Carrot (Gajar): Benefits, Remedies, Research, Side Effects

Carrot is an excellent vegetable with good amounts of anti oxidants. In Ayurveda pharmacopoeia for the treatment of piles, diarrhea, localized swelling and diseases related to uterus.
Latin Name- Daucus carota Linn.
Family- Umbelliferae

Table of Contents
Vernacular names
Names in different languages:
Hindi name- Gajar
English name- Carrot
Marathi name- Gajar
Kannada name- Gajjari, Carrot
Telugu name- Gajaru gadda
In other Indian languages the word ‘carrot’ itself is used, mostly for convenience.
Sanskrit synonyms
Synonyms synonyms of Carrot –
Grunjana, Gajaram, Shikimoola
Naranga varnaka, Peetaka – The tuber is having orange color.
Yavaneshta – Liked by the westerners
Vartula – cylindrical shape
Granthimoola – nodular tubor
Swadumula – Root is sweet in taste
Narangakanda – Root tuber is orange in colour
Shikhimoola, Shikhakanda, Dindeeramodaka,
Carrot is an annual herb with tuberous root bearing white clustered flowers. It is cultivated all over India in the regions having cold and temperate climate. The plant is a native to temperate regions of Europe and southwest Asia, and naturalized to North America and Australia. When they were first cultivated, carrots were grown for their aromatic leaves and seeds rather than their roots. The carrot (Daucus carota sub sp. sativus) is a root vegetable, usually orange in color, though purple, black, red, white, and yellow varieties exist.
Classical categorization
Bhavaprakasha- Poorvakanda-Shakavarga
Kaiyyadeva Nighantu- Oushadhi varga
Raja Nighantu- Moolakadi varga
Scientific classification
Kingdom: Plantae
Order: Apiales
Family: Apiaceae
Genus: Daucus
Species: D. carota
Properties, part used, dosage
Carrot – medicinal properties:
Rasa- Madhura (Sweet), Tikta (Bitter)
Guna (Qualities) – Laghu (Light for digestion), Tikshna (Pungent)
Vipaka –Madhura (undergoes sweet taste after digestion)
Veerya (Potency) – Ushna (Hot)
Karma (Actions) – Kapha vatahara (reduces vitiated kapha and vata dosha), Deepana (induce appetite), Grahi
The seed of the carrot acts as an abortifacient.
Part used – Root, Seed
Dosage -Powder 1-3 g, Juice – 50 – 100 ml

Properties as per Bhojana Kutuhalam
According to Bhojana Kutuhalam eleventh chapter, Carrot is sweet and slightly pungent in taste.It imparts taste and alleviates kapha, treats bloating of abdomen, worm infestation, colicky pain, burning sensation vitiated pitta and thirst.
Chemical constituents, Uses
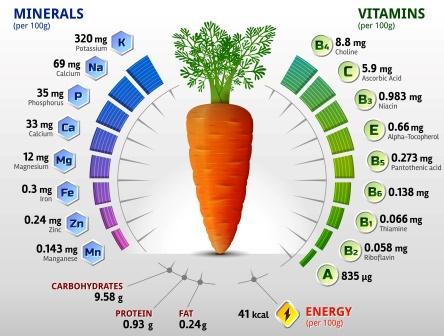
Carrot contains flavones including apigenein, chypsin and luteolin. The furanocoumarins, 8- methoxypsoralen and 5- methoxypsoralen are found in the carrot plant. The seed oil contains terpinen- 4- ol which is a renal irritant and can cause diuretic activity. In cooked carrot beta carotene content is higher than in raw carrot. The tuber of the plant contains alpha and beta carotenes.
Daucus carota medicinal uses:
- Carrot is used as vegetable all over the world, for its culinary benefits in the form of raw salads and in cooked form.
- The cooked carrot tuber is consumed to treat the condition of piles.
- Carrot is consumed raw to strengthen the cardiac muscles.
- The seed of the carrot is used as abortificant in the early stages of pregnancy.
- Fresh juice of carrot is consumed in a dose of 25-30 ml to treat cases of irritable bowel syndrome.
- The fresh juice of carrot is consumed daily to treat cases of vitamin A deficiency, to improve the appetite.
- Consumption of carrot regularly can regulate the outflow of sweat and control the bad odor due to sweat.
- Consuming carrot regularly can boost the immunity of the person as the vegetable contains anti- oxidants.
- Slightly heated and peeled carrots are mixed with sugar candy to bring down the blood pressure in hypertensive patients.
- The cold infusion prepared from the carrot acts like liver protector agent.
Sanskrit verse

