Student’s Elbow: Ayurvedic Concept, Treatment, Medicines
Article by Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay)
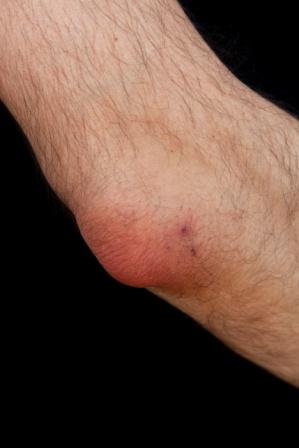
Student’s Elbow / Olecranon bursitis is an inflammatory swelling, it can be treated on the lines of Shotha Chikitsa (treatment of swelling) as explained in Ayurveda. The bursa is either filled with inflammatory or infected fluid, many times sterile fluid. When there is active inflammation and pain predominates with signs of inflammation like redness, pain, burning etc the treatment shall be pitta alleviating and when the fluid fills the bursa, the treatment should be kapha alleviating.
In short, the Student’s Elbow should be managed on the below said guidelines:
- Management of vitiated Pitta
- Management of vitiated Kapha
- Shotha Chikitsa with special reference to Pitta predominant Shotha and Kapha predominant Shotha in non-oedematous inflammatory swelling and oedematous inflammatory swelling respectively
- Krimighna (anti-bacterial, antibiotic) chikitsa in presence of infection
- Vidradhi chikitsa (treatment of abscess or pus pockets) when the swelling is filled with pus
Table of Contents
Pittahara Chikitsa
Treating Student’s Elbow on the lines of ‘treating pitta vitiation’
Inflammation basically suggests involvement of Pitta. In the initial conditions of Bursitis it might not be actively associated with ‘fluid filled bursa’.
Therefore in the earlier stages the swelling and oedema are not obvious, but the pain and burning, redness with mild to moderate swelling and limited movements may be present.
In such conditions we can adapt pitta alleviating measures or pitta-vata alleviating management because all sorts of inflammation are associated invariably with pitta vitiation.
The strategy of combating Pitta helps in preventing the progression of inflammatory process and might check the process of fluid accumulation also. At the same time, the symptoms of pitta vitiation i.e. inflammatory signs and symptoms like pain, burning sensation, rise in warmth, swelling and redness will reduce.
To control Pitta or high pitta activity in the body, the pitta vitiating causes should be first avoided. Avoid these Pitta Aggravating factors
For this, management of high Pitta with Virechana (purgation) treatment and medicines with sweet, astringent and bitter tastes are administered.
Kaphahara Chikitsa
Treating Student’s Elbow on the lines of ‘treating kapha vitiation’
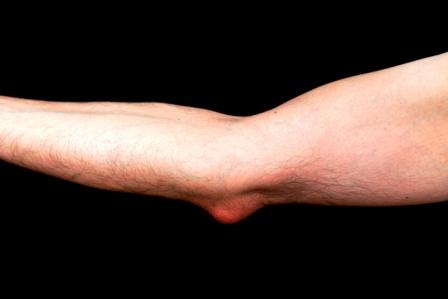
In the second stage of inflammation, the fluid starts accumulating in the bursa. This causes swelling over the olecranon region of the elbow. In this stage there is an involvement of kapha, because the water or fluid component belongs to kapha.
If the inflammation is high and the fluid accumulation is less, it might be inflammatory in nature. In such conditions it is high pitta and moderate kapha involvement in bursitis. On the contrary, if the fluid is more sterile and the inflammation (or inflammatory symptoms) has considerably subsided, if the fluid accumulation predominate the signs and symptoms of inflammation, then we should consider high kapha morbidity with mild to moderate pitta involvement.
Thus, in olecranon bursitis (or any type of inflammatory swelling), both pitta and kapha are involved. But the oedema being inflammatory or non inflammatory in nature depends on the severity of pitta and kapha respectively.
When the fluid accumulation is more we should approach in terms of combating the vitiated kapha, this in turn helps in reducing the fluid collection or reducing the oedematous swelling.
