Understanding the relationship between Dosha’s and Arthritis
Article by Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay)
Man learnt to walk, run, sit, jog and jump during the lessons of evolution. Little did he or she know that they have to face the untoward consequences of over-using or under-using these gifted mechanisms somewhere in the later part of evolution?
We are higher forms of creation with basic intelligence software governing our highly skilled day-to-day functions. Our limbs and spine are the most sophisticated machinery in the creation. The fine movements occurring in them make many activities possible.
These movements occur due to the uninterrupted articulation between the ends of 2 or more bones. But when something goes wrong in the structure or function of the joints of the body, all our activities come to a stay. Arthritis is one condition which afflicts the joints and soft tissues of the body making us crippled and dependent.
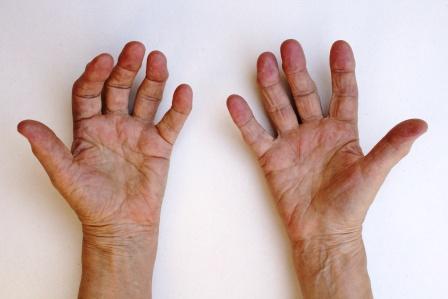
Arthritis is one of the painful diseases haunting the mankind and has been a gift of evolution. We all suffer from arthritis at some point of life, it is not diagnosed in some, some don’t go to a doctor thinking that it is their destiny and part and parcel of life, others have no time to look at it until things get worse and some don’t admit!!
Table of Contents
What is arthritis?
The word is derived from the Greek words Arthro-meaning joint, It is-meaning inflammation. Arthritis is a form of joint related disorder. It involves inflammation in one or more joints of the body.
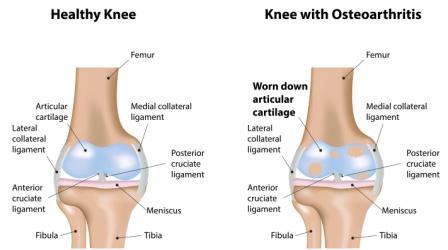
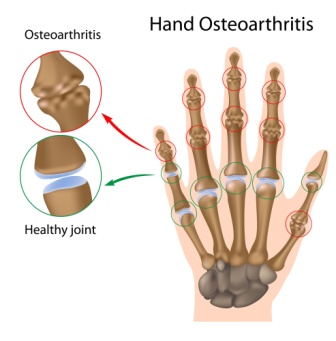
There are more than 100 forms of arthritis. The most common and popular arthritis we know are – Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis, Gout, Septic arthritis etc.
Causes
Common causes of joint pain and arthritis –
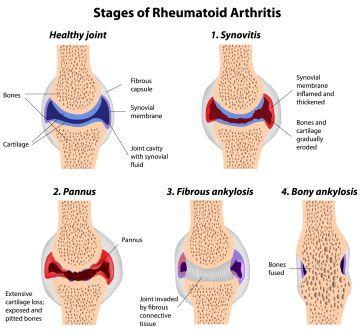
Inflammation of joints – like in Rheumatoid arthritis
Joint damage – due to accidents, traumas, occupation
Degeneration (wear and tear of joint on daily basis) – Ex. Osteoarthritis
Accumulation of crystals (uric acid or urate) in the joints – Ex. Gout
Muscle strains due to forceful movements
Fatigue
Low immunity and autoimmune process in the body wherein the body’s protective mechanism itself is harming the body by becoming destructive mechanism – Ex. Rheumatoid arthritis
Infection – Ex. Septic arthritis etc
Collagen vascular disorders – Ex. Lupus Erythematosus
Symptoms
Symptoms of Arthritis –
Joint pain (it may be due to inflammation, joint damage, wear and tear in the joint or joints on a daily basis, muscle strains caused due to forceful movements and fatigue).
Intensity and severity of pain varies among different types of arthritis:
Joint Swelling
Joint stiffness (catch)
Aching around the joints
Arthritis disorders like Lupus and Rheumatoid Arthritis can affect other organs in the body. This gives raise to many symptoms like –
Inability to hold or walk
Stiffness – worsening at morning or after use
Malaise and fatigue
Weight loss
Sleeplessness
Muscle pain and weakness
Joint tenderness
Difficulty in moving the joint and loss of flexibility of joints
All these symptoms would not only make us helpless, disable and crippled but also will impact on our socio-economic status. Arthritis limits day-to-day activities leading to sickness absenteeism and frequent hospital visits and hospitalizations.
Chronic arthritis becomes cause for physical inactivity leading to obesity, high levels of bad fat and susceptibility for heart diseases, multiple organ damage.
Arthritis will not only affect the body but also will affect the mind. People with arthritis are at increased risk of developing anxiety disorders and depression.
Arthritis or musculoskeletal disorders prevalence has increased by 45% from 1990 to 2010. Osteoarthritis is the fastest increasing major health condition. (Musculoskeletal disorders MSD’s are injuries or pain in the body’s joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons and structures that support limbs, neck and back)
Ayurvedic concept of Arthritis and the involvement of individual Doshas in the causation of Arthritis –
According to the principles of Ayurveda the involvement of morbid or contaminated Doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha) either individually or in combinations is mandatory in the manifestation of any disease pathology. Arthritis is no exception.
Like any disease, contaminated or vitiated Vata, Pitta or Kapha either singly or in combination will produce the pathogenesis of arthritis. They get lodged in the weaker dhatu’s (tissues) especially bones, muscles, and bony joints, soft tissues like tendons, ligaments, joint capsule etc and cause arthritis. The damage and consequent changes caused by the morbid doshas in the weak tissues will cause signs and symptoms of arthritis.
Joints are the parts of our body which are formed by the ends of 2 or more bones. The bony ends get connected to each other by cartilages. The joints are surrounded by soft tissues like muscles and tendons. Smooth articulation taking place between the bony ends at the joints enable many movements.
We do all the activities when these movements happen uninterruptedly within the joints. For this to happen, the joints should be healthy and free from the affliction of morbid doshas.
Even according to Ayurveda, arthritis can manifest in Primary and secondary forms:
Primary arthritis – This type of arthritis is caused due to vitiation of one or more of the 3 dosha’s in the body.
Secondary arthritis – This happens as a consequence to some other systemic disorder i.e. arthritis develops due to some other systemic disorder (as a complication, symptom or sequel).
In these types of arthritis also, the same dosha or dosha’s which would have caused the primary disease will be responsible for the symptoms of arthritis. If the main diseases are effectively treated, the arthritis will go away.
In this article I shall be discussing only the primary arthritis and their relation to the Dosha.
Role of Doshas
Role of Doshas in the movements of the joints –
All the 3 dosha’s take place in bringing about the smooth and uninterrupted movements at the joints. This happens when the dosha’s are balanced and not vitiated.
Kapha – Joints basically belong to the Kapha. Kapha helps in lubrication of the joints, maintains stability and integrity of the joints. Kapha is basically nutritive (by nature) to the joints. When Kapha morbidity occurs in the form of its decrease, this stability and integrity of the joints is lost, the immunity of the joints too will reduce.
The lubrication and wetness of the joint get reduced, dryness will dominate. Vata and Pitta will get vitiated in this favorable environment; especially Vata will increase in the prevailing dry environment.
Hyper-functioning of Vata in the joints will lead to structural damage, degeneration and pathological fractures along with free broken bodies, crepitus (sounds in the joints) and swelling.
If Pitta gets involved in the pathological process inflammation of joints will set in worsening the condition. When Kapha morbidity increases in the joints, fluids accumulate within the joint spaces causing effusion and swelling.
Excessive fluidity exerts constant pressure on the joints and soft tissues around. Excessive dampness also sets a suitable environment for infections to occur.
Vata – Vata helps in free movements, keeps up the flexibility of the joint, and allows free movements to take place within the components of the joints. Vata conducts this role on the backdrop of a suitable lubrication, integrity and strength provided to the joint by Kapha.
Kapha and Vata are antagonistic when not present in mutual agreement of balance. Too much Kapha activity in the joints will lessen the activities of Vata due to non-availability of free space due to accumulation of excessive fluids.
On the contrary, if Vata gains a pathological increase, it will dry off the fluidity of Kapha, cause excessive dryness and set in the degeneration process. The joints quickly get damaged on this backdrop. Pathological reduction of Kapha also provides a suitable environment for aggravation of Vata.
Pitta – Pitta helps in the metabolism taking place in the joints. It keeps up the warmth of the joint, keeps infections at bay, destroys pathogens, enhances and balances blood flow (and nutrition) to the joints (being located as an active component within the blood).
Pitta also provides lubrication to the joint along with Kapha. Pitta balances and buffers between Vata and Kapha. Owing to its hot property, it balances the dual cold elements i.e. Vata and Kapha in the joints.
The involvement of Doshas in the joint pathology, especially arthritis and musculo skeletal disorders can be known by the signs and symptoms. By looking at the signs and symptoms in the arthritis we can infer so as to which dosha (dosha’s) morbidity is involved in the causation or aggravation of the disease.
Signs and Symptoms of Dosha involvement in Arthritis –
Signs of Vata involvement
Vata type of Arthritis (Involvement of Vata):
Severe Pain – Excess Vata vitiation in the joints causes damage of joints and soft tissues at a brisk rate. Involvement of Vata in any joint disorder reflects degeneration and can be known by very high intensity of pain. Pain is a common symptom in any type of Arthritis but its intensity varies with involvement of different Doshas and combinations. If Vata Dosha is severely aggravated the intensity of pain will be severe.
Swelling – Mild to moderate swelling can be seen in Vata type of arthritis. The swelling is often compared to Vata-purna-driti sparsha (looks and feels like a bag filled with air)
Crepitus – Sounds in the joints will be highest in Vata affliction of joints due to severe degeneration, damage, dryness and consequent production of loose bodies in the joints.
Mobility – Movements may be severely impaired and restricted due to severe damage of the joints
Time of Pain – All the signs and symptoms of Vata arthritis will worsen during evening and or night.
Season – Symptoms aggravate in Varsha ritu (monsoon season / rainy season), during cold and damp weather, cloudy environment and naturally regress in summer and hot season
Vega – symptoms of Vata arthritis flare up due to forcible withholding of natural body reflexes especially the urges for defecation, urination, hunger, sleep, etc. Forcibly expelling them also will flare up Vata.
Emotions – Extremes of emotions especially anxiety, fear and unnecessary tensions (nervousness) will exacerbate the condition
Relation to food – The symptoms of Vata type of arthritis will worsen on empty stomach. Pungent (Katu), Bitter (Tikta) and Astringent (Kashaya) tastes will increase or worsen pain. Cold, dry, fried and stale foods will also worsen the pain.
Relation to activity – Excessive and exhausting exercises, workouts and sexual activities will worsen symptoms of Vata arthritis.
Relieving factors – The pain and other symptoms of Vata type of arthritis will get relieved –
By hot and warm comforts or treatments
Application of soothing herbal oils and massages (abhyanga)
Sudation or sweat inducing treatments (swedana)
Local treatments like Janu Vasti (oil pooling for knee arthritis), Kati Vasti (oil pooling for low back pain), Greeva Vasti (oil pooling for neck pain), Pinda Sweda (bolus fomentations) etc
Consumption of medicated oils
Virechana (therapeutic purgation) and Vasti (therapeutic enemas)
Intake of light digestible food, hot and fresh, more of sweet (madhura), sour (amla) and salt (lavana) tastes
Rest
Signs of Pitta involvement
Pitta type of Arthritis (Involvement of Pitta):
Burning Pain – When Pitta afflicts the joints, it causes inflammation. If Kapha is not able to provide an antagonistic effect to this inflammatory process, the Pitta morbidity will burn the joints to destruction.
Since Pitta involvement reflects inflammatory process the patient finds burning sensation in the joint, a feel of fire or burning coal in the joints and fumes getting released
Warmth – Owing to its hot property, vitiated Pitta will cause increased warmth or heat in the joints. The pitta afflicted joints will be hot on touch.
Swelling – In pitta type of arthritis, the swelling will reflect the quantum of inflammation. If the inflammation is severe we can find severe swelling and if the inflammation is moderate, the swelling will be moderate.
The swelling will be of an inflammatory type (unlike Kapha type of swelling wherein the swelling is large owing to accumulation of fluids within the joint spaces. Generally moderate to severe inflammatory swelling (associated with warmth, redness) can be seen.
Redness – The inflamed joints in Pitta joint disorder will be red in color. This is a reflection of the inflammatory destruction taking place in the joints and soft tissues. More redness will reflect more inflammation.
Mobility – Movements restricted to varied extent depending on the quantum of inflammation. Inflammation causes burning type of pain and the pain will restrict the movements. But the restriction of movements is not as severe as in Vata type of arthritis which is caused due to joint damage and degeneration.
Time of Pain – The spike of the complaints in Pitta arthritis will be more during afternoon. It is generally a notion that Pitta symptoms including pain and swelling will increase with the intensity of Sun towards noon and get reduced towards sunset. It is obvious that the symptoms will be at surge at afternoon.
Season – Symptoms aggravate in Sharad ritu (autumn or later summer season), during hot and humid weather, and naturally regress in cold season
Emotions – Extremes of emotions especially anger, jealousy and hatredness.
Relation to food – The symptoms of Pitta type of arthritis will worsen after 1-2 hours of taking food, i.e. when the digestion process is going on. Pungent (Katu), Sour (Amla) and Lavana (salt) tastes will increase or worsen symptoms. Hot and spicy, fried foods will also worsen the pain.
