Ascites: Ayurvedic Treatment, Remedies, Medicines
Article by Dr. Mahesh Annapure M.Sc., D. N., M.D. (A.M.)
Table of Contents
Introduction
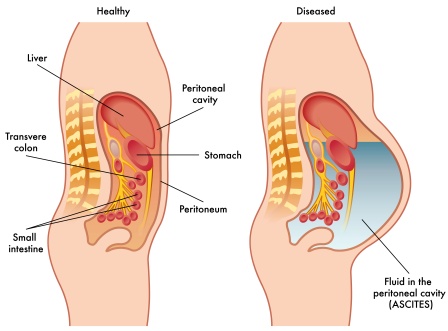
Ascites is a gastro-enterological term to describe the accumulation of a fluid in the peritoneal cavity which leads to abdominal distension. It is called Jalodar in Sanskrit.
Jal means water or fluid.
Udar means abdomen.
Fluid secreted by the liver is exceeded on large scale and the abdominal cavity is distended with such fluid. A severe liver cirrhosis and heart failure is a common cause for this disease. If not cured in proper time, this disease may lead to severe complications.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms / Lakshanas :-
In different stages the symptoms differs.
In mild ascites it is hard to notice the disease externally. The presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity can only be detected by ultrasound examination.
In moderate ascites, slight progressive distention of the abdominal flanks is see. This leads to enlarged abdominal cavity. It may be noticed externally by examining the abdominal structure, visible bulging of the flanks. In the patient with reclining situation, difference in the percussion note in the flanks which shifts at the time when the patient turns on the other side.
In severe or massive ascites patient complains progressive abdominal heaviness, he feels pressure and stiffness of the abdomen, shortness of breath due to pressure on the diaphragm (muscle layer between chest and abdomen. When the abdomen is pressed slightly on one side, it will generate a wave like movement through the fluid which can be noticed on the other side. Edema of feet – Padashotha is also seen.
Dilated veins (blood pipes) are seen on either side of abdomen.
Due to liver cirrhosis, leg swelling and bruising with slight changes in mental behaviour may be noted.
Sudden weight loss may be due to carcinogenic ascites.
Wheezing and shortness of breath may be due to ascites arising due to heart failure.
Risk factors
Risk factors leading to ascites:
Heart failure
Excess alcohol consumption
Sitting work, without any exercise
Sleeping in daytime
Irregular salt water balance of body/ osmoregulatory disorder.
Causes
Causes of ascites:
Depending on the accumulation of abdominal fluid and its water level, it may be described in three ways.
The most common causes is of two types, due to the high Serum Ascites Albumin Gradient (SAAG). It is transudate type, means, a fluid that passes through a membrane, which filters out of the cells and much proteins yielding watery solution. It has considerable low proteins.
The another type is of due to low SAAG, which is extrude type in which a fluid with high proteins and cellular debris including pus cells, blood, plasma protein, blood cells, white blood cells and platelets may be present, which escapes from vessels and deposited in tissues or tissue surface. It has considerably high proteins.
High SAAG –
Viral, cryptogenic or alcoholic cirrhosis.
Heart failure
Veno – occlusive disease
Low SAAG :-
Carcinogenesis of liver
Diseases like pancreatitis, tuberculosis, nephritic disease,
Other rare causes :-
Thyroid disorder
Dialysis
Vascular disorder
Diagnosis
It can be detected by the Blood, Urine examinations and ultrasound sonography.
Blood tests fo ascites:
Complete Blood Count for basic metabolism, liver enzymes, protein, albumin, cell count,SGOT, SGPT, SAAG etc.
Liver function tests will show high serum bilurubin, low HB, RBC/WBC, enzymes test.
Complete Urine Examination:-
CUE for sugar, minerals, sodium level, etc.
Ultrasound examination :-
Ultrasound examination for abdomen and related organs is performed.
The ultrasound diagnosis may show-
Liver – Shrunken with course ecotexture, irregular borders, may appear smaller in size, intrahepatic undilated bilary radicals.
Gall bladder – Distended with thickened walls , sometimes stones inside.
Spleen – Splenomegaly, focal lesions, disturbed splenic vein.
Pancreas – Obscured.
Kidneys – Calculus or focal lesion, pelvicalceal system dilated.
Urinary bladder – Distended.