Management of such a condition caused with evident Kapha Dosha aggravation is by therapies such as
Vamana – Vomiting Panchakarma treatment,
Deergha kala sthitam madhyam – old fermented medicinal alcoholic drinks
Prajagarana – awakening late nights
Aneka roopa vyayama – various types of physical exercises
Ruksha vimardana – dry massages
Yusha – soups
Kshoudra – honey
Medaghnam aushadham – fat depleting medicines (medicines for obesity and weight gain)
Upavasa – fasting, starving etc
Shotha Chikitsa
Treating on the lines of Shotha Chikitsa (swelling, inflammatory oedema)
Because there is clear swelling and inflammation involved, Popeye elbow can be treated in the lines of Shotha treatment. Read related: Shotha: Causes, Types, Treatment, Medicines
Krimi Chikitsa
Treating on the lines of Krimi Chikitsa (treatment for worms, healing infections)
Simple formulations to destroy Krimi –
Vidanga churna – Embelia ribes powder with honey
Vidanga rasa – decoction of Embelia ribes
Nimba twak churna (powder of bark of Neem plant) and Hingu (powder of asafoetida) mixed with honey
Nimba patra rasa – juice of tender leaves of neem with honey
Palasha beeja churna – powder of seeds of Butea monosperma with honey
Decoction of Dadima twak (bark of pomegranate tree) mixed with Tila taila (sesame oil)
Khadiradi kwatha – Decoction of Khadira (Acacia catechu), kutaja (Holarrhena antidysenterica), nimbi twak (neem bark), Vacha (Acorus calamus), shunti (ginger), pippali (long pepper), maricha (black pepper), amalaki (Indian gooseberry), Haritaki (Terminalia chebula), Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica) and Trivrit (Operculina turpethum) mixed with urine of cow (gomutra)
Nimbadi churna – Powder of Nimba twak (bark of neem), vatsaka twak (bark of Holarrhena antidysenterica), Vidanga (Embelia ribes), Saindhava Lavana (rock salt) and Hingu (purified asafoetida) taken with honey
Other formulations:
Krimi mudgara rasa
Krimi kutara rasa
Krimighna vati
Krimi ghatini vati
Vidangarishta
Vidanga churna
Vidradhi Chikitsa
Treatment on the lines of Vidradhi (abscess)
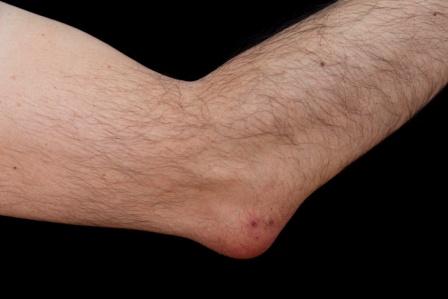
General principles of treatment:
Raktamokshana – All types of vidradhi should be dealt with by effective administration of Raktamokshana or bloodletting. Jalauka or leech application is the best one.
Mrudu virechana – mild purgation
Swedana – fomentation or sweating treatment (sudation) except in pittaja vidradhi
External applications:
Shobhanjanadi lepa – the roots of Shobhanjana (drumstick) should be ground and its paste should be applied, the juice of its root should be mixed with honey and given for internal consumption
Yavadi lepa – paste of fried or boiled barley, wheat and green gram.
Shigru upanaha – the paste of roots of drumstick should be used for giving fomentation and as poultice (swedana and upanaha) in Vataja Vidradhi
Sarivadi Lepa – paste of Sariva (Hemidesmus indicus), Laja (parched rice or popped rice), Yashtimadhu (Indian Liquorice), Sharkara (sugar) should be applied (Pittaja, Raktaja and Abhighataja Vidradhi)
Internal medications:
Punarnavadi kwatha – relieves Vata type of Vidradhi
Punarnavadi kwatha – decoction of equal quantities of Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa) and Varuna mula (root of Crataeva nurvala)
Dashamuladi kwatha
Triphala Kwatha – decoction of Triphala (Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellirica and Emblica officinalis) mixed with paste of Trivrit (Operculina turpethum) should be given to drink (pittaja, Raktaja and Abhighataja vidradhi)
Varunadi Kwatha – decoction of Varuna (Crataeva nurvala) mixed with purified Kasisa (ferrous sulphate), rock salt and purified asafoetida.
All the above mentioned medicines or formulations are also helpful in reducing inflammation and also the fluid collection in the bursa, even in the absence of abscess. Thus these are broad spectrum medicines.
Read related: Vidradhi: Causes, Pathogenesis, Types, Treatment, Medicines
Formulations
Disease modifying formulations from treatises
Anti-inflammatory medicines explained in the contexts of Vatarakta (gout) and Amavata (Rheumatoid arthritis) –
Vasadi Kwatha – Decoction made from Vasa (Adhatoda vasica), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia), Aragwadha (Cassia fistula) mixed with Eranda Taila (castor oil)
Guduchyadi Kwatha – Decoction of Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia) mixed with Guggulu (Commiphora mukul), specially used in Vata predominant Vatarakta
Dashamula Kashayam – decoction of 10 roots mixed with eranda taila (castor oil)
Shunti-guduchi kwatha – decoction of shunti (ginger) and guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Shuntyadi Kwatha – decoction of shunti (ginger) and gokshura (Tribulus terrestris)
Pippalyadi Kwatha – decoction of Pippali (long pepper), pippalimula (root of long pepper), chavya (Piper retrofractum), chitraka (Plumbago zeylanica) and Shunti (ginger)
Kokilakshyadi Kwatha – Decoction of Kokilaksha (Asteracantha longifolia) and Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Laghu Manjishtadi Kwatha – Decoction of Manjishta (Rubia cordifolia), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia), Katuki (Picrorrhiza kurroa), Vacha (Acorus calamus), Nimba twak (neem bark), Amalaki (Emblica officinalis), Haritaki (Terminalia chebula) and Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica)
Navakarshika Kwatha – Decoction prepared from Daruharidra (Berberis aristata), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia), Katuki (Picrorrhiza kurroa), Vacha (Acorus calamus), Manjishta (Rubia cordifolia), Nimba twak (neem bark), Amalaki (Emblica officinalis), Haritaki (Terminalia chebula) and Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica)
Shatyadi kwatha – decoction of shati (Hedychium spicatium), shunti (ginger), haritaki (Terminalia chebula), vacha (Acorus calamus), devadaru (Cedrus deodara), Ativisha (Aconitum heterophyllum), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Panchakola churna – powder of Pippali (long pepper), pippalimula (root of long pepper), chavya (Piper retrofractum), chitraka (Plumbago zeylanica) and Shunti (ginger) taken with hot water
Nagara churna – powder of nagara or ginger taken with kanji (fermented herbal drink)
Panchasama churna – powder of shunti (ginger), haritaki (Terminalia chebula), Pippali (long pepper), trivrit (Operculina turpethum) and Saindhava lavana (rock salt)
Shunti-guda – Powder of shunti (ginger) taken with powder of guda (jaggery)
Bhallatakadi churna – powder of bhallataka (Semecarpus anacardium), tila (sesame) and haritaki (Terminalia chebula) with guda (jaggery)
Phalatrikadi churna – powder of amalaki (Emblica officinalis), Haritaki (Terminalia chebula), bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica) and shunti (ginger)
Hingwadi churna – powder of hingu (asafoetida), chavya (Piper retrofractum), vida lavana (bida salt), shunti (ginger), pippali (long pepper), jeeraka (cumin) and pushkara mula (Inula racemosa)
Eranda Beeja – the payasa (sweetened milk recipe) prepared from purified eranda beeja (seeds of castor plant)
External medicines –
Shatahva lepa – paste of Shatahva (Dill seeds) made in milk
Tila lepa – paste of fried sesame ground in milk
Atasyadi lepa – paste of Atasi (flaxseed) and Eranda beeja (seeds of castor) ground in milk
Prapaundarikadi lepa
Grihadhumadi lepa (Read more about these here)
Panchakarma Chikitsa
Role of Panchakarma in the management of Student’s Elbow
Panchakarma doesn’t have a big role in Student’s elbow. Most of the cases respond to oral medication and external applications. Panchakarma might be needed only when the inflammation is more or when the fluid collection in the bursa is repeatedly getting collected in spite of many schedules of medications.
The below mentioned Panchakarma methods are useful:
- Snehapana – internal administration of medicated ghee and oils, especially the pitta alleviating ghritas like tiktakam ghrita, guggulutiktakam ghritam, patoladi ghritam etc when there is active inflammation and the fluid collection is not evident. It is good to start them as soon as the inflammatory signs are seen. The same ghritas shall be administered in higher quantity if the cleansing treatments i.e. Vamana or Virechana are planned in recurrent cases.
- Swedana – sweating treatment or steaming, especially in kapha predominant conditions, wherein the fluid has occupied bursa
- Vamana – therapeutic emesis, in kapha predominant conditions
- Virechana – therapeutic purgation, in pitta predominant conditions
- Nitya Virechana – daily purgation at home with pitta and kapha alleviating medicines, as a part of oral medication
- Ksheera vasti – enemas with medicated milk, in very stubborn conditions of inflammation
The panchakarma treatments keep flushing out the toxins and morbid doshas and malas (excreta) on regular basis. This makes sure that the disease doesn’t progress further and the pathogenesis stops at the initial stages itself.
Panchakarma treatments shall be repeated at short intervals in stubborn cases. They also heal infections apart from getting rid of the inflammation and reducing the swelling. Or else, nitya virechana shall be administered after a course of vamana or virechana has been completed.
External Treatments in Student’s Elbow
External treatments in Olecranon bursitis should be oriented towards the relief of inflammation and reduction of fluid collection. They will provide good results if combined with Panchakarma treatments, chiefly Virechana. Below mentioned are the best treatments which can be conducted over the swollen joints:
Abhyanga – massage with medicated herbal oils
Swedana – steaming, basically done in the form of pinda sweda or bolus fomentation, chiefly:
- Valuka sweda (sand bolus fomentation) in kapha predominance
- Churna pinda sweda (herbal powder fomentation) in presence of both pitta and or kapha predominance
- Patra pinda sweda (leaf bolus fomentation) chiefly in pitta and vata predominance when pain and inflammation dominate the picture
- Bashpa sweda (vapour steaming with herbal decoctions and or medicated milk) after abhyanga will also help
- Nadi sweda – tubular fomentation (same as bashpa sweda)
Dhara – stream pouring of medicated liquids, mainly decoctions in case of kapha predominance (fluid filled swelling) and ghrita (medicate ghee) or ksheera (medicated milk) dhara in pitta predominant conditions wherein the symptoms of inflammation are more in comparison to fluid collection. Though it is also a type of swedana, I have counted it separately because at times we need to do the dhara with cold medicines, when the pitta vitiation is very severe whereas in Swedana every procedure includes heat.
Lepa – application of medicinal pastes
Upanaha – poultices
Avagahana – dipping of joints in the medicinal liquids
Classical formulations –
Kashayam (herbal decoctions) –
- Punarnavadi kashayam
- Rasnaerandadi Kashayam
- Dashamulam kashayam
- Patolamuladi kashayam
- Patolakaturohinyadi kashayam
- Pathyakshadhatryadi kashayam
- Brihatyadi kashayam
- Lashunaerandadi kashayam
- Varanadi kashayam
- Vasaguluchyadi kashayam
- Guluchyadi Kashayam
- Balaguluchyadi Kashayam
- Kokilaksham Kashayam
- Guggulutiktakam Kashayam
- Mahamanjishtadi Kashayam
- Amrutottaram Kashayam
- Gandharvahastadi kwatha
- Dashamulapanchakola kashayam
- Drakshadi kashayam
- Ardhavilwam kashayam
- Punarnavashtakam kashayam
Asava-Arishta (fermented herbal drinks) –
- Dashamularishtam
- Punarnavasavam
- Punarnavadyarishtam
- Arjunarishtam
- Draksharishtam
- Ayaskriti
- Dantyarishtam
Churnam (herbal powders) –
- Ajamodadi churna
- Vaishwanara Churna
- Shaddharana Churna
- Chopachinyadi churna
- Panchakola churnam
- Pathyadi churnam
- Amritadi churna
- Triphala churnam
- Avipatti churnam
Churnam for external application and poultice –
- Rasnadi churnam
- Kottamchukkadi churnam
- Jatamayadi churnam
- Grihadhumadi churnam
- Kolakulatta churnam
- Dashanga lepa churnam
Vati (tablets), Bhasma (ash), Ras (herbomineral preparations) and Guggulu preparations –
- Amavatari ras
- Amritadi guggulu
- Simhanada Guggulu
- Saptavimshati guggulu
- Kaishora Guggulu
- Triphala Guggulu
- Yogaraja guggulu