Benefits, Indications
Carrot benefits as per Ayurveda:
Deepana – improves digestion strength
Sangrahi – absorbent, useful in diarrhea, IBS
Laghu – light to digest
Indicated in –
Raktapitta –Bleeding disorders such as nasal bleeding, heavy periods, etc
Arsha – haemorrhoids
Grahani – IBS, sprue, altering diarrhea and constipation
Arsha – haemorrhoids
Druk roga – eye disorders
Aruchi – anorexia
Jantu – worm infestation
Side effects
Side effects and Contraindication:
The seed of the carrot should be avoided during pregnancy as it can cause abortion.
Excess usage is to be avoided in diabetic people with uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
Interaction with medicines, supplements
Can this be used while taking Homeopathic medicine?
Yes. This product does not react with homeopathic medicine.
Can
this medicine be continued while taking supplements like multivitamin tablets,
Omega 3 fatty acids etc?
Yes. Generally, this product goes well with most
of the dietary supplements. However, if you are taking more than one product
per day, please consult your doctor for an opinion.
With western
medicines
Seek your
doctor’s advice if you are taking this product along with other western
(allopathic / modern) medicines. Some Ayurvedic herbs can interact with modern
medicine.
If both Ayurvedic and allopathic medicines are advised together, then it is
best to take Allopathic medicine first, wait for 30 minutes and then take the
Ayurvedic medicine.
Ayurvedic formulations
Formulations containing Garjara:
Nobab capsules: This is a proprietary ayurvedic medicine used to treat primary and secondary amenorrhea and dysmenorrhoea.
Abana tablet: This is a proprietary ayurvedic medicine used to treat variety of heart related disorders such as high cholesterol, cardiac pain etc. It normalizes lipid profile- Lowers low density lipoprotein cholesterol [LDL], very low density lipoprotein cholesterol [VLDL] and triglycerides levels. It increases the high density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL] levels.
Pause capsules: This is a proprietary ayurvedic medicine used to treat Secondary amenorrhea, oligomenorrhoea, irregular periods, and menstrual disorders.
Research
Research articles about Daucus carota:
Anti- oxidant activity: Antioxidants and antioxidant capacity of seven colored carrots were determined. Five anthocyanins, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and four carotenoids were quantified by HPLC. Total phenolic content was determined according to the Folin?Ciocalteu method. Antioxidant capacities of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic fractions were determined by using the 2,2?-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) and 2,2?-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) methods. The relative antioxidant capacity index was determined.
Nephro- protective action in rats: Nephro toxicity in rats was induced by intra peritoneal administration of gentamicin (100 mg/kg/day) for 8 days. Gentamicin intoxication induced elevated serum urea, BUN, uric acid, and creatinine levels which was found to be significantly (P < 0.01) decreased in a dose-dependent manner in groups received D. Carota which was also evidenced by the histological observations.
Hepato protective action in rats: Oral administration of carrot extract (25?mL/kg/day) for 30 days produced significant hepatoprotection against lindane (20?mg/kg/day) induced hepatotoxicity in rats. The increased levels of serum enzymes namely aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase, alkaline phosphatase and the levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL-cholesterol in lindane administered rats were observed to be decreased significantly in the lindane?+?carrot extract group. The carrot extract also restored the depressed antioxidants and HDL-cholesterol levels to near normal.
Health benefits of carrot seed extract: Anti-diabetic, cholesterol and cardiovascular disease lowering, anti-hypertensive, hepato -protective, reno- protective and wound healing benefits of carrot have also been reported. The cardio- and hepato -protective, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effects of carrot seed extracts are also noteworthy.
Carrots, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
Taste – sweet, bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing (more Kapha balancing than raw carrots as it is more light)
Carrots, canned, regular pack, solids and liquids
Taste
– sweet, bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka )
– sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing (more Kapha balancing than raw carrots as it is more light)
Carrots, canned, regular pack, drained solids
Taste – sweet, bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing (more Kapha balancing than raw carrots as it is more light)
Carrots, frozen, unprepared
(Includes foods for USDA’s Food Distribution Program)
Taste – sweet, bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing
Carrot, dehydrated
Rasa – sweet, bitter
Guna – light
Veerya – hot
Vipaka – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha decreasing (as it is dried, it is more Kaphahara)
Carrots, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt
Taste – sweet, bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing (more Kapha balancing than raw carrots as it is more light)
Carrots, canned, no salt added, solids and liquids
Taste – sweet, bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing (more Kapha balancing than raw carrots as it is more light)
Carrots, canned, no salt added, drained solids
Taste – sweet, bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing (more Kapha balancing than raw carrots as it is more light)
Carrots, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, with salt
Taste – sweet, bitter, slightly salty
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing (more Kapha balancing than raw carrots as it is more light)
Carrot juice, canned
Rasa – sweet
Guna – light, sharp, piercing
Veerya – not very hot (carrot is hot veerya but dilution with water makes it less hot)
Vipaka – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta neutral (due to decreased hotness)
Kapha balancing
Carrots, baby, raw
Taste – sweet, slightly bitter
Properties – light, sharp, piercing
Potency – hot
After digestion taste transformation ( Vipaka ) – sweet
Effect on Doshas
Vata balancing
Pitta nourishing
Kapha balancing
Morphology
Annual herb
Stem – Herbaceous, aerial, erect stem
Leaf – Compound, triangular to oblong, alternate, petiolate
Inflorescence – Compound umbel
Flowers – Complete, 5 petals
Fruit – Cremocarp
Useful part – Root, Seeds
Author:
Dr.B.K.Prashanth M.D (Ayu), Ph.D
E mail: [email protected]