Floating bowel loops in peritoneal cavity in the free fluid.
Precautions
Drink minimum water
Get proper sleep at night, avoid sleeping in day time.
Be active, don’t be lazy.
Completely avoid alcohol, tobacco, salts.
Ayurvedic Treatment
Treatment given for ascites is of three types.
Diet Management :-
It is only way of prevention in liver is to strictly follow the rules of avoidable and take proper food.
Avoid
Avoid alcohol, medicines preserved by alcohol, tobacco,
Avoid excess use of salts, oils, excess starch like rice- wheat, potato,etc,
Limit on fried foods, oils and its derivatives like ghee, vanaspati ghee- dalda, Milk – as it contains animal fats and is hard to digest, milk derivatives like chass, curd, lassi, paneer, shrikhand, ice creams, deserts, cakes, chocklets, milk cream, etc.
Flatulent foods, rice flakes- Poha, etc.
Sour and tangy fruits like tomato, kokam, mango, termerind, orange, citrus fruits, etc as it may cause cough and trouble to breathing.
Potato, corn, pearl sago sabudana, it contains starch.
Pulses/ lentils like pigeon pea or red gram- increases acidity. Bengal gram- Chanadal produces gases.
Seeds like ground-nuts, sesame, coconut- contains oil.
Fast foods- contains excess oil/ preservatives/ synthetic colour and essences.
Take–
Breakfast- Germinated green gram- Moong, and fruits.
Lunch- jowar- sorghum , wheat roti without oil. Vegetables boiled with little garlic, karela.
Dinner- sorghum- jowar , wheat roti without oil. Vegetables boiled with little garlic, karela. Moong, Masoor dal, little Rice.
Diuretics:-
Restriction of salt is a basic concept to remove the abdominal fluid.
Stage 1 – Gokhru(puncture spine)/ Kulthi (horse gram)/ Arjuna, (any one)
Stage 2 – Gokhru(puncture spine)/ Kulthi (horse gram)/ Arjuna, punarnava,
( any two)
Stage 3 – Gokhru(puncture spine)/ Kulthi (horse gram)/ Arjuna ,Punarnava
(any two)
Laxatives:-
Laxatives are remedies that looses stool and increase bowel movement.
Stage 1 – Amalaki powder
Stage 2 – Triphala powder
Stage 3 – Gandharvaharitaki, Gomutraharitaki. Or in addition Behada, Amala, Hirad, Haritaki any one
Digestives:-
These are essential for proper digestion of food.
Cumin seeds, Black pipper, sunthi, aamla, hirad, chitrak, lavana, Cummins etc
Liver supportive therapy:
These are essential for generating liver cells and maintaining liver function.
For all stages combinations of above may be given. Behda, Katuki, Kalmegh, Punarwasu, Guduchi, Kamdudha ras, Praval panchamrut, yashad bhasm, Akik Pishti, Giloy satva, Arjuna, Bhrangaraj, fumaria indica, kasni, vidanga, milk thistle, goji berry etc.
Heeng – Asafoetida, himsra,
Kutki – Picrorrhiza kurroa,
kateli, black nightshade, are also useful in ascites.
Ayurvedic medicines
Ayurvedic medicines useful in the treatment of ascites:
(Click on the medicine name to know more about them)
Medicines to improve liver functions:
Punarnavasavam – It is a liquid Ayurvedic medicine useful in gastritis, edema, fiver and liver diseases
Yakrit Pilhari Loha – used in the treatment of liver and spleen disorders.
Kottakkal Chitraka Leham
Arogyavardhini Vati – It is used in the treatment of liver diseases, fever, skin diseases, etc.
Medicines used for Nitya Virechana therapy – daily purgation –
Ichhabhedi Ras – used in the treatment of ascites, constipation and bloating.
Jalodarari Ras – used exclusively in treatment of ascites.
Gandharvahasthadi Thailam – oil used in the treatment of bloating, abdominal pain, etc.
Other useful medicines:
Naracha Ras
Udarari Rasa
Shankha Dravaka
Naturopathy treatment
Naturopathy treatment for ascites:
Take fresh air bath
Avoid darkness.
Take vitamin A rich diet.
Drink magnetic water twice a day.
Little walking and little movements of body parts regularly.
Paracentesis
It is a process of letting out the accumulated fluids from the body. It is also known as tapping.