Relation to activity – Excessive exposure to heat, fire and Sun-light (Sun-heat) will worsen symptoms of Pitta arthritis.
Relieving factors – The pain and other symptoms of Pitta type of arthritis will get relieved –
By cold comforts or treatments
Application of soothing herbal oils made up of pitta alleviating and anti-inflammatory herbs, Ksheeradhara (stream pouring of medicated milk over the joints and soft tissues), Lepa (anointments or pastes having anti=inflammatory property)
Treatments like Virechana (therapeutic purgation), Raktamokshana (blood-letting treatment) etc
Consumption of Tikta Ghritas (herbal ghee prepared with herbs having pitta alleviating and bitter tasting herbs)
Intake of light digestible food, cold in nature, more of sweet (madhura), tikta (bitter) and kashaya (astringent) tastes
Signs of Kapha involvement
Kapha type of Arthritis (Involvement of Kapha):
Heaviness – Kapha is a watery element. When Kapha accumulates in excess within the joint spaces it causes effusion. The Kapha involvement indicates accumulation of some fluid in and around the joints. This causes a heavy pain around the joints. The fluid is most often non-inflammatory type.
Stiffness – This is the hallmark feature of a Kapha joint disorder. The stiffness of the joints and soft tissues is due to accumulation of fluids in the cells. Stiffness or catch will be predominantly sensed around early part of the morning and will come down as the day passes.
Swelling – Swelling of a severe proportion will be seen in the Kapha type of arthritis. Due to the accumulation of fluids we could observe some shine around the swelling area.
Coldness – The affected joints are cold on touch. This is because of the cold nature of Kapha.
Dampness – Feeling of a Wet cloth wrapped around the joint cans be felt from the person suffering from Kapha type of arthritis.
Mobility: The movements in Kapha arthritis will be restricted due to stiffness caused by fluid accumulation.
Time of Pain – The complaints will get more during early morning and day time and will gradually come down as and when the Sun-light and heat increases towards the mid day.
Season – Symptoms aggravate in Vasantha ritu (spring season / Early summer season), during cold and damp weather, cloudy environment and naturally regress in summer and hot season
Emotions – Extremes of emotions like introversion, depression unable to express etc will support in accumulation of kapha and watery contents in the tissues
Relation to food – The symptoms of Kapha type of arthritis will worsen after intake of food. Madhura (sweet), Amla (sour) and Lavana (salt) tastes will increase or worsen symptoms. Cold, oily, and stale foods will also worsen the symptoms.
Relation to activity – Lack of exercises and physical activity
Relieving factors – The pain and other symptoms of kapha type of arthritis will get relieved –
By hot and warm comforts or treatments
Application of lepa (medicinal pastes), upanaha (medicinal poultices) etc which ward off the fluid collection and relieve stiffness and catch in the joints
Sudation or sweat inducing treatments
Treatments like Vamana (therapeutic emesis)
Intake of light digestible food, hot and fresh, more of pungent and spicy (katu), bitter (tikta) and astringent (kashaya) tastes
Good physical activity
Arthritis caused by involvement of more than 1 dosha –
When more than 1 dosha is involved in causation of arthritis or pain, the signs and symptoms will be in mixed proportions. Let us have a look at these sub-types of arthritis wherein more than 1 dosha is involved in the pathogenesis.
Vata-Pitta arthritis – When Vata-Pitta Doshas are involved, as the name indicates, Vata will be more aggravated (predominant vitiated dosha) in comparison to Pitta (associated vitiated dosha) while Kapha will remain dormant. In these conditions Pain due to Vata (predominant dosha) will be more but burning sensation as caused by Pitta vitiation (associated dosha) too will be present in a mild form.
Pitta-Vata arthritis – When it is Pitta-Vata afflicted joint, as the name indicates, Pitta will be the predominant vitiated dosha and its symptoms will be seen in higher proportion.
Vata will be the associated dosha and its contribution to symptomatology will be lesser in comparison to that of Vata. Kapha in this case too will be dormant. Thus, in Pitta-Vata type of arthritis, burning sensation caused by Pitta will be more than pain caused by Vata.
By the above said explanation it is clear that Vata-Pitta arthritis and Pitta-Vata arthritis are 2 different forms of arthritis though the morbid factors are the same. In these cases, the permutation and combination of the dosha manifestation or vitiation in causation of arthritis is the key. The symptoms will be manifest accordingly.
Dual and Tridosha involvement
The other forms of Joint disorders too should be similarly understood. They are –
Vata-Kapha arthritis – In this, Vata will be predominant dosha and Kapha will be subordinate dosha. As the name suggests, Vata symptoms (pain etc) will be more than Kapha symptoms (stiffness etc). Pitta will be the least vitiated or dormant dosha whose symptoms are not manifested.