8 comments
Mari
What about carrot oil infused? It should be useful for skin . Thanks
Gary
Any opinions of other varieties such as wild carrots, or other members of the Genus Daucus? I was recently looking through the Astanga Hrdyam, and am currently searching for healthier vegetables than what is commonly available. Much like mooli leaves are in some ways much better than the normally eaten cruciferous, there are too many vegetables no longer or not often eaten by even traditional peoples. The list of recommended vegetables from the Astanga Hrdyam are:
jivanti (Leptadenia reticulata), sunisannaka (Marsilia minuta), bala mulaka (Raphanus sativus, tender radish root), vartaka (??), tanduliyaka (Amaranthus spinosus, spiny amaranth), vastuka (Chenopodium album, lamb’s quarters), karavella (Momordica charantia, bitter gourd), karkota (Momordica dioica, spiny gourd), patola (Trichosanthes cucumerina) and katukaphala (??).
From available data in one study, compared to tanduliyaka (amaranthus spinosus), amaranthus polygonoides looks to be the healthier variety. If you are aware of the better vegetables, ones such as moringa and methi are already fairly well known, please share.
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
I will cover as much vegetables as possible in future. Regarding varieties of carrot, we know only the information that we have provided above, in the article.
Sunny
Since carrots are heating, is it okay for somebody with pitta imbalances to eat carrots with yogurt?
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Yogurt or cucumber or any such coolants are fine to use
Cook
Carrots are hot for digestion, but cool after digestion. They stimulate digestion and appetite, but lead to cooling of the body afterwards.
Pat
Can carrots and milk be combined (cooked carrots boiled into milk to make carrot milk?)
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Yes