- Mahayogaraja guggulu
- Chandraprabha vati
- Punarnavadi manduram
- Navayasa loham
- Mandura vatakam
- Mandura bhasma
- Trivanga bhasma
- Shilajit
- Shotari mandura etc
Ghrita (medicated ghee for intake or for snehapana) –
- Guggulutiktakam ghritam
- Tiktakam ghritam
- Rasnadi ghritam
- Mahatiktakam ghritam
- Patoladi ghritam
- Aragwadhadi ghritam
- Ardraka ghritam
Tailam (oils for external application) –
- Mahavishagarbha tailam
- Kottamchukkadi tailam
- Ksheerabala tailam
- Pinda tailam
- Chandanabala lakshadi tailam
Rasayana / Leham (immune-modulators, confections) –
- Kalyana gulam
- Trivrit leham
- Danti haritaki
- Narayana gulam
- Manibhadram leham
- Dashamula haritaki
- Amrita bhallataka lehya
Proprietary medicines –
- Cap Arnopen (Phyto Pharma)
- Cap Arthozen (ZEN)
- Cap Arthozen Forte (ZEN)
- Cap Amavatari (Pavaman)
- Tab Myostal (Solumiks)
- Neurocare liquid (Pentacare)
- Cap Orthofit (Fizikem)
- Tab R-Compound (Alarsin)
- Tab R-Pairyn (Ban)
- Rheumat 90 liquid (Nagarjuna)
- Tab Rhumayog with Gold (Zandu)
- Tab Rumalaya / Rumalaya Forte (Himalaya)
- Cap Arjit / Arjit Forte / Arjit liniment (Capro)
- Tab Rumastal Forte (Gufic)
- Tab Shallaki / Shallaki Plus (Gufic)
- Cap Rheumarthro with Gold (Baidyanath)
- Tab Rumastal (Gufic)
- Amrutayolepam churna (Vaidyaratnam)
- Tripalayolepam churna (Vaidyaratnam)
- Punarnavayolepam churna (Vaidyaratnam)
External application –
- Arnopen liniment (Phyto Pharma)
- Arthrum oil (Vital care)
- Dazzle ointment / oil (Vasu)
- Mobyl ointment (Ayulabs)
- Orthofit tab / oil / gel (Fizikem)
- Penwel oil (Ayulabs)
- Pyroflex liniment / gel (Solumiks)
- Rheumat liniment (Nagarjuna)
- Rhuma oil (Baidyanath)
- Rhumasyl ointment (Zandu)
- Rumalaya cream and gel (Himalaya)
Pathya
Pathya (beneficial foods, lifestyle) –
- Yava – barley
- Purana yava – old barley
- Shashtika shali – paddy or rice grown in 60 days
- Purana shali – old rice
- Aruna shali – red rice
- Mudga – green gram
- Godhuma – wheat
- Kulattha – horse gram
- Mamsa – flesh of lava (common quail), tittira (black partridge), varteeka (bush quail), tamrachuda (cock), vishkira (wild birds), pratuda (pecker birds like pigeon etc), shuka (parrot), kapota (pigeon), chataka (sparrow), shasha (rabbit), daatyooha (big sized parrots) etc
- Jangala mamsa – meat of animals and birds living in desert regions
- Kachchapa – meat of tortoise
- Purana ghrita – old ghee
- Takra – buttermilk
- Sura, Madhu, asava – fermented herbal drinks
- Madhu – honey
- Karavella – bitter gourd
- Shigru – drumstick
- Lashuna – garlic
- Karkotaka – Momordica dioica
- Balamulaka – tender radish
- Punarnava – Boerhavia diffusa
- Patola – pointed gourd
- Grunjanaka – carrot
- Vetragra – Garcinia indica
- Dhatri phala – fruit of Emblica officinalis , Gooseberry
- Mulaka – radish
More pathya which are mentioned in Vatarakta, are also useful in Shotha (inflammatory arthritis), they are:
- Chanaka – Bengal gram
- Tuvara – Tor dal
- Makushtaka – Vigna aconitifolia
- Avi ksheera – sheep milk
- Aja ksheera – goat milk
- Mahisha ksheera – Buffalo milk
- Go ksheera – cow milk
- Upodika – Basella rubra
- Kakamachi – Solanum nigrum
- Sunishannaka – Blepharis edulis
- Vaastuka – Chenopodium album
- Kaaravellam – bitter gourd
- Tanduleeyam – Amaranthus polyganus
- Srungavera – ginger
- Soorana – Amorphophallus campanulatus
- Sharkara – sugar or candy
- Mrudveeka – raisins
- Kushmanda – ash gourd
- Navaneetam – butter
- Agaru – Aquilaria agallocha
- Devadaru – Cedrus deodara
- Sarala kashta – Stem of Pinus roxburghii
- Mardana – massaging or tapping with herbal oils and ghee
- Tikta – bitter foods and vegetables
Apathya
Apathya (unwholesome food, lifestyle) –
- Gramya mamsa – meat of animals living in neighbourhood, like cow etc
- Shushka mamsa – dry flesh
- Anupa mamsa – meat of animals living in marshy areas
- Andaja – meat of animals and birds which are born from eggs (fish, birds etc)