Read more about indications and contra indications of paracentesis here
Conclusion, clinical experience
Ayurveda had proper best effective remedies for ascites.
Ascites may be cured by Ayurveda without tapping or dialysis, if the treatment is started in early stage.
Proper remedies may be prescribed according to the patient.
Time duration for getting cure is mostly depends on the strong will power and response of the patient and experience of the practitioner.
Dr. Mahesh Annapure
M.Sc., D. N., M.D. (A.M.)
Address:- 303, Chintamani Park, Shashtrinagar,
Bhawsar Chowk, Nanded. 431605
Maharashtra
Jalodara
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) and Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Jalodara is compared to ascites, a condition wherein there is fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity. Jalodara is a form and one of the types of Udara Roga (Abdominal disorders).
The morbid doshas which have accumulated in the body over a period of time contaminate and block the srotas (channels) related to conduction and transportation of sweda (sweat) and ambu (water) and cause Udara roga (abdominal disorders) by further contaminating Prana Vayu, Agni (metabolic fire) and Apana Vayu. This Udara Roga is of 8 types and Jalodara is one among them.

When the person who has undergone treatments in the form of sneha pana (oral intake of medicated oils and or ghee, oleation), anuvasana vasti (oil enemas), vamana (therapeutic emesis), virechana (therapeutic purgation) and or niruha vasti (decoction enemas) in excess happens to drink water immediately after the procedures or if the srotas (channels) especially jalavaha or udakavaha srotas (channels carrying or transporting water in the body) gets coated by excess sneha (fats, oil, ghee etc administered through treatments), the udakavaha srotas get contaminated. As a result fluid accumulates in the udara (abdominal cavity) and causes a disease called Jalodara (ascites).
Ayurvedic treatment
Ayurvedic Treatment for ascites – Jalodara –
Ayurveda too has suggested surgery and removal of fluid as the first line of treatment in Jalodara.
Vyadhana – should be done over the udara or abdomen. Vyadhana means puncturing and removal of fluid. The vyadhana should be done using Vrihi mukha shastra (instrument similar to a curved needle or scalp vein) at a distance of 4 angulas (1 angula = 1.5-2cm, 1.89 cm or ¾ inches respectively) towards the left of Nabhi (navel). The depth should be of the length of half finger. The puncture should be done after having tied (band) a sterile cloth tightly around the abdomen. Into the depth of the opening a nadi (tubular instrument open at both ends) should be inserted and the fluid should be drained. The opening should later be applied with taila (oil) and lavana (salt) and later should be cauterized with fire (agni karma). Sterile dressing should be done. The fluid should be evacuated on alternative days in little quantities.
Virechana – Virechana or therapeutic purgation should be administered regularly so as to avoid recurrence. It should also be administered once there is evidence of accumulation of even a small amount of fluid.
Shodhana – Regular gut cleansing should be done by administering milk or urine of cow with eranda taila (castor oil)
Some Ayruvedic medicines:
Ashwagandha churna (powder of Withania somnifera) with Go mutra (urine fo cow)
Vardhamana Pippali – 1000 Long peppers taken over a period of 20 days, initially increased by 10 pippalis for first 10 days and later tapered in the same order so as to finish with 10 pippalis on 20th day. (According to strength of the patient and quantity of fluid collection, the pippalis may be used in 5 or 3 numbers, increased in same proportions. Pippali is either used in the form of paste or decoction. Milk should be kept aas diet during the procedure.)
Formulations like Narayana Churna and Dashamula Panchakoladi Kashayam
Haritakyadi kwatha – Decoction prepared using Haritaki (Terminalia chebula), Shunti (ginger), Devadaru (Cedrus deodara), Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia) added with Guggulu (Commiphora mukul) and Gomutra (urine of cow)
Punarnavadi Kashayam – Decoction of Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa), Nimba twak (bark of neem), Patola patra (leaves of pointed gourd), Shunti (ginger), Katuki (Picrorhiza kurroa), Haritaki (Terminalia chebula), Daruharidra (Berberis aristata), Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Mahisha ksheera (buffalo milk) with Gomutra (urine of cow)
Mahisha mutra (buffalo urine) in Go dugdha (milk of cow)
Triphala churna used with cow’s milk
Gomutra pana – drinking cow’s milk
Dashamula kwatha (decoction of 10 roots) mixed with Eranda Taila (castor oil)
Pathya apathya – Yogaratnakara
Wholesome herbs, diet and habits
Purgation, fasting, one year old horse gram, green gram, red variety of rice, barley, soup of meat of animals & birds living in desert like lands, gruel, alcohol, honey, fermented sugarcane juice, rock salt, butter milk, garlic, castor oil, ginger, pointed gourd, bitter gourd, hog weed, drumstick, Chebulic myrobalan, betel, cardamom, calx of ron, milk and urine of goat, cow, camel & buffalo, herbs having light, potent & carminative properties etc.
Unwholesome herbs, diet and habits
Excessive intake of water, day sleeping, intake of heavy & burning sensation causing food, exercise, travelling etc.
Effective Decoctions for Abdominal Enlargement and Ascites
Abdominal disorders in Ayurveda are known as udara .They are of eight kinds and involve enlargement of abdomen by vitiated doshas, enlargement of spleen and liver, accumulation of fluids i.e. ascites, obstruction of intestines and intestinal perforation.
Read – Charaka Udara Roga Chikitsa – 13th Chapter

1. Mahodarahara Kashayas – decoctions effective against enormous enlargement of abdomen
a. Pathyadi Kashayam
Ref – Sahasrayogam, Kashaya Prakaranam, 45a
| Ingredients | Botanical Name | Method of using | Indications |
| Haritaki | Terminalia chebula | The decoction prepared with these ingredients should be served fresh with alkali of barley and asafetida | Cures – 1. Abdominal tumors 2. Enlargement of spleen 3. Piles 4. Indigestion 5. Enlargement of prostate gland 6. Flatulence 7. Colic / abdominal pain caused by vitiated vata and kapha 8. Ascites |
| Putikaranja | Pongamia pinnata / Holoptelea integrifolia | ||
| Ginger | Zingiber officinale | ||
| Chitraka | Plumbago zeylanica | ||
| Long pepper | Piper longum | ||
| Root of Pippali | Piper longum | ||
| Chavya | Piper retrofractum | ||
| Ajagandha | Cleome gynandra | ||
| Rakta Punarnava | Boerhavia diffusa, red variety | ||
| Bilwa | Aegle marmelos | ||
| Horse gram | Dolichos biflorus | ||
| Castor | Ricinus communis | ||
| Sahachara | Strobilanthes heynianus | ||
| Ginger | Zingiber officinale | ||
| Agnimantha | Clerodendrum phlomidis |
b. Dashamoola Panchakoladi Kashayam
c. Nikumbhadi Kashayam
Ref – Sahasrayogam, Kashaya Prakaranam, 45c
| Ingredients | Botanical Name | Method of using | Indications |
| Nagadanti | Baliospermum montanum | The decoction prepared with these ingredients should be served fresh | 1. Upward movement of vata 2. Enormous enlargement of abdomen |
| Trivrit | Operculina turpethum | ||
| Triphala | Fruits of – Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellerica Emblica officinalis | ||
| Indravaruni | Citrullus colocynthis | ||
| Snuhi | Euphorbia neriifolia | ||
| Tilvaka | Viburnum nervosum | ||
| Swarna ksheeri | Argemone mexicana | ||
| Long pepper | Piper longum |
Read – Kashayam (Kwath) – Herbal Teas Preparation [Video], Benefits, Usage
2. Tavidvamadi Kashayam
Ref – Sahasrayogam, Parishishta Prakaranam, 71
| Ingredients | Botanical Name | Method of using | Indications |
| Punarnava | Boerhavia diffusa | The decoction prepared with these ingredients should be served fresh | 1. Enormous enlargement of abdomen |
| Haritaki | Terminalia chebula | ||
| Bark of Aragwadha | Cassia fistula | ||
| Chirabilva | Holoptelea integrifolia / Caesalpinia bonduc | ||
| Ginger | Zingiber officinale | ||
| Bhunimba | Andrographis paniculata |
Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)








2 comments
Yash Ashok Mehta
I am having refractory ascites due to dialysis..
No fluid in abdomen prior starting the dialysis, as dialysis continued fibrosis increased in the liver.
What should be the line of treatment…
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Please consult Dr Gururaja sir
https://www.easyayurveda.com/gururaja/