Kapha-Vata arthritis – This condition is just the reverse of Vata-Kapha arthritis. In this, Kapha will be predominant dosha and Vata will be the associated dosha. As the name indicates, Kapha symptoms (stiffness etc) will be more than Vata symptoms (pain etc). Pitta again is a subtle dosha which doesn’t surface.
Pitta-Kapha arthritis – In this, Pitta will be predominant dosha and Kapha will be subordinate dosha. As the name suggests, Pitta symptoms (burning pain etc) will be more than Kapha symptoms (stiffness etc). Vata will be the least vitiated or dormant dosha whose symptoms are not manifested.
Kapha-Pitta arthritis – This condition is just the reverse of Pitta-Kapha arthritis. In this, Kapha will be predominant dosha and Pitta will be the associated dosha. As the name indicates, Kapha symptoms (stiffness etc) will be more than Pitta symptoms (burning pain etc). Vata again is a subtle dosha which doesn’t surface.
Vata-Pitta-Kapha arthritis or Tridosha arthritis – In these types of arthritis, all 3 doshas i.e. Vata, Pitta and Kapha are all vitiated. The symptoms of vitiation of all the 3 doshas (as explained above) will be evident in these joint disorders.
Again the permutation and combination will come into the question. It is left out to the expertise of the experienced Ayurvedic doctor to diagnose the proportionalities of individual dosha vitiation in comparison to the other two.
Ex. Pitta-Vata-Kapha type of Tridosha arthritis will be diagnosed on the fact that these 3 doshas are relatively vitiated in that order, Pitta the highest vitiated, Vata, the 2nd highest associated and Kapha the least vitiated among the lot. The symptoms too will be manifested in a similar chronology.
Pitta symptoms like burning pain etc will be predominant in comparison to severe pain of Vata, the stiffness caused by Kapha will be the least. In this way, the permutations and combinations of dosha vitiations in Tridosha arthritis shall be understood.
Note – I am not covering the minute aspect of different Tridosha arthritis with a fear of unnecessary detailing and since this article is only written to give a nutshell idea about the dosha involvement in arthritis and their manifestation.
Immaterial of the joint involved and immaterial of the type of arthritis, the Dosha symptoms will be as said above. This rule is applicable in back and neck pain, spinal problems, and musculo-skeletal disorders.
Other contributing factors
Other factors contributing towards arthritis manifestation and aggravation –
Ama – Improperly processed digestive juices in circulation which will neither be recognised by the cells as nutrition nor will further be metabolized by the cells is called ama. This is formed at the gut level due to weak digestion.
When ama is not processed by the cells, the ama blocks and clogs the channels of circulation and nutrition due to its sticky nature. The ama further accumulates in the cells and disturb tissue metabolism and also will hamper the tissue formation.
Gradually this ama accumulates in the body in the form of ama-visha or endo-toxins. Ama and amavisha will lead to manifestation of many systemic psychosomatic illnesses and also auto-immune disorders like Amavata (Rheumatoid arthritis) etc.
Association of this ama with morbid doshas will add fuel to the fire. These doshas are now called sama doshas (doshas associated with ama). Sama Vata, Sama Pitta and Sama Kapha also will produce painful syndromes and various forms of arthritis.
Weak dhatus – Weak tissues provide a suitable environment for the morbid doshas to invade and cause arthritis, especially bone, muscle and fat tissues are susceptible to be attacked by vitiated doshas so as to cause arthritis. Weak dhatus may be congenital or acquired. Weak tissue metabolism (dhatwagni mandhya) and ama accumulation in dhatus (sama dhatus) also predispose for arthritis.
Formation and collection of ama, their association with morbid doshas and manifestation of many joint related disorders like arthritis explains the auto-immune process.
Just before finishing –
I hope that the above said discussion would focus some light on ‘how the dosha’s are involved in the causation and aggravation of arthritis’ or any pain in that matter.
The article is an attempt at showing how certain symptoms will help a doctor to reach the diagnosis by tracking down the morbid dosha or dosha’s involved in the causation of arthritis.
I would like to end this article with a sincere appeal to use this article in good sense as an informative and educative stuff and not for making self-diagnosis. Remember that there is always an Ayurvedic doctor available in your neighbourhood to do that part of work.
Article by Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)
Email:
[email protected]











3 comments
Sundaram
Excellent article sir.
Sundaram
Dr Malini Bhat
Namaste Sir, Thank you for the appreciation 🙂
haresh
clearly explained. thankyou dr.