- Lavana – excessive salt
- Amla rasa – excessive sour
- Shushka shaka – dry vegetables
- Nava anna – fresh paddy or rice
- Viruddha ahara – mutually incompatible foods
- Dadhi – curds
- Gauda – jaggery and its derivatives
- Pishta – flours
- Madhya – alcohol
- Madira – excessive consumption of alcohol
- Ikshu – sugarcane
- Guru ahara – excessive consumption of heavy (to digest) foods
- Bahu ashanam – excessive intake of foods
- Katu – excessive consumption of pungent foods
- Ushna – excessive consumption of hot foods
- Vidahi anna – corrosive foods
- Asatmya anna – incompatible or unwholesome foods
- Kanji – fermented drinks
- Tila – sesame
- Maithuna – excessive indulgence in sex
Other avoidable factors:
- Agni santapa – exposure to the heat of sun
- Vyayama – excessive exercise
- Atapa – heat of sun
- Masha – black gram
- Nishpava – flat bean
- Kalaaya – peanut
- Kshara – alkalis
Single herbs
Single herbs used in the treatment of Student’s elbow
- Punarnava – Boerhavia diffusa
- Guduchi – Tinospora cordifolia
- Devadaru – Cedrus deodara
- Amalaki (Emblica officinalis)
- Haritaki (Terminalia chebula)
- Bibhitaki (Terminalia bellirica)
- Dashamula – Roots of 10 drugs
- Rasna – Alpinia galanga
- Guggulu – Commiphora mukul
- Shallaki – Boswellia settata
- Eranda – Ricinus communis
- Haridra – Turmeric
- Daruharidra – Berberis aristata
- Vidanga – Embelia ribes
- Nimba – Neem
- Pippali (long pepper)
- Pippalimula (root of long pepper)
- Chavya (Piper retrofractum)
- Chitraka (Plumbago zeylanica)
- Shunti (ginger)
- Aragwadha – Cassia fistula
- Kushta – Saussurea lappa
- Agnimantha – Clerodendrum phlomidis
- Shatavari – Asparagus racemosus
- Kokilaksha – Asteracantha longifolia
- Vasa – Adhatoda vasica
- Manjishta – Rubia cordifolia
- Katuki (Picrorrhiza kurroa)
- Chandana (sandal wood)
- Yashtimadhu (Glycyrrhiza glabra)
- Patola – pointed gourd
- Prapaundarika – lotus variety
- Ushira – Vetiveria zizanioidis
- Padmakashta – stalk of lotus
- Atasi – flaxseed
- Kumari – Aloe vera
Clinical experience
My experience in handling Student’s Elbow through Ayurveda –
I would confess and admit that I did not get to see many cases of Student’s Elbow in my long standing clinical practice. We won’t get to see too many cases of olecranon bursitis because people would get some analgesic or anti-inflammatory drug from the counter and manage these things even without the consent of doctor, thinking that it is easy to handle and not a serious issue to handle.
But a few cases I have encountered, I have managed to handle them very well with external applications and anti-inflammatory (anti-pitta and anti-kapha) medicines and formulations. In a couple of cases I had to prefer virechana. Nitya Virechana is my favourite prescription. I have seen good results when nitya virechana is advised along with anti-inflammatory medicines. Many medicines used for nitya-virechana like nimbamritadi eranda tailam are by themselves good anti-inflammatory medicines.
Limitations
Limitations in handling olecranon bursitis through Ayurvedic methods of treatment –
With effective medicines and line of treatment and the variety of treatments Ayurveda provides in handling the bursitis, I don’t feel we have limitations in handling these cases.
Just before finishing –
Student’s elbow or olecranon bursitis can be effectively handled through effective Ayurvedic remedies. But the key is prevention. Since the disease mainly occurs due to repeated minor or single major injury to the elbow or due to the constant pressure over the elbow as happens in students leaning their elbow and forearm against hard writing tables and also in other professions as mentioned, students and those in profession which causes these traumas should be well educated so that they can avoid these traumas and avoid themselves being victims of this condition.
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)









