Hypertension Causes, Types, Symptoms, Ayurvedic Treatment
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu).
High blood pressure is the increased pressure of the flowing blood on the walls of the blood pipes. As per Ayurveda, it can be caused due to increase of Vata and Pitta Dosha in Ayurveda.

Table of Contents
Prevention tips
Ayurvedic health tips for hypertension:
Practice Pranayama at least for 2 -3 minutes in a day. Learn a simple pranayama
Quit alcohol and smoking.
Wake up before six, sleep at around 11 pm. Learn why?
Undergo Abhyanga – oil massage at least once a week. It keeps stresses and tensions at bay. Read more – Does massage work?
Avoid white sugar.
Go full vegetarian: If you are into excess of non vegetarian food, consider going fully vegetarian. It is scientifically proven that a vegetarian diet cuts high blood pressure. Research
Have more of – Vegetables, fruits, whole grains and low-fat dairy foods, including meat, fish, poultry, nuts and beans.
Celery, carrot, garlic, flaxseed, flaxseed oil, Tulsi tea, green tea, ginger cardamom tea, orange juice, non fat yogurt, tender coconut water, water melon, wheat bran, black plum, ginger, pomegranate, drumstick (moringa), banana, almond, walnut, olive oil.
Have less sugar-sweetened foods and beverages, red meat and added fats.
Beneficial foods
The below said are beneficial in hypertension (Good foods):
- Studies have shown that Fish oil / omega-3 fatty acids, Hibiscus tea, Dark Chocolate (Cocoa, chocolate) reduce blood pressure
- Green Coffee extract – Raw coffee beans from Coffee fruits which have not been roasted is called Green Coffee. Chlorogenic acid and Ferulic acid present in Green Coffee extract is said to reduce Blood Pressure.
- Caffeine is said to increase blood pressure especially in those who are already having High Blood Pressure, therefore its use should be limited. Green Tea or Green tea extracts are found to reduce blood pressure. EGCG present in a compound in green tea is said to reduce diastolic blood pressure.
- Magnesium is also found to reduce blood pressure though in small proportions
- Vitamin D – This is naturally found in Sunlight, Fish, Eggs, Fortified Milk, Cod liver oil etc may help in reducing blood pressure. BP is often elevated when there is reduced exposure to sunlight / Vitamin D (during winter, greater distances from equator and dark skin pigmentation.
- Bananas in plenty – High salt or sodium can raise blood pressure. Potassium on the other hand counters sodium’s ill effects. People with hypertension can benefit from intake or supplementing Potassium. Good sources of Potassium are Bananas, a baked potato with skin, orange juice and non-fat or low-fat yoghurt
- Coconut Water has good quantities of Potassium and Magnesium and is found to be beneficial for those suffering from hypertension. It reduces the systolic pressure and also supports the functioning of cardiac muscles
- Eating Watermelon or drinking melon juice will be handy for those suffering from Hypertension. Citrulline, an amino acid present in Watermelon lowers vascular resistance and hence lowers BP. It should be consumed early in the morning
- Ginger-Cardamom tea is said to be beneficial for those having Hypertension
Exercise options:
Brisk walking for at least 30 minutes a day.
Moderate intensity dynamic aerobic exercise like walking, jogging, cycling or swimming
Isometric resistance exercise, aerobic exercise, resistance exercise and device guided breathing.
DASH diet
DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) Diet:
- This is a dietary pattern prompted by the U.S. based National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute to prevent and control hypertension.
- The DASH diet is rich in – vegetables, fruits, whole grains and low-fat dairy foods, including meat, fish, poultry, nuts and beans. This diet recommends to decrease the amounts of sugar-sweetened foods and beverages, red meat and added fats.
- It is designed to be a well-balanced approach to eating for the general public in addition to its effect on blood pressure. Reference
Effective physical exercises – Isometric resistance exercise, aerobic exercise, resistance exercise and device guided breathing
Stress reduction techniques – Biofeedback or transcendental meditation
Preventive measures
Preventive Measures:
Population strategies, awareness about this global epidemic and preventive counselling for those prone to get hypertension is basically aimed at reducing the consequences of high blood pressure and the need for antihypertensive drugs.
Even before starting high BP treatment, lifestyle changes are recommended as a natural measure.
Below mentioned are the proposed lifestyle changes (2004 British Hypertension Society guidelines) for the primary prevention of hypertension:
- Body weight maintenance – Adults should maintain normal body weights (BMI 20-25kg/m2)
- Reduction of Dietary Sodium intake – To less than 100mmol/day (less than 6 gram of sodium chloride or less than 2.4 gram of sodium per day)
- Regular aerobic physical activity such as brisk walking (more than or equal to 30 minutes per day on most days of the week or almost daily) Moderate intensity dynamic aerobic exercise like walking, jogging, cycling or swimming should be done on 5 to 7 days per week basis
- Limiting alcoholic consumption to not more than 3 units/day in men and no more than 2 units / day in women
- Consumption of a diet rich in fruit and vegetables (at least 5 portions per day) People with high blood pressure are advised to eat fish at least twice a week and between 300 and 400 grams of fruit and vegetables a day
- Giving up smoking should also be considered
- Dinacharya and Rutucharya: Following the principles of diet, lifestyle, ethics, code and conduct of ideal living on a daily regimen (Dinacharya) and seasonal (Rutucharya) basis and Sadvritta – wholesome daily regimen as explained in Ayurveda
- Achara Rasayana – Principles,behaviour and conduct of life which by themselves act as rejuvenation. Example: Brahmacharya – celibacy, courteous behavior etc.
- Vega Dharana and Udeerana – Helping the body in releasing the naturally manifested reflexes and urges by not forcibly controlling them (Reflexes of Hunger, Thirst, Sleep, Defecation, Urination etc). We should also not force the non-impending reflexes from the body. We should forcibly control within ourselves the urge for emotional reflexes like those of greed, enviousness, anger, lust etc
Read related: Secret of Ayurveda – Do not suppress natural urges - Properly following Trayopasthamba – Rules and regulations laid on Diet, Sleep and Celibacy
- Nidana Parivarjana (Avoiding the causative factors) – Avoid taking foods and activities which disturb the equilibrium of 3 Dosha’s (Vata, Pitta and Kapha) which are the primary culprits in the causation of Hypertension. 3 Dosha balancing diet (good, healthy, fresh and balanced nutrition) – should be taken on a regular basis (predominant in fruits and vegetables). Mainly excessive cold or hot, dry or oily, stale, preserved and packed foods, spicy, sour, heavy to digest foods and junks should be avoided.
Hypertension in Ayurveda
We do not have any straight references regarding the explanation of a disease or syndrome in Ayurveda which resembles Hypertension. But we can make a close comparison to a few conditions and draw an inference from the basics of physiology and pathology as explained in Ayurveda.
Causes for stress and tension:
There are many diseases in the modern day world which are caused, triggered and worsened by lifestyle, mainly our un-monitored stress and innumerable tensions.
Erratic methods of living,
Incompatible food habits (click to read more about it),
uncontrolled stress and competition,
insufficient sleep,
bad habits like smoking & addiction to alcohol,
climatic and geographic influences and lot more things are contributing towards the ‘rise to the peak’ of lifestyle health issues. Among these lifestyle disorders, Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) is on the top list among the disorders which are causing morbidity and mortality.
Increased blood pressure
There is a wrong notion that Kapalbhati is useful to reduce belly fat and obesity. So, elderly people tend to do this very frequently. It is, sadly, not true.
If the person has high blood pressure, then doing Kapal Bhati can further increase blood pressure and anxiety. Hence, it is best to avoid it during hypertension.
Vata involvement
The Game of Vayu:
Basically Vayu or Vata is the force which drives and motivates all the activities in the body. It is a sum total of all the input and output mechanisms, sensory and motor functions taking place in the body. Vayu is also said to control the functions of mind, sense organs and other higher centres of thoughts and emotions.
Vayu is thus all pervading. All the other Doshas (Pitta and Kapha), Dhatu’s (tissues) and Mala’s (excreta – waste products) are dependent on Vayu for their normal or abnormal movements. When in equilibrium, Vata Dosha is responsible for all the normal life activities (psycho-somatic).
The same Vayu when gets disturbed is said to initiate the disease process in the body (and mind) by displacing, misplacing, pulling or pushing the other Dosha’s and Mala’s from their normal and natural seats to abnormal places.
The morbid Dosha’s getting lodged in the tissues cause tissue damage and thus cause disease process. Similarly the Mala’s (excreta, cellular toxins) can get held back in abnormal places, contaminate the body and cause diseases.
How is Hypertension caused as per Ayurveda?
We can tell that High Blood Pressure or Hypertension is a result of abnormal functioning of Vyana and Udana Vayu, Ranjaka Pitta and Avalambaka Kapha including loss of their functional integrity and coordination.
Raktagata Vata
Hypertension can be compared to a condition called Raktagata Vata. In this condition the vitiated Vata gets lodged in the circulating Rakta Dhatu (blood) and causes disturbances in its circulation. Since Rakta and Pitta are related in an inseparable relationship the disturbance of Rakta also leads to the disturbance of Pitta. In this context Raktagata Vata is basically a disorder of blood caused by morbid Vata and Pitta. The Kapha component will also be disturbed leading to loss of support and integrity to the cardiac functions.
When the Avalambaka Kapha gains a pathological increase, they cause blocks in the arteries and arterioles leading to atherosclerosis and peripheral resistance. This further causes Hypertension and cardiac disorders.
The further pathological processes may lead to the aggravated Rakta blocking the normal movements and functions of Vata leading to a condition called Raktavrita Vata. This may lead to many complications of Hypertension as mentioned above. The concept of Vatarakta or Vatashonita too can be included in studying Hypertension from an Ayurvedic perspective
Other Body factors contributing to manifestation of Hypertension
The other Dosha’s can also be involved in the backdrop or in a later condition.
- Pachaka Pitta (Kayagni) and the associated Samana Vayu will be disturbed at the backdrop of Hypertension leading to disturbance of gross and tissue metabolism.
- The Prana Vayu disturbed due to stress, anxiety etc. factors might worsen the disease in a later condition.
- Apana Vayu functions when disturbed can cause Udavarta (upward and haphazard movement of Vayu) leading to increased pressure in the abdominal and chest organs putting them under physiological stress.
- Sadhaka Pitta in the Hridaya (Heart/Brain) and Tarpaka Kapha (Lubricants of nervous system) when disturbed – cause disturbances in heart functions and a disturbance of brain-heart coordination.
The involvement of mind factors in the causation of hypertension or as aggravating factors in the later context of an established disease cannot be ruled out. The disturbed Raja and Tama bhava’s (the mind factors responsible for morbidity according to Ayurveda) definitely contribute to the pathogenesis of Hypertension either in the initial or terminal stages.
Ayurvedic treatment principles
Treatment principles in Ayurveda
The treatment approach should be in identifying the extent of morbidity of the Dosha’s and their subtypes, the immunological components, the tissue strength, the strength of the disease and the diseased and metabolic errors.
The Prakruthi (Basic constitution of the patient) and Vikriti (Pathological state of the disease and diseased) shall be studied in detail. The basic principles of treatment lie in prescribing Vata-Pacifying diet, medicines, treatments and lifestyle advice. The pathological states of Rakta, Pitta and Kapha too should be considered.
Ayurvedic Management of Hypertension
Natural Measures (Preventive):
Internal treatments
Treatment options:
Internal treatments (Antah-Parimarjana)
Panchakarma or Ayurvedic cleansing (detoxification) treatments are a must in throwing away the unnecessary morbid Dosha’s and Mala’s from the system so as to re-establish the heart health and cure Hypertension and Cardiac disorders.
- Virechana or therapeutic Purgation is an ideal way of controlling and eliminating the morbid Pitta (Kapha) and associated Vayu. Virechana also corrects the metabolism and provides lightness to the body. The blocks in the body cells and blood vessels will be removed. The functions including heart functions will be resuscitated. Virechana also removes the morbidity of blood and restores blood health.
- Basti (Medicated Enemas) – This is an unparalleled treatment to control Vayu which is the chief causative factor in Hypertension. If Vayu is controlled the other things will be put in place and the health will be restored.
- Raktamokshana – Bloodletting therapy is used to let out the contaminated blood and to relieve blocks in circulation. This further aids to free circulation, reestablishment of heart and circulatory functions and relief from peripheral resistance. This was used as a key remedy for Rakta Dushti Janya Vikara’s (Diseases caused due to contamination or morbidity of blood tissue) and is rarely administered nowadays.
External treatments
Bahir Parimarjana (External therapies):
- Takra Shiro Dhara – This is a special treatment from the home of Ayurveda in relieving Hypertension. In this medicated buttermilk will be poured in streams on a shaved scalp while the patient sleeps on the Dhara table in supine position. The treatment is carried on for a period of 35-45 minutes.
- Ksheera Dhara – This is a similar method like Takra Dhara. Here the medicated milk shall be poured in streams not only on the head but also on the whole body.
- Taila Dhara – Medicated oil is used for pouring on the body and head in streams. (Other forms like Shiro Pichu – Keeping cotton pieces dipped in medicated oil on the scalp and tying it in place, Shiro Vasti – Pooling of medicated oil in a cabin created on the head etc are also used alternatively)
Note: The above said Dhara’s help in relieving one from stress, calms the nerves, improves circulation, relieves hypertension and insomnia, relaxes the person physically and mentally and re-establishes health.
- Shiro Lepa – Application of medicated pastes of herbs on the scalp
- Avagaha – Tub bath in medicated oil (Sitz bath)
Single herbs
Single herbs that are useful in Hypertension
- Sarpagandha – Rauwolfia serpentina – This is said to be the most powerful hypotensive plant. It has been traditionally used in Ayurveda to treat snakebite, insanity, insomnia and many other diseases apart from Hypertension. Reserpine, the purified alkaloid of R.serpentina was the first potent drug widely used in the long term treatment and management of HTN.
Read more about uses and side effects of Sarpagandha - Lashuna / Rasona – Allium sativum – It is said to lower the blood pressure especially, the systolic part. The sulphur containing compounds found in garlic including allicin is said to act on the body’s nitric oxide system which relaxes the arteries and lowers systolic blood pressure. Doctor’s opinion should be taken because Garlic may not go well with other medications.
Read more about usage of garlic - Arjuna – Terminalia arjuna – It is said to be the best in the business of treating heart ailments. It is an ideal drug to correct circulation disturbances and also to alleviate stress.
Read more about Arjuna
Other useful drugs which can be used either singly or in combination, in essential HTN or as a co-prescription in secondary HTN –
(Click on the herb name to learn more about it).
- Ashwagandha – Withania somnifera – Relieves stress, strengthens the muscles of the heart, good rejuvenator and anti-ageing medicine
- Amalaki – Emblica officinalis – Best anti-oxidant and anti-stress agent
- Bala – Sida cordifolia – Good anti-stress drug and strengthens the nervous system
The best Rasayana’s (rejuvenator, anti-ageing and anti-stress, health promoters and immune-modulators)
- Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri)
- Shankapushpi (Convolvulus pluricaulis)
- Ash gourd – winter melon Kushmanda
- Jatamansi (Nardostachys jatamansi)
- Gotu kola – Mandukaparni (Centella asiatica)
- Giloy – Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Other drugs which have been proved to have antihypertensive property by research works are:
- Celery – Apium graveolens
- Bishop’s weed – Carum Capticum (Ajawain)
- Colius forskohlii (Karpurvali)
- Carrot – Daucus carota
- Flaxseed / Linseed – Linum usitatissimum
- Tomato – Lycopersicon esculentum
- Drumstick – Moringa oleifera (Shigru)
- Tulsi – Holy Basil – Ocimum basilicum
- Bhumi Amla – Phyllanthus niruri
- Pome granate – Punica granatum
- Radish – Raphanus sativus
- Sesame – Sesamum indicum
- Triticum aestivum – Wheat bran
- Vitex doniana – Black plum
- Ginger – Zingiber officinale
Ayurvedic medicines
Effective formulations from the house of Ayurveda for Hypertension and Cardiovascular diseases
(Click on the medicine names to know more about them)
- Sarpagandha churna, Sarpagandha vati – As explained above, Sarpagandha is very effective in controlling high BP. It can be consumed in churna (herbal powder) or Vati – tablet form. Your physician should fix the proper dose. Self medication with Sarpagandha can be very dangerous.
- Brahmi Vati – used in the treatment of depression, blood pressure etc.
- Giloy Satwa – used in Ayurvedic treatment of burning sensation of feet, bleeding diseases etc.
- Ayaskriti – mainly used in anaemia, weight loss therapy, skin diseases etc.
- Kumaryasavam – used in the treatment of gastritis, urinary tract disorders etc.
- Draksharishtam – Balances Pitta Dosha. used mainly in the treatment of respiratory and intestinal disorders
- Partadhyarishtam – A very good cardiac tonic. Useful in the treatment of chest injury, weakness, fatigue etc.
- Punarnavasavam – useful in gastritis, oedema, fever and liver diseases.
- Lodhrasavam – used in leucoderma, anaemia, obesity etc.
- Balarishtam – used mainly in neurological conditions. vata imbalance.
- Sarivadyasavam – used in the treatment of many skin diseases.
- Saraswatharishtam – a very effective anti ageing medicine and a brain tonic.
- Ashwagandharishtam – used in the treatment of sexual disorders, depression etc.
- Nayopayam Kashayam – used in the treatment of respiratory diseases like bronchial asthma. It also relieves hiccups.
- Kalyanaka Ghritam– Herbal ghee, used for the treatment of cough, anaemia, epilepsy, psychosis, schizophrenia, etc
- Mahakalyanaka Ghritam – used for cough, anaemia, epilepsy, psychosis, schizophrenia,
- Ksheerabala Tailam 101 – Balances Vata, a good nervine tonic.
- Sarpagandhadi Churnam
- Lohasinduram
- Sringa Bhasmam – used in the treatment of gastritis, hiccup, intercostal neuralgia, asthma, etc.
- Cheriya Chinchadi Leham
- Dantiharitaki Leham – used in the treatment of skin diseases, fever, liver conditions etc.
- Chyavanaprasham – an all round anti oxidant rich rejuvenating product.
- Narasimha Rasayanam – Though it contains butter as its base, it is useful in hypertension caused by excessive Vata imbalance.
- Brihat Vasavaleha – mainly used in the treatment of respiratory conditions.
- Vidaryadi Leham
- Hridayarnava Rasa – used in the treatment of heart diseases associated with heaviness of chest and dyspnoea etc.
- Hemamruta Rasa
- Loha Bhasma – used in Ayurvedic treatment of anaemia, eye disorders, skin diseases etc.
- Mandura Bhasma – It is used in Ayurