Fatty Liver: Symptoms, Ayurvedic Treatment, Remedies, Tips
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay).
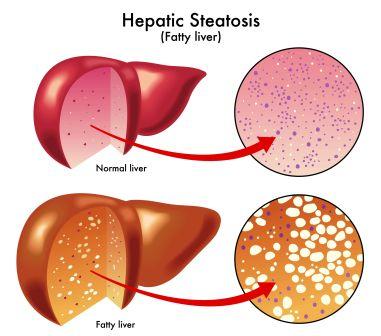
The tricky thing about fat is that, it can accumulate underneath the skin (to cause obesity) and also in some organs. Liver is one such organ wherein excessive fat accumulation can lead to a condition called Fatty liver disease or Steatosis.
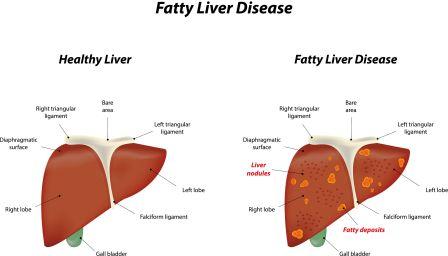
Liver is located in the right upper part of abdomen, its upper surface being just below your right lung (right chest cage) separated by a muscular layer called diaphragm. A part of right rib cage protects your upper part of liver.
Some amount of fat is normally present in the liver. But when the quantity of accumulated fat increases so as to contribute to more than 5-10% of its weight, the condition is known as Fatty Liver Disease.
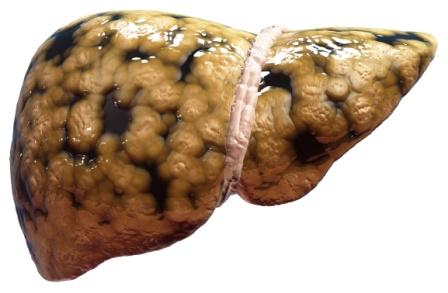
Table of Contents
Fatty Liver Disease (FLD)
It is a condition in which the liver cells accumulate abnormally increased amounts of fat. Excessive consumption of alcohol is a very common cause of Fatty Liver.
It is a reversible condition wherein large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells via a process of steatosis (abnormal retention of lipids within the cell).
FLD is associated with other diseases that influence fat metabolism. When this process of fat metabolism is disrupted, the fat can accumulate in the liver in excessive amounts, thus resulting in fatty liver. Accumulation of fat may also be accompanied by a progressive inflammation of the liver (hepatitis) called steato-hepatitis.
By considering the contribution of alcohol, fatty liver may be termed as alcoholic steatosis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the more severe forms as alcoholic steatohepatitis and Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
Diet
Eat a balanced and healthy diet. Limit extra-carbs from the food schedule such as bread, grits, rice, potatoes and corn. Cut down on consuming sugar-rich drinks like sports drinks and juices.
Have food rich in vitamin E – Sunflower seed, almond, pine nuts, peanuts, spinach, taro root, flaxseed oil, soyabean, pistachio. Broccoli, carrots, chard, mustard and turnip greens, mangoes, nuts, papaya, pumpkin, red peppers
Have food rich in Omega 3 fatty acid – Flax seeds, walnut, sardines, salmon, soyabean, tofu, shrimp, brussel sprout, cauliflower, winter squash, fish oil, egg oil, krill oil, chia seeds, Canola oil, camellia
Have food rich in Vitamin D – yogurt, cheese, orange juice, zuccini, tomato,Salmon, Tuna, Cod liver oil, Fish, fortified cereals, oysters, fortified soy products, ham, dairy products, egg, mushroom,
Quit alcohol.
Avoid excess use of oily foods, fried foods, milk, dairy products and heavy-to-digest non veg food.
Obesity predisposes you to have fatty liver disease. Follow these obesity tips to lose weight.
Obesity and diabetes enhances risk of fatty liver disease. Follow these diabetes tips to keep your sugar levels in check.
Liver Disorders in Patient with Diabetes and Obesity
Tips
- Excess of Iron intake can cause it. If you are taking iron supplement, then have a talk with doctor. Many of Ayurvedic medicines also contain natural iron. Example: Lohasava, Saptamrit lauh, etc.
- Malnutrition and starvation also causes it. Make sure to eat healthy and eat nutrition rich diet.
- Certain drugs like Tamoxifen, Methotrexate, Diltiazem etc cause it. (full list of medicines given below). Talk to your doctor.
- Inflammatory bowel disease causes it. if you have it, get proper treatment.
- Avoid Kapha increasing foods and lifestyle activities in FLD Read how to balance Kapha Dosha
Types
There are mainly 2 types of Fatty Liver Disease (FLD). They are –
- Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD)
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Note: Some women get Fatty liver changes during pregnancy
Home remedies
1. Triphala Kashaya – 20 ml, mixed with a teaspoon of honey, 2 times a day, before food. Learn how to prepare Triphala Kashaya
2. Giloy Kashaya: Decoction of Tinospora cordifolia – 30 ml, mixed with a teaspoon of honey and is administered once a day.
3. Regular consumption of 2 grams of long pepper powder along with a teaspoon honey, once or twice a day for a month time.
4. Guduchi Churna (Giloy – powder of Tinospora cordifolia) + Musta Churna (Powder of Cyperus rotundus) – 2 grams of each of these two mixed and administered once a day, along with hot water.
5. 3 grams of Paste of the roots of Sharapunkha (Tephrosia purpurea) is mixed in a cup of buttermilk and is administered once a day.
6. 20 ml of Water decoction (Kashayam) prepared by steam heating the flowers of Shalmali (Bombax malabaricum) tree is given after mixing it with mustard powder.
7. Powders of cardamom, cumin seeds, Bhumyamalaki (Phyllanthus niruri) and Sugar – taken in equal quantities – 3 grams, mixed with half a teaspoon of ghee should be taken early in the morning
8. The powder of dry garlic, long pepper root and Haritaki (Terminalia chebula) – 3 – 5 grams per day should be consumed for a period of 2 months time.
9. Paste of turmeric – 2 grams, mixed with 3 teaspoons of juice of Amalaki (Emblica officinalis) is administered once or twice a day.
Symptoms
Fatty liver rarely causes symptoms until the liver disease is far advanced. Fatty liver is found or suspected when:
- Abnormal liver tests are found on routine blood testing
- Fat is seen in USG, when USG of abdomen is performed for other reasons ex. For the diagnosis of gallstones
- Infrequently when the liver is enlarged on physical examination of the patient
Early symptoms of Liver dysfunction due to FLD
As already said you may have a FLD and still not realize it. At the beginning FLD is asymptomatic (no symptoms). The symptoms manifest in a later period of time. It often takes years to decades for the symptoms to manifest.
The common symptoms of FLD are:
- Feeling tired
- Loss of weight
- Loss of appetite
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Confusion
- Poor judgement
- Trouble in concentrating
Other symptoms:
- Hepatomegaly (your liver may get larger in size than normal)
- Pain: You may feel pain or discomfort in the centre or right upper part of your abdomen (belly)
- Dark coloured patches: You may find dark patches on your neck or under your arms
Note: If you have an ALD, you may notice that the symptoms get worse after a period of heavy drinking
Liver Cirrhosis
If you have FLD or ALD, you may get Liver Cirrhosis (scarring of liver). When the liver disease is far advanced (cirrhosis), signs and symptoms of cirrhosis predominate. They are as said below:
Liver Cirrhosis presents with:
- Fluid accumulation due to portal hypertension that causes fluid to leak from blood vessels and the inability of liver to make the major blood protein, albumin
- Wasting of muscles
- Excessive bleeding due to inability of the liver to make blood-clotting proteins
- Gastro-intestinal bleeding due to portal hypertension that increases the pressure in intestinal blood vessels
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes) due to inability of the liver to eliminate bilirubin from the blood
- Mental changes (encephalopathy) due to the liver’s inability to eliminate chemicals from the body those are toxic to the brain. Coma too may occur.
- Liver cancer
- Liver failure
Associated diseases
Diseases associated with NAFLD:
Diseases associated with metabolic syndrome:
- Obesity
- Elevated blood triglycerides
- Low – HDL cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Elevated blood sugar (diabetes)
Other associations:
- Fatty pancreas
- Hypothyroidism
- Colon polyps
- Elevated blood uric acid
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Poly-cystic Ovaries
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
Note:Half patients with NAFLD have obstructive sleep apnoea and most patients with obstructive sleep apnoea have NAFLD.
Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD)
This form is reserved for those who enjoy their alcohol at will. ALD can even show up after a short period of heavy drinking.
Parent Link:
Alcoholic parents can influence their child to get ALD. They can just pass on ALD genes to their offspring.
If you are addicted to alcohol and have alcohol related fatty liver changes, there is every chance that you pass on the genes that play a role in ALD. They (genes) can affect the chances that your child becomes an alcoholic. They can also have an impact on the way the body breaks down the consumed alcohol in your children.
So if your child becomes an alcoholic like you when he or she grows up, the ALD affecting genes transmitted by you will make the alcohol breaking process in their body difficult. This also means that your alcoholism has an extended version of story that runs in successive generations too.
Read related: Alcohol Intoxication – Symptoms, Treatment As Per Ayurveda
Other factors that can influence the chances of you getting ALD are:
- Hepatitis C (which causes inflammation in your liver)
- Too much iron in the body
- Being obese
Effect of Alcohol and Pain Killers on Liver
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
The causes of this type of fatty liver disease is not clear.
NAFLD has a tendency to run in families
NAFLD is more likely to happen to those who are middle aged and are overweight to obese. These people often have high cholesterol and diabetes.
What happens in Non alcoholic fatty liver disease?
NAFLD is a manifestation of abnormality of metabolism within the liver. Liver handles metabolism of fat. Liver makes and exports fat to other parts of the body. It also removes fat from the blood that has been released by other tissues in the body, ex. By fat cells or absorbed from the food we eat.
In NAFLD, the mechanism by which the Liver handles fat and its metabolism gets disturbed. Increased amounts of fat are removed from the blood and / or increased amounts of fat are produced by liver cells.
On the other hand not enough amount of fat is disposed of or exported out by the liver cells. Thus there is an imbalance between input and output of fat. There is imbalance between fat deposition (accumulation) and fat clearance. As a result excess fat accumulates in the liver.
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is further classified as –
- Isolated Fatty Liver or Fatty Liver (IFL)
- Non Alcoholic Steato-Hepatitis (NASH)
In both Fatty liver and NASH, there is an abnormal quantity of fat accumulation in the liver cells. In addition, in NASH there is inflammation of liver. As a result, the liver cells are damaged. The liver cells die and are replaced by scar tissue.
Why is NAFLD important?
- It is a very common disease now days, it is increasing in prevalence
- Non Alcoholic Steato Hepatitis is an important cause of serious liver disease leading to cirrhosis and the complications of cirrhosis like – liver failure, gastro-intestinal bleeding and liver cancer.
- NAFLD is associated with other very common and serious non-liver diseases, the most important ones being cardiovascular disease – that leads to heart diseases and stroke. Fatty liver is probably not the cause of these diseases but is a manifestation of an underlying causes that the disease shares. Fatty liver is therefore a clue to the presence of other serious diseases which need to be addressed.
What causes NAFLD? (The mechanism of patho-physiology)
The mechanism of NAFLD is complicated and not completely understood
Important factors are presence of:
- Obesity
- Diabetes Mellitus
Presence of excessive fat in the body as in Obesity and Presence of (manifestation) Diabetes predispose for fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Presence of these conditions alters the physiology of Liver. The liver in turn fails to process and dispose excess fat leading to the accumulation of large amounts of fat in the liver. This condition is called FLD.
Predisposing factors
How Obesity and Diabetes predispose for FLD?
The role of fat and fat cells in disturbing the metabolism:
- Obesity is much more than simple accumulation of fat in the body. Fat tissues are not inert. They are very active metabolically and have interactions and effects on other tissues throughout the body.
- When large amounts of fat are present in the body as in obesity, the fat becomes metabolically active (inflamed)
- This metabolically active fat gives rise to production of many hormones and proteins that are released into the blood. These hormones and proteins have effects on the cells throughout the body.
- Among many effects, these hormones and proteins promote insulin resistance in the cells.
Insulin resistance and its effect on the cells:
Insulin resistance is a state in which the cells of the body do not respond adequately to the insulin, a hormone produced by pancreas (an organ which is related to your sugar metabolism, located in the left upper part of your belly). Insulin promotes glucose (sugar) uptake from the blood by cells. i.e. cells take up glucose in the blood only in the presence of insulin. For this to happen, the cells need to respond sensitively to the insulin.
At first, the pancreas compensates for the insensitivity to insulin by making and releasing more insulin. Eventually the pancreas fails to produce sufficient amount of insulin due to overload. Later it produces decreasing amounts of insulin.
When the cells become insensitive to insulin (not recognising insulin), sugar in the blood fails to enter the cells in a quantity it should have entered (though there is adequate amount of sugar in the blood). All this sugar starts accumulating in the blood and leads to a condition (disease) called Diabetes. Since sugar is an important source of energy for the cells which allows them to carry out their specialized functions, deficit sugar alters the way in which the cells function.
Fat and Fatty Acids:
Some fat cells get converted into fatty acids. This leads to increased level of fatty acids in the blood. Large amount of fatty acids are toxic to the cells.
Thus the release of hormones, proteins and fatty acids from fat cells affects cells throughout the body in different ways.
Effect on Liver:
- Liver is affected by the above said processes triggered by the presence of excessive fat in the body.
- Liver cells also become insulin resistant.
- Their metabolic process including handling of fat becomes disturbed and altered.
- The liver cells increase their uptake of fatty acids from the blood where they are in abundance.
- Within the liver cells, the fatty acids are changed into storage fat and the fat accumulates.
- At the same time, the ability of the liver to dispose of or export the accumulated fat is reduced.
- In addition, the liver itself continues to produce fat and to receive fat from the diet.
- All these events eventually lead to the accumulation of excessive fat in the liver leading to FLD.
Relationship between fatty liver, obesity and diabetes:
- Obesity and Diabetes have important roles in the development of Fatty liver. 1/3 of population including obese and diabetics may develop fatty liver. More than 2/3 of people with diabetes develop NAFLD
- Majority of obese patients undergoing surgery for obesity have NAFLD
- The risk of Non Alcoholic Steato Hepatitis (fatty liver with liver damage) is less than 5% among lean individuals, the risk is more than a third in obese
- Fatty liver increases both in prevalence and severity as the degree of obesity increased. FLD begins in those having weights that are considered overweight (less than obese)
NAFLD (IFL) and NASH
- In both these conditions we can find excess amounts of fat in the liver.
- In NASH there is inflammation and damage to the liver cells. The inflammation and damage of liver cells are caused by the toxic effects of the fatty acids released by fat cells but fatty acids are elevated in the blood in both these conditions. Damage is absent in IFL.
- 1/3 of general population who has fatty liver, out of this, 10% have NASH. About 1/3 of NAFLD patients have NASH.
- NASH progresses through the formation of scar (fibrous tissue) to cirrhosis of liver. The complications of cirrhosis like gastro-intestinal bleeding, liver failure, liver cancer etc will occur consequentially.
- IFL does not progress to form liver disease.
Note: The consequences of fat in the liver depend greatly on the presence or absence of inflammation and damage in the liver, whether there is fat alone or NASH is also present.
Non alcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD) and Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic Syndrome is a syndrome defined by the association of several metabolic abnormalities that are believed to have a common cause. These metabolic abnormalities result in:
- Obesity
- Elevated blood triglycerides
- Low – HDL cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Elevated blood sugar (diabetes)
NAFLD is considered as a manifestation of the Metabolic Syndrome and thus occurs frequently with the other manifestations of the syndrome. Occasionally it may occur without the other abnormalities of the syndrome.
More Causes:
Metabolic:
- Abetalipoproteinemia (a disease of fat transport)
- Glycogen storage disease
- Weber-Christian disease
- Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
- Lipodystrophy
Nutritional
- Malnutrition
- Starvation
- Total parenteral nutrition (Intravenous nutrition)
- Severe weight loss
- Refeeding syndrome
- Jejunoileal bypass
- Gastric bypass
- Jejuna diverticulosis with bacterial overgrowth
Drugs and Toxins:
- Amiodarone
- Methotrexate
- Diltiazem
- Expired Tetracycline
- Highly active antiretroviral therapy
- Glucocorticoids
- Tamoxifen
- Environmental hepatotoxins (phosphorus, mushroom poisoning)
Others
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- HIV
- Hepatitis C (especially genotype 3) and
- Alpha 1-antityrpsin deficiency
- Auto-immune or inherited liver diseases
- Wilson’s disease
- Lipodystrophy (a disease of fat storage)
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
- Fat can build up in the liver when you are a pregnant (though rare). This might become risky for both you and your child.
- It can lead to liver failure or kidney failure in either of you.
- It might also cause a serious infection or bleeding
- It is not understood why Fatty Liver occurs during pregnancy, but the hormones might play a role in their manifestation.
- Once FLD is diagnosed, it is important that your baby gets delivered as soon as possible
- You may need an intensive care for several days but your liver often returns to normal within a few weeks
Pathology of fatty liver
Fatty changes represent the accumulation of triglycerides (neutral fats) in the cytoplasm of liver cells.
- Initial changes: Hepatocytes present small fat vacuoles (liposomes) around the nucleus (micro-vesicular fatty change). Here liver cells are filled with multiple fat droplets.
- Acute fatty liver of pregnancy and Reye’s syndrome are examples of severe liver disease caused by micro-vesicular fatty change
- Late stages: Size of the vacuoles increases, nucleus is pushed to the periphery of the cell giving a characteristic ‘signet ring’ appearance (macro-vescicular fatty change). These vesicles are well delineated and optically empty because fats dissolve during tissue processing. Large vacuoles may coalesce and produce fatty cysts which are irreversible lesions.
- Macro-vescicular steatosis is the most common form. It is typically associated with alcohol, diabetes, obesity and corticosteroids.
- The diagnosis of steatosis is made when fat in the liver exceeds 5-10% by weight
- Defects in Fatty Acid Metabolism
This is responsible for pathogenesis of FLD which may be due to imbalance in energy consumption and its combustion, resulting in lipid storage.
Defect in fatty acid metabolism also can be a consequence of peripheral resistance to insulin, whereby the transport of fatty acids from adipose tissue to the liver is increased.
- Impairment or inhibition of receptor molecules (PPAR-a, PPAR-g and SREBP1) that control the enzymes responsible for the oxidation and synthesis of fatty acids appears to contribute to fat accumulation.
- Alcoholism is known to damage mitochondria and other cellular structures, further impairing cellular energy mechanism.
- NAFLD may begin as excess of un-metabolised energy in liver cells.
- Hepatic steatosis is considered reversible and to some extent non-progressive if the underlying cause is reduced or removed
- ASH, NASH and FLD progression: Severe fatty liver is sometimes accompanied by inflammation (steatohepatitis). Progression to alcoholic steatohepatitis (ASH) or Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) depends on the persistence or severity of the inciting cause. Pathological lesions in both conditions are similar. The extent of inflammatory response varies widely and does not always correlate with degree of fat accumulation. Steatosis (retention of lipid or fat) and onset of steato-hepatitis may represent successive stages in FLD progression.
- Progression to Hepatic fibrosis: Liver disease with extensive inflammation and high degree of steatosis often progresses to more severe forms of disease. Hepatocyte ballooning and necrosis of varying degrees are often present at this stage.
Liver cell death and inflammatory responses lead to the activation of stellate cells, which play a pivotal role in hepatic fibrosis. The extent of fibrosis varies widely. Perisinusoidal fibrosis is most common, especially in adults and predominates in zone3 around the terminal hepatic veins
- Progression to cirrhosis: The progression to cirrhosis may be influenced by the amount of fat and degree of steato-hepatitis by a variety of other sensitizing factors. In alcoholic FLD the transition to cirrhosis related to continued alcohol consumption is well documented, but the process involved in non-alcoholic FLD is less clear
Epidemiology
- Prevalence of FLD in the general population ranges from 10-24% in various countries
- It is observed in up to 75% of obese people, 35% of whom progressing to NAFLD despite no evidence of excessive alcohol consumption
- FLD is the most common cause of abnormal liver function tests in the United States
- Fatty liver occurs in 33% of European-Americans, 45% of Hispanic-Americans and 24% of African-Americans
Complications of NAFLD
The complications of NAFLD are essentially the complications of NASH that has progressed to cirrhosis. They include:
The complications of NAFLD are essentially the complications of NASH that has progressed to cirrhosis. They include:
- Liver failure
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Liver cancer
Note: up to 10% of cirrhotic FLD patients develop hepatocellular carcinoma. The overall incidence of liver cancer in NAFLD has not yet been quantified, but the association is established.
NAFLD in children:
- The current epidemic of obesity begins in childhood. Therefore NAFLD is also found in children.
- Estimated prevalence among children 2-19 years of age is approximately 10%, the prevalence increases with the degree of obesity and there is progression to cirrhosis.
- There is not enough evidence of benefit of treatment and therefore no general recommendation has been made to screen the overweight and obese children for NAFLD.
- It is recommended that children with suspected NAFLD in whom diagnosis is not clear should have a liver biopsy
- Children should not be started on any drug treatment for NAFLD without a biopsy confirming the presence of NASH
- Loss of weight and regular exercise is recommended for children with NAFLD (no studies have been made to support recommendations in children)
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of FLD
For the first time, you might find that you have FLD during a routine check up. Your doctor might notice that your liver is a little larger than usual.
Your doctor may recommend the below said investigations to clinch the diagnosis that you have a FLD for sure:
- Blood Tests – a high number of certain liver enzymes could mean that you have a fatty liver
- Ultrasound – It demonstrates the picture and status of the liver using sound waves. The liver will show abnormal findings in Ultrasound.
- Biopsy – After marking the area, your doctor puts a needle through your skin and takes out a piece of liver. He may send it for microscopic examination to know if signs of fat, inflammation and damaged liver cells are be found.
Diagnosis of NAFLD:
Abnormal liver tests on blood testing (mild abnormalities and in few people)
Elevated liver biochemistry is found in 50% of patients with simple steatosis. The serum alanine transaminase level (ALT) usually is greater than the aspartate transaminase level (AST) in the non-alcoholic variant and the opposite in alcoholic FLD (AST:ALT more than 2:1)
Common methods are imaging studies:
- Ultrasonography
- Computerized Tomography (CT)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Note:
The above said when obtained for reasons other than diagnosing NAFLD accidentally might display FLD
NAFLD can be discovered when patients develop complications of the liver disease like cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer – due to the presence of NASH
Liver Biopsy
It is difficult to distinguish between IFL and NASH with imaging studies. Liver biopsy is the best means to differentiate between the presence of fat (IFL), or fat and inflammation (NASH)
Majority of individuals will have IFL, but it is important to identify patients with NASH because of the need to look for complications of liver disease. This also will help avoiding the progression of the disease and further damage to the liver. Patients with Metabolic syndrome, obesity and diabetes are good candidates to undergo biopsy of the liver because the incidence of NASH is higher among these groups.
As the scarring progresses to cirrhosis in NASH, the fat disappears. That is why it becomes to diagnose NASH as the cause of severe scarring or cirrhosis. The disappearance of fat in later conditions leads to cryptogenic cirrhosis (i.e. cirrhosis in which there is no clear cause). In cryptogenic cirrhosis, the common causes of cirrhosis – alcohol and viral hepatitis – are not involved. Half of cryptogenic cirrhosis occurs in patients with obesity and / or diabetes and probably is due to NASH
Ayurvedic aspect of FLD and treatment
It is very difficult to compare any particular condition explained in Ayurveda with FLD. In fact I have tried to get some extracts from different contexts so as to compile some approximate material which falls into the discussion area with FLD.
In Ayurveda, Yakrit is a name given to the Liver. Pleeha / Pliha is the name given to the Spleen. According to Ayurvedic science Yakrit and Pleeha are both inter-related organs which serve the same physiology and are related to the formation and maturation of blood. The roots of Raktavaha Srotas (channels which are related to the formation and carrying of matured blood) lie in Yakrit and Pliha.
Yakrit is said to be the place of origin or the centre of production and maintenance of Pitta. A subtype of Pitta called Ranjaka Pitta is said to be located in Yakrit vis-à-vis Liver and Pleeha vis-à-vis Spleen. Ranjaka means to colour. When the Rasa Dhatu (the first tissue formed in the gut in the form of essence of food, as a result of action of the Agni or digestive fire over the food – lymph / chyle) enters the Yakrit and Pleeha, it is subjected to action by Ranjaka Pitta i.e. Ranjaka Pitta acts on the Rasa Dhatu and imparts red colour to it and transforms it into Rakta Dhatu or blood tissue. Thus Yakrit and Ranjaka Pitta are responsible for the formation and maturation of Rakta.
In this context we shall discuss only about Yakrit as the Pitta sthana (seat of Pitta).
Kapha Pitta involvement in FLD
Cold environment in Hot Zone
Since Yakrit is a Pitta Sthana, it should be a seat of Agni or fire. Because according to Ayurvedic theory the fire is located in our body in the form of Pitta and there is no other Agni apart from Pitta. Thus the basic temperature of Yakrit is hot owing to the presence of Pitta, a form of fire. Yakrit controls many activities in our body including emotions and thought processing. As long as its area remains hot, its immunity and physiology is at its best. But when it loses its heat due to some reason and if cold prevails and dominates this hot zone of Yakrit, it slows or shuts down in terms of its functions. This forms a point of origin for many systemic diseases.
This Ranjaka Pitta when gets diminished in its quantity and quality along with its neighbouring Pachaka Pitta (sub type of Pitta located in the stomach and intestines), the whole Pitta zone or Zone of Fire gets weak, thus reducing their micro-fragments located in each and every cell and also influencing negatively on their other sub types. Thus the whole metabolism becomes sluggish, immunity of cells take a dip and leads to wide array of health issues, some stubborn and long standing ones too.
What do we mean by cold building in the hot zone?
As per Ayurveda theory all the 3 factors which rule and control our life, the Tridosha’s i.e. Vata, Pitta and Kapha are moving all through the body through blood media, being motivated and pushed by Vata.
Vata and Kapha are cold elements which balance and buffer the body and cellular heat. On the contrary they have the capacity to reduce the heat when they gain pathological increase and to empower the heat zone. Thus when the heat of Yakrit gets reduced by the predominant coldness of Kapha and Vata passing through Yakrit, the liver tends to slow down in its functions and get lazy. Vata being a self motivated entity doesn’t get stagnant at one place but it is Kapha which has a tendency to accumulate and get stagnant in areas and conditions favourable to it.
Every cell of our body is also an abode of Vata, Pitta and Kapha. If the Pitta located in the liver cells decrease it leads to favourable conditions for the kapha to get increased.
Other than Rakta (blood) and Asthi (bones) all other tissues of the body are predominant in Kapha bhava or cold factors (more fluidity). This includes Rasa dhatu (essence of food or primary nutrient), Mamsa dhatu (flesh), Meda dhatu (fat), Majja dhatu (marrow) and Shukra dhatu (semen). All these tissues (or nutrients or forming elements of these tissues – parinamamapadhyamaana dhaatu) in their micro-form are also passing through the Liver before entering into the circulation to nourish the tissue proper. When the liver fails to metabolize or process these Kapha predominant dhatus, mainly abaddha medas (unbound fat or free fat) they tend to accumulate in the liver (liver cells) and cause local blocks, further deteriorating the liver physiology.
Thus according to Ayurveda we can put forth a hypothesis that Fatty Liver occurs when there is excess concentration or accumulation of the below said (by reducing the heat in the liver):
- Kapha in circulation
- Local Kapha
- Kapha predominant dhatus especially the free medas (fat)
Thus FLD can be termed as a ‘Kaphavrita Pitta’ (Kapha blocking or enveloping Pitta, cloud around the sun or snow around fire condition) condition taking place in Liver. The concealed Pitta or fire within the envelope of Kapha also does some pathological damage in the form of causing inflammatory changes in the liver. The Vayu getting blocked by both Pitta and Kapha or aggravated due to the destructive process within the liver tends to destroy the liver cells and cause fibrosis and cirrhosis, though this part of pathology is expected to take place in a later context.
Note: Kapha accumulates due to its Guru (heavy), Snigdha (unctuous), Picchila (Slimy or sticky) etc nature
Kapha balancing measures
Avoid Kapha increasing foods and lifestyle activities in FLD
Kapha Prakopaka Hetu (Factors influencing pathological increase of Kapha) –
Among many causative factors leading to pathological increase of Kapha the below said also influence the progression of FLD:
- Divasvapna – Day sleep, sedentary lifestyle
- Avyayama – Absolutely doing no exercise or activities
- Alasya – Spending the day lazily, Procrastination
Excessive consumption of the food predominant in:
- Madhura – Sweet taste
- Amla – Sour taste
- Lavana – Salt
- Sheeta – Cold
- Snigdha – Oily or fatty
- Guru – Heavy to digest
- Picchila – Slimy or sticky
- Abhisyandi – Those which cause blocks in the body passages Ex. Curds etc
Good Exercise, Healthy and digestible and balanced food, Avoiding Sweet and Fat predominant foods are also recommended as lifestyle changes to be adapted in the treatment and management of FLD.
Thus we can infer that the Kapha increasing foods and activities can cause or trigger the progression of FLD and on the contrary avoiding or minimising them can help in the progression of the disease.
Treat Excess Kapha in FLD:
Food which are antagonistic to Kapha –
- Katu – Hot / Spice / Pungent taste
- Tikta – Bitter taste
- Kashaya – Astringent taste
- Ushna – Hot
- Ruksha – Dry
- Teekshna – Sharp, penetrating, intense
- Laghu – Light
- Anabhisyandi – Those which do not cause blocks in the body passages
Activities antagonistic to Kapha –
- Vyayama – Exercise
- Vyavaya – Sexual activities
- Jagarana – Vigil or keeping awake at night
- Dhavana – Running
- Plavana – Leaping
- Langhana – Jumping / Jolting
- Niyuddha – Wrestling
- Unmardana – Rubbing and thumping the body
- Snana – Hot bath
- Parisarana – Walking, Brisk Walking
- Ushna Vasa – Staying in warm places
- Sukha pratisheda – Abstinence from comforts
Therapeutic:
- Vamana – Therapeutic Emesis
- Teekshna Ushna Samshodhana – Intense, vigorous cleansing of the body by administering Vamana (therapeutic emesis) and Virechana (therapeutic purgation)
- Utsadana – Application of Kapha reducing pastes on the body and rubbing them
- Dhoomapana – Smoking (with kapha alleviating drugs)
- Upavasa – Fasting
- Pipasa – withholding the urge of thirst (not drinking too much water)
- Atapa – exposure to sun
- Pachana – Medicines which have Katu, Tikta rasa, hot and intense in action to improve digestion and to digest the ama (metabolites) and get rid of excessive fluid / moisture / toxins from the cells
- Udwartana – Massaging with medicated powders and pastes in the reverse direction of the hairs
Note: Also avoid the Kapha prakopaka hetu’s mentioned above
Meda balancing measures
Meda (Fat) Link in ALD
Medo-vriddhikara hetu: Foods and activities which increase fat
Other cause for the manifestation of ALD might be the excessive consumption of foods and activities which tend to increase fat in the body and also reduce the capacity of the liver to process and digest Fat.
But in the above said context we have found that Meda or fat is a Kapha element (rich in kapha). Therefore the same causes which bring about a pathological increase in Kapha also will increase Meda in the body. In the Medo-roga context (chapter dealing with fat related disorders and treatment – Ref- Yoga Ratnakara, Medoroga Nidanam) among many causes, Shleshmanahara Sevanam (consumption of Kapha increasing food and activities) is one chief cause which is said to cause a disturbance in fat metabolism leading to fat related disorders.
Thus the same treatment, food and lifestyle changes which are advised in tackling excess Kapha and Kapha related diseases also hold good in tackling excess Meda and Meda related diseases including ALD.
Other avoidable foods (avoid excessive usage):
- Masha – Black grams, Godhuma – Wheat
- Tila pishta vikruti – Preparations and dishes made up of paste of sesamum
- Dadhi – Curds, Dugdha – Milk
- Payasa – Sweet dish prepared on milk base
- Ikshu Vikara – Derivatives of Sugarcane like sugar, jaggery etc
- Anupa Mamsa – Flesh of animals living in
- marshy land
- Audaka Mamsa – Flesh of aquatic animals etc.
Treat Excess Meda:
The same measures which have been mentioned above in treating excess Kapha shall be adapted in treating Excess Meda too.
Care should be taken while following Upavasa (fasting) in Sthoulya or Medo Roga (metabolic fat disorders including obesity and excessive weight) and should be done with the consent and in the observance of the doctor.
स्थूले स्युर्दुस्तरा रोगा विसर्पाः सभगन्दराः।
ज्वरातिसारमेहार्शःश्लीपदापचे अकामलाः॥{यो.र.मेदोरोग}
sthūle syurdustarā rogā visarpāḥ sabhagandarāḥ|
jvarātisāramehārśaḥślīpadāpace akāmalāḥ||{yo.ra.medoroga}
Kamala (jaundice) is one among the complications of Medo Roga. Kamala is a disease which takes its origin from the liver and often due to negligence or improper treatment of PanduRoga (Anaemia). This points towards the relationship between liver and fat (fat metabolism and fat related diseases) as proved by Ayurvedic literature.
Treat Excess Meda and Medo Roga (Sthoulya) in FLD
The treatment principles and medicines explained in the context of MedoRoga should be tried in FLD. They are highly effective. The below mentioned are the treatment and medicines of MedoRoga:
Preferred treatments in Medo Roga:
- Udwarthana – Medicated powder, pastes are used to massage in the reverse direction of the hairs
- Vamana – Therapeutic emesis
- Virechana – Therapeutic Purgation
- Vasti (Teekshna Kashaya Vasti) – Strong enemas with decoctions which reduce fat should be given
- Lekhana Vasti – Enemas prepared with drugs having a capacity to scrap the excess fat accumulated in the body
- Shiro Dhara – streamed pouring of medicated oils, buttermilk or milk for a scheduled period on head / body / head and body
Classical and home remedies for Medo Roga:
- Triphala Kashaya with Honey
- Boiled and cooled water mixed with honey
- Hot gruel of rice taken regularly
- Guduchi Churna (powder of Tinospora cordifolia) + Musta Churna (Powder of Cyperus rotundus)
- Triphala churna
- Takrarishta (fermented medicated buttermilk)
Good foods in Medo Roga:
- Purana Shali – Old rice
- Mudga – Green grams
- Kulattha – Horse gram
- Yava – Barley
- Kaphahara Ahara – All food and diet which can reduce Kapha
Read more about Ayurvedic treatment for obesity
Pandu and Kamala link in FLD
Adapt treatment of Pandu Roga and Kamala:
Already we have seen the relationship between Liver, Fat related disorders, Anaemia and Jaundice as established by Ayurveda literature. The medicines and treatment concepts which have been explained in the context of Pandu Roga Chikitsa (Treatment of Anaemia) and Kamala Roga Chikitsa (Jaundice treatment) shall be adapted in treating FLD.
Madhya (excess alcohol) and Divaswapna (Excessive sleeping during day which denotes sedentary activities, lack of exercises etc) are the important ones among the causative factors mentioned for Pandu Roga. This also proves the link between alcohol consumption and liver disorders as explained by Ayurveda texts. The same are the causative or aggravating factors of ALD.
Read related: Ayurvedic treatment for liver diseases – Pandu and Kamala
Good foods for Liver:
Yava – Barley
Godhuma – Wheat (in limited quantities)
Jangala Mamsa Rasa – Flesh or meat soup of animals living in dry lands
Mudga – Green Gram
Aadhaki – Cajanus cajan (Pigeon pea)
Masura – Red lentils
Things to be avoided:
Vahnim-aatapam – Exposure to fire, sun,
Ayasa – Excessive / strenuous exercises or activities
Pittalam – Food and activities which increase Pitta
Maithunam – Excessive indulgence in sex
Krodha – Anger and extremes of emotions
Adhwagamanam – Excessive walking
Best medicines for Pandu and Kamala :
Guluchyadi Kashayam
Drakshadi Kashayam
Ardhavilwam Kashayam
Lodhrasavam
Drakshasavam
Draksharishtam
Shotari Mandura
Madhu mandura
Yakritpleehari Lauha
Navayasa Lauham
Svarnamakshika bhasma etc.
Other classical medicines and home remedies for Pandu-Kamala
- Loha Bhasma (ash of iron) – with honey and ghee
- Shunti churna (ginger powder) with Loha Bhasma
- Loha bhasma with Gomutra (urine of cow)
- Powders of Ela (cardamom), Jeeraka (cumin seeds), Bhumyamalaki (Phyllanthus niruri) and Sita (sugar) – taken in equal quantities and mixed with ghee should be taken early in the morning
- Haridra churnam (turmeric powder) with curds early in the morning
Herbs beneficial for Liver:
Bhumyamalaki – Phyllanthus niruri
Amalaki – Emblica officinalis
Sharapunka – Tephrosia purpurea
Katuki – Picrorrhiza kurroa
Punarnava – Boerhavia diffusa
Kakamachi – Solanum nigrumhttps://www.easyayurveda.com/2012/12/08/licorice-benefits-medicinal-qualities-complete-ayurveda-details/
Kalamegha – Andrographis paniculata
Loha – Iron
Kumari – Aloe vera
Guduchi – Tinospora cordifolia
Yashtimadhu Licorice– Glycyrrhiza glabra
Haridra – Curcuma longa
Bhringaraja – Eclipta alba
Vasa – Adhatoda vasica
Kiratatikta – Swertia chirayata
Daruharidra – Berberis aristata etc
Yakrutodara and Plihodara link in FLD
Yakrutodara / Pleehodara:
Udara Roga’s are a set of disorders explained in Ayurvedic Texts wherein different abdominal disorders have been dealt with along with their treatment.
The main symptom (sign) of Udara Roga is the protuberance or enlarged abdomen (belly). They are of 8 types. Yakrutodara / Yakruddalyudara (enlargement of liver) and Pleehodara (enlargement of spleen) are 2 among those 8 types.
Atisanchita Dosha (excess accumulation of dosha’s or contaminants) is said to be one of the chief causes that gives origin to all the types of Udara Roga. In FLD, Atisanchita Dosha can be taken as excessive accumulation of Kapha and Abaddha Medas in Liver. Likewise excessive consumption of Abhishyandi (food causing blocks in the body’s transport system) and Vidahi (foods which cause excessive burning leading to pathological increase of Pitta) food is said to be the chief causative factors in Yakrutodara and Pleehodara. These foods are said to aggravate Kapha and Rakta and cause Yakrutodara and Pleehodara. Both these types of Udara will present signs and symptoms of Kapha (steatosis) and Pitta (Hepatitis). We have already discussed ALD as a condition called Kaphavrita Pitta (Kapha obstructing Pitta) taking place in the Liver. Abhishyandi foods are known to increase Kapha and Kapha group of tissues especially Fat leading to their accumulation in the Liver and consequentially causing Liver Disorders, FLD in this case.
Adapting Yakrutodara and Pleehodara treatments in ALD:
Treatments preferred in Yakrutodara and Pleehodara:
- Vamana – Therapeutic Emesis
- Virechana – Therapeutic Purgation
- Raktamokshana – Blood-letting from the veins of the forearm
Medicines preferred in Yakrrutodara and Pleehodara:
The same medicines explained in the treatment of Pandu Roga and / or Kamala shall be used in these 2 conditions.
Other medicines:
- Dashamoolapanchakoladi Kashayam
- Vizhalveradi Kashayam
- Dantiharitaki Leham
- Dashamulaharitaki Leham
Other classic preparations and home remedies for Enlargement of Liver and Spleen:
Shalmali Pushpa Kwatha:
- Decoction prepared by steam heating the flowers of Shalmali (Bombax malabaricum) tree is given after mixing it with mustard powder
Sharapunkhamula Kalka:
- Paste of the roots of Sharapunkha (Tephrosia purpurea) mixed in buttermilk
Yavanyadi Churna:
The powder of the below said is given with hot water or curd water:
- Yavani – Trachyspermum ammi
- Chitrakamula – Roots of Plumbago zeylanica
- Yavakshara – Alkali of Hordeum vulgare plant
- Pippalimula – Root of Piper longum
- Pippali – Piper longum
- Dantimula – Root of Baliospermum montanum
Sindhwadi Churnam:
Powder of:
- Saindhava Lavana – Rock Salt
- Chitrakamula – Root of Plumbago zeylanica
- Shigrumula – Root of Moringa oleifera
- Pippali – Piper longum
- Jeeraka – Cumin seeds – Cuminum cyminum
Shobhanjanadi Yoga:
Shigru Kwatha (Decoction of Moringa oleifera bark) should be taken mixed with Saindhava Lavana (powdered rock salt), Chitrakamula Churna (Powder of roots of Plumbago zeylanica) and Pippali churna (Piper longum powder). To this the Kshara (alkalies) of Palasha (Butea monosperma) or Yava (Hordeum vulgare plant) should be added and mixed.
Lashunadi Yoga:
The powder of Lashuna (Alium sativum, Garlic), Pippalimula (Root of Piper longum) and Haritaki (Terminalia chebula) should be consumed. Later gargling should be done with Gomutra (Cow’s urine).
Shigru Kwatha:
Shigru kwatha (Decoction of Moringa oleifera, Drumstick) should be taken mixed with powders of Pippali (Piper longum), Maricha (Piper nigrum), Saindhava Lavana (Rock salt) and Amlavetasa (Garcinia pedunculata)
FLD and Prameha
We know that Obesity and Diabetes predispose to the formation of fatty liver.
Read related: Home remedies and Ayurvedic treatment for diabetes
The below mentioned are the causative factors of Prameha vis-à-vis Diabetes Mellitus:
- Asyasukham – Comfortable seating (luxury, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activities and exercise)
- Swapnasukham – comforts of sleeping
- Dadheeni – Excessive consumption of Curds and its preparations
- Gramya-oudaka-anupa mamsa – flesh or meat soup of animals living in water and marshy regions
- Payamsi – Excessive consumption of milk, its derivatives and preparations
- Navaannapanam – Food, drinks and dishes prepared from freshly harvested grains etc
- Guda vaikruti – Jaggery, its derivatives and dishes made out of it
- Kapha krut cha sarvam – All foods and lifestyle activities which increase Kapha
Most of these causes match with the causative factors leading to FLD. We have seen that FLD is caused by excessive Kapha elements and Medas accumulating in the Liver.
We have also learnt that the Kapha aggravating factors can cause or trigger the progression of FLD because the same causes increase Meda (fat) too. Thus the causative factors of Kapha and Medas are the same. By cutting off on the Kapha increasing diet and lifestyle activities we can reverse FLD and obesity.
Even the Prameha (Diabetes) is said to be caused by the same causes that increase Kapha. Thus Ayurveda has proved the link between the causes of Diabetes, Obesity and FLD. The causative, aggravating and relieving link to all these diseases is the same Kapha.
Having a common aetiology means to tell that all these diseases share a common platform and is linked by the same pathological process. This also means to tell that the above said diseases can predispose to the formation of the other disease. Thus through common aetiology, Prameha can predispose to the formation of FLD just like the MedoRoga does. When Prameha and Medoroga are kept under control by giving good treatment and medicines, FLD can be checked and reversed. The modern view also tells the same.
The pathogenesis of Prameha is explained as below said:
‘When the Meda (fat), Mamsa (flesh), Shareera kleda (Fluids of the body) and Kapha on entering the Basti (Urinary apparatus) causes Prameha’
Here too we see the involvement of fat, kapha and body fluids causing Prameha just as they had caused blocks in the Liver and caused FLD.
Fat and Kapha are thus linked both in the pathogenesis of FLD and Diabetes.
Meda is mentioned in the Dushya Varga (one of the tissue to get contaminated in the pathogenesis of Prameha) of Prameha and Kapha in the Dosha Varga (contaminants). Acharya Charaka has mentioned that Abaddha Medas (free fat) causes Prameha.
Medovaha sroto dushti:
…मेदःसंश्रयांस्तु प्रचक्ष्महे।
निन्दितानि प्रमेहाणां पूर्वरूपाणि यानि च॥{च.सू.स्था.२८/१५}
…medaḥsaṃśrayāṃstu pracakṣmahe|
ninditāni pramehāṇāṃ pūrvarūpāṇi yāni ca||{ca.sū.sthā.28/15}
When the cells and channels related to the formation and maintenance of Fat (structures and factors controlling fat metabolism) get contaminated it leads to the manifestation of Ashtanindita’s and Prodromal (premonitory) symptoms of Prameha.
Ashtanindita means 8 categories of body frame which are said to be socially unfit. Atisthoulya (Obesity) is one among the Ashtanindita’s.
Here Ayurveda establishes a link between Obesity, Diabetes and Disturbance of Fat deposition (resulting in conditions like FLD).
When the channels related to fat metabolism are contaminated, Sthoulya and premonitory symptoms of Prameha are formed. Sthoulya and Prameha further contaminate Medas and predispose for its accumulation in the liver forming FLD.
The patient of Prameha is also classified as:
- Sthula Pramehi (obese patient)
- Krusha Pramehi (thin patient)
This also shows that Sthoulya and Prameha are interrelated diseases.
Since Prameha, Sthoulya and Medas are inter-related we shall try to implement Prameha Chikitsa too in FLD.
Treat Prameha in FLD:
Prameha Chikitsa –
Beneficial Treatments in Prameha:
Depending on the type and condition of Prameha and considering its Dosha-Dushya dushti (pathogenesis and pathological elements) and strength of the patient the below said Shodhana procedures can be skilfully adapted under strict supervision of a qualified Ayurvedic doctor.
- Vamana – Therapeutic Emesis
- Virechana – Therapeutic Purgation
- Vasti – Enema treatment
Brumhana Therapy (Bulk promoting treatment) is a treatment of choice in the patient of Prameha who is thin and debilitated. On the other hand Samshodhana is a treatment of choice in the patient of Prameha who is obese and strong.
Best Medicines for Prameha:
Nishakathakadi Kashayam
Ayaskriti
Chandraprabha vati
Vasantakusumakar ras
Amalaki rasayanam etc.
Other classical and home remedies:
Triphaladi kwatha:
Decoction prepared from equal quantity of
- Triphala (Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellirica, Emblica officinalis)
- Devadaru – Cedrus deodara
- Daruharidra – Berberis aristata
- Musta – Cyperus rotundus
It should be taken mixed with honey
Guduchi Kwatha:Decoction or juice of Tinospora cordifolia mixed with honey
Nisha kalka: Paste of Nisha (Curcuma longa) mixed with juice of Amalaki (Emblica officinalis)
Kataka beeja: Powder of Strychnos potatorum should be taken mixed in buttermilk and honey
Nisha-triphala Yoga: The powders of the below said should be kept in water over night and should be strained through a sterile cloth or sieve in the morning. It should be consumed mixed with honey.
- Nisha – Curcuma longa
- Daruharidra – Berberis aristata
- Haritaki – Terminalia chebula
- Bibhitaki – Terminalia bellirica
- Amalaki – Emblica officinalis
Other simple and effective remedies:
- Triphala Churna with honey
- Shilajit with honey
- Haritaki (Terminalia chebula) Churna with honey
- Loha Bhasma (ash of iron) with honey
- Vanga bhasma with Amrita satwa and honey
- Abhraka bhasma with Triphala churna and honey
Useful drugs in Prameha:
- Haridra – Curcuma longa
- Daruharidra – Berberis aristata
- Amalaki – Emblica officinalis
- Haritaki – Terminalia chebula
- Kataka – Strychnos potatorum
- Guduchi – Tinospora cordifolia
- Lashuna / Rasona – Allium sativum
- Jambu – Eugenia jambolana
- Karavella- Momordia charantia (Bitter melon or bitter gourd)
- Tulasi – Ocimum sanctum
- Bhumyamalaki – Phyllanthus niruri
- Beejaka / Vijayasar – Pterocarpus marsupium / Indian Kino
- Methika – Trigonella foenum-graecum (fenugreek)
- Nimba – Azadirachta indica (neem)
- Meshashringi – Gymnema sylvestre
- Ashwagandha – Withania somnifera etc
Good foods in Diabetes:
- Shyamaka – Setaria italic
- Kodrava – Echinochloa frumentacea
- Godhuma – wheat
- Chanaka – Cicer arietinum
- Aadhaki – Cajanus cajan (Pigeon pea, Red gram)
- Mudga – green gram
- Kulattha – horse gram
- Tikta shaka – Vegetables which are bitter in taste
- Patola – Pointed gourd
- Jangala rasa – Flesh / meat of animals living in dry lands
- Saindhava lavana – rock salt
- Maricha – Black pepper
The drugs until Kulattha also destroy excess fat in the body and thus beneficial in FLD
To sum up:
Fatty Liver Disease (FLD) is not just a disease entity. It is a syndrome by itself because it is related to many systemic, hormonal and lifestyle diseases like Obesity, Diabetes, Metabolic syndrome etc. it is not enough to treat the Liver. In fact dealing with the diseases at the backdrop of FLD will also help in the later.
While dealing FLD via Ayurveda too we need to remember the same rules and regulations of treatment, diet, lifestyle and medicinal protocol. Ayurveda would have possibly been the first medical science to establish a relationship between disturbed fat metabolism, liver disorders, diabetes and obesity.
FLD treatment in Ayurveda involves:
- Treating morbid Kapha and Pitta
- Treating on the lines of Medo Roga and Sthoulya
- Treating on the lines of Pandu Roga and Kamala Roga
- Treating on the lines of Yakrutodara and Pleehodara
- Treating on the lines of Prameha
Allopathic treatment of FLD
There is no specific treatment for FLD
- Manage Diabetes: You can improve your condition by managing your sugar levels (if you have it)
- Quit Alcohol: If you have ALD and if you are a heavy drinker the most important thing you can do to help yourself is to quit alcohol. You can get a counselling about de-addiction from your doctor or counsellor. If you do not stop taking alcohol you can land up with severe complications like alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis of liver.
It is best to avoid drinking even if you are diagnosed with NAFLD
Alcohol: There is no evidence of harmful effects of light alcohol consumption (2 or fewer drinks per day for men, one or fewer for women) on NAFLD though there is also no evidence that it is safe. Larger amounts of alcohol consumption should be avoided by everyone, including individuals with NAFLD
Alcoholism produces toxic metabolites like aldehydes during metabolism of alcohol in the liver
Work on your weight and Regular Exercises: If you are overweight or obese, you have to do everything possible to lose that extra bit of you. Take care that you don’t work on a drastic weight loss programme which can harm your health further. Don’t lose more than 1 or 2 pounds in a week. It is better to lose weight or plan on it in consultation and under observance of a qualified doctor.
Weight loss and Exercise is among the most promising of treatments for NAFLD. A less than 10% decrease in weight may be enough to bring good changes in conditions of Fatty Liver. Vigorous exercise results in a reduction of liver fat and also may reduce the inflammation of NASH.
The long-term effects of weight loss and exercise on the important development of cirrhosis and its complications are unknown. Still it should be considered as the best approach towards ALD.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced and healthy diet. Limit extra-carbs from the food schedule such as bread, grits, rice, potatoes and corn. Cut down on consuming sugar-rich drinks like sports drinks and juices.
- Supplements (antioxidants)
- Surgery
- Liver transplantation
Medicines for ALD:
Insulin Sensitizers:
Metformin – Increases the insulin sensitivity of cells and counteracts insulin resistance accompanying NAFLD, but no clear improvement in the status of liver injury associated with NASH has been found
Pioglitazone and Rosiglitazone – These too increase insulin sensitivity and are found to reduce liver fat and signs of liver injury. Pioglitazone on the other hand might reduce scarring that result from inflammation in NASH. Weight gain and increased heart attacks may be the known complications of these drugs.
- Antioxidants:
Vitamin E: Vitamin E has shown to reduce liver fat, inflammation and possible fibrosis. Its long-term effectiveness and safety have not been studied. Thus it can be used in selective patients of NASH.
- Pentoxifylline – found to be effective in NASH according to some studies. Its effectiveness and safety has not been established.
- Omega-3-fatty acids
Some studies have shown omega-3-fatty acids to reduce liver fat in NAFLD. It has shown to reduce cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and overall mortality. Therefore it is appropriate for patients with NAFLD AND Metabolic syndrome because these patients have a high incidence of CVD and death
- Lipid lowering drugs:
Lipid lowering drugs like statins and ezetimibe are used to treat abnormal blood lipids associated with metabolic syndrome. They have beneficial effects on liver in NAFLD but there is no enough experience to recommend them in patients with NAFLD unless they are primarily being used for treating abnormal lipids in blood.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid:
This drug has been studied in NAFLD but has been abandoned due to its ineffectiveness and concerns about toxicity at very high doses.
Diet for Fatty Liver:
Fats and Sugar: NAFLD is associated with reduced amounts of unsaturated fats (diet high in saturated fats) and increased amounts of fructose (commonly added to the diet as high-fructose corn syrup)
Thus the diet including the below said should be given to patients of NAFLD:
- Increased unsaturated fat (diet lower in saturated fat and higher in unsaturated fat) and
- Reduced high fructose corn syrup
Note: Benefits of this diet has not been demonstrated in NAFLD but there may be benefits of these dietary modifications unrelated to liver
Coffee: Less scarring is seen in the livers of NASH patients who drink more than 2 cups of coffee per day
Vitamin D – Vitamin D deficiency is associated with NAFLD. It is good to measure vitamin D levels in patients with NAFLD and treat them with Vitamin D if they are deficient
Bariatric surgery:
It is the surgery of the gastrointestinal tract that results in loss of weight. Obesity is believed to be an important factor in causation of NAFLD. Loss of weight has been shown to have beneficial effects on NAFLD. Therefore Bariatric surgery is a potential treatment for NAFLD.
Liver transplantation:
When the liver becomes cirrhotic and when complications have developed we need to resort to:
- Treating the complications as and when they arise
- Replace the diseased liver with a transplanted liver
NASH has become the 3rd most common cause (the other 2 being alcoholic liver disease and hepatitis C) of transplanting livers. It is expected to climb to the number one position due to the epidemic of obesity and diabetes that is occurring (especially in US).
Unfortunately NASH recurs frequently in transplanted liver and then progress to cirrhosis because the underlying causes – ‘obesity and diabetes’ continue.
Differential Diagnosis of NAFLD
Wilson’s disease
Inherited disorder of biliary excretion of copper metabolism
Results in copper accumulation in specific tissues
Presents with
- Liver disease
- Very mild elevated liver enzymes
- Minimal damage in the liver to acute liver failure or cirrhosis
Histological findings: Mild steatosis, Glycogenated nuclei, Lobular inflammation
Medication induced Steatosis:
Excessive use of Steroids, Pshychotropic medication, Psychiatric medication
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV):
Some children with HCV will have elevated ALT levels although 1/3 can have normal levels and another 1/3 will have fluctuating numbers
Presents with
Insulin resistance
Liver steatosis
Prevalence of steatosis can be 40-80% in all patients
Patients with suspected fatty liver should be tested for HCV using Hepatitis C antibody
Cholesterol Ester Storage Disease (Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency):
CESD is a rare genetic disease caused by deficiency in lysosomal acid lipase.
