, say a red colored pen lying on the table, the mind do not register the object since the object was left free from noticing its presence. Eventually the object though lies in its actual form and presence over the table do not get registered in the mind and gets immune or mukti of the particular knowledge of the object, the pen with specific regards to its red color, the size, the nature (ball point / ink / micro tipped pen).
Thus when explained by another person of having seen the pen over the table could not be recollected. Since there was no registry of event or the object recollection of the same gets impossible.
When Soul is linked with object, sensory organ and mind, the knowledge is gained. This is how, we remember childhood memories.
Even though the event of cognition and recollection happens independently, the process happens only due to the initiative of the observer the Atma or soul.
Be it the cognitive bonding or cognitive release, (Bandha or moksha), the result is imminent. The doer by its own cause enacts the bonding and releasing factors to initiate the cognitive bonding and cognitive release to take place respectively between the satva-indriya-artha axis of cognition.
The activity of cognition can never happen in human body without without the Atman’s involvement.
Location of Soul
Ten places where Soul resides – Jeevita Dhama:
Shira – head
Rasana bandhana – Area where the tongue is fixed in oral cavity –Frenulum
Kantha – throat
Asra – blood
Hrudaya – heart
Nabhi – umbilicus
Basti – urinary bladder
Shukra – sperm
Ojasi – Vital fluid maintaining immunity
Guda – Anal region – AH. Sha. Anga Vibhaga Shareera 13.
Sarvanga Sundari teeka clarifies
एतेषु स्थानेषु विशेषेण जीवितं-शरीरेन्द्रियसत्वात्मसंयोगलक्षणं, अवतिष्ठते|
These locations the soul, responsible for sharIra-indriya-satva-Atma samyoga, resides.
Some term these points as Marma points.
सोममारुततेजांसि रजःसत्त्वतमांसि च | मर्मसु प्रायशः पुंसां भूतात्मा चावतिष्ठते ||३५||
मर्मस्वभिहतास्तस्मान्न जीवन्ति शरीरिणः |३६| Su.sha.६/३५-३६ (प्रत्येकमर्मनिर्देशशारीरम्)
The Kapha, Vata and Pitta Doshas, along with Rajas, Satva and Tamas along with Bhutatma – human soul stays inside the Marmas (Vital and vulnerable spots).
So, when a vital spot gets severely inflicted with a piercing injury the soul exits the human body.
निबन्धसङ्ग्र:- इदानीं मर्मणां शरीरमनोदोषनिवासभूतानां शरीरमनोदोषैरेव मर्मविद्धकुपितैर्मनः शरीरं च नश्यति, तयोराधारभूतयोर्नाशादाधेयभूतो भूतात्माऽपि नश्यतीति दर्शयितुमाह- सोमेत्यादि||३५||-
Dalhana states –
The Tridosha, body and mind + soul located within the precinct of marmas become the sole reason for causing body. When the AdhArabhuta (substratum factor) namely the marma gets disturbed and nonfunctional, the AdheyabhUta (attributed factor) namely the bhUtAtma (human soul) too gets distrubed and becomes non functional.”
By Vd.A.Rangaprasad Bhat
“Padmanilayam”, (Ayurveda & Non Conventional Marma Chikitsa Clinic) 49/46,
Kanagaraya Malaiyappan St,
Raja Annamalaipuram,
Mandavelipakkam, Chennai- 600028.
Email: [email protected]