This leads to accumulation of cholesterol esters (CE) and Triglycerides (TG) in the lysosomes of liver cells
CESD presents with 2 phenotypes:
- More severe neonatal presentation Wolfman’s disease
- Milder variant that may present later in the life
Clinically Wolman’s disease presents with:
- Vomiting, Diarrhoea, Anaemia, Failure to thrive, Hepato-splenomegaly, Adrenal calcification
Milder forms of LAL deficiency can present in childhood or adolescence with a clinical scenario that is very similar to NAFLD namely
- Hepatomegaly,
- Elevated Serum liver enzymes
- Low HDL
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Fatty liver on ultrasound
Diagnosis of LAL deficiency is made through either decreased LAL activity in cultured fibroblasts or in dried blood spots
A suspicion of LAL deficiency is when low HDL is present in the setting of hepatomegaly and fatty liver.
Type 1 Diabetes and Fatty Liver:
- Maurice et al in 1946 described uncontrolled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) leading to growth failure, short stature and hepatic steatosis
- The prevalence of steatosis in T1DM patients by ultrasound is 44%
- This hepatic steatosis is easily reversible with improved and tighter control of diabetes
- Diagnosis of T1DM associated hepatic steatosis can be made on the basis of a liver biopsy though an ultrasound showing increased liver echogenicity which proves the presence of FLD
- If the person is not overweight or only slightly overweight and the T1DM diagnosis is well established this condition should be considered
Mitochondrial Dysfunction Disorders:
- There is a consistent pattern of hepatic steatosis when mitochondrial function is compromised.
- These include disorders of fatty acid oxidation resulting in macro-vesicular steatosis especially if the biopsy is after a period of significant fasting
- The different long-chain fatty acid oxidation defects present with multi-organ involvement including but bit limited to heart, liver and skeletal muscles.
- Congenital mitochondrial hepatopathies on the other hand have more micro-vesicular hepatic steatosis and portal fibrosis such as seen in a patient with Alper’s syndrome
- These disorders may be confused with NAFLD, especially in recessive carriers for mutations in nuclear genes such as POLG, DGUOK and MPV17 or mitochondrial DNA depletion.
- These are usually affecting multiple-systems including neurological and musculoskeletal systems not the case in simple NAFLD
Studies:
- Too much bacteria in your small intestine and other changes in the intestine may be linked to NAFLD
- Bariatric surgery decreased fat and inflammation and halts progression of mild fibrosis to more severe fibrosis in NAFLD
- Gut bacteria may increase the risk of metabolic syndrome. NAFLD is a manifestation of metabolic syndrome. Thus gut bacteria also is a risk factor for NAFLD. Researchers have found a link between unchecked bacterial fermentation, short chain fatty acids and increased liver lipids can cause NAFLD leading to liver damage.
Read related – Gut bacteria may increase risk of metabolic syndrome
- In children, reducing sugar intake reverses chronic metabolic diseases even without reducing calories or reducing weight. It also helps in NAFLD.
Read related – Reducing sugar intake reverses chronic metabolic diseases in children
- Prolonged sitting time and reduced physical activity contributes to NAFLD
Read related – Prolonged sitting time, reduced physical activity contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- NOX1 and NOX4 (proteins) have been found as core mediators for liver fibrosis which is a scarring process underlying chronic liver disease. NAFLD is one of the conditions leading to liver fibrosis.
Read related – Researchers demonstrate direct connection between NOX proteins and liver fibrosis
Fatty Liver Disease (Hepatic Steatosis)
Fatty Liver (Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver) Symptoms, Causes, and Complications
Fatty liver disease
You have the best remedies in the form of treatments and medicines to relieve your fat and fatty liver in Ayurveda. Simultaneously you will enjoy the luxury of having got rid of your obesity and diabetes. But don’t forget to consult an Expert Ayurveda Doctor for an opinion before starting on with anything.








21 comments
tanishqa
Thank you, Dr which is the best honey i can buy , genuine and safe, or organic can you help please
Shishir Gupta
One of the major reasons of increasing fat is the improper diet. It results to weight gaining and severe health problems. More amount of fast foods and junk food you consume, more calories and fats are produced in the body. Therefore, it is important to quit the habit of eating such food if you really want to to get rid of those fats and reduce weight.
raju
sir for morbid obese(bmi>35) people with fatty liver generally docs prescribe medohar vidangadi lauh which contains iron, is it safe to consume it 1 tab 2 times a day
Nitesh
Sir, fatty liver also happens in the bodies of underweight people.
No explaination on that?
Nagesh
Good morning sir
Which one medicine or homeremedies is cure to fatty liver without operation
Paulo Ramos
Dear Dr. In case of Bladder fat or stones the same ptotocol for the liver above should be applied? Thank you
Chandresh
Sir, here is very effective treatment for all kind of Liver problem. Liver cleanse by naturopathic treatment. Can refer very popular treatment of Dr.phius saxena Mumbai. Cure yourself
Chandresh
Liver and gallbladder cleansing
It’s very simple….
U need approximately 2 days..
Start
Breakfast and lunch very light or
go on fruits preferably apples.
Buy
Epsom salt 20 grams..
4 packets
250 ml extra Virgin olive oil
1.5kg oranges
day1:
At 6pm
One dose of Epsom salt with 200 ml of water
8pm repeat 2nd dose of Epsom salt
At 10 pm
175 ml Virgin olive oil
plus 175 ml orange juice
Mixer in mixe just 3-4 second and drink.
Sleep on right side for 30 min
And sleep off
Day 2:
6 am
3rd dose of Epsom salt
8 am
75 ml of olive oil and 75 ml of orange juice drink
10 am4th dose of Epsom salt
Program over.
You can start your regular diet from 11 am with light food.
…………………
Effects
Day 1
Flush out motion will start at 7 pm…
Around 4 – 6 times till… 10 pm
All ur intestinal stools will be out.
Day 2:
Start from 6am ur motion will flush out liver gallbladder toxins also stones.
It will be four to five times
Anil
Hello Chandresh, Is 175ml of olive oil really needed for day1? It is like 10 tablespoons (not tea spoons) right?
– Thanks
tugga82
Hello,
In one paragraph you mention avoid wheat and at another instance you say wheat is very good for liver. What should I take?
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Hi, Sorry for the confusion. wheat in limited quantities, 2 – 3 times a week is fine to take.
Muhamed Avod
Hello Dr.
I was diagnosis with Fatty liver and my weight is 93 Kg. in you article you mentioned that Diltiazem also cause fatty liver. I am using Dilzem 90 mg since many years as I am having HOCM.
Malavika
Hello. Please could you tell me if Obstructive Sleep Apnea can be cured with Ayurvedic medicine? Thanks.
Samuel
Thank you Sir.
Samuel
Regarding the Giloy Kashala decoction.
Would this product be helping as well ( and as much ) ?
https://ch.iherb.com/pr/Himalaya-Herbal-Healthcare-Guduchi-60-Caplets/3720
Nirav patel
Hello sir, I am niravpatel pg scholar from rachana sharir department. Sir I want to know why there is a controversy on weither sira is vein or dhamani as we do only vinous puncture in term of sira vedhana?
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Hi, Sira is considered as vein, in general. There is no controversy in that.
Julie
Is there any treatment in Ayurveda for liver cirrhosis grade 3
Sajal Puri
Hello, I have heard Kutki is also good for fatty liver. I have kutki roots. How do we convert it to Powder – Do we simply grind these or we need to do (Soak etc) before grinding. What is the best way to have this for fatty liver pls?
Jaideep
The reason I’m confused is in one of the home remedies you mentioned to take long pepper with honey. Although it pacifies kapha but wouldn’t it aggravate pitta the process?
So I’m confused whether it’s a kapha disease or a pitta-kapha diseaes.
Because if it’s just kapha disease then I need to take pungent, bitter and astringent herbs whereas in the case of pitta-kaphah only possibilities are bitter and astringent.
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Pippali is very specific to improve liver functions. The Pitta aggravation, if at all happens, can be countered by taking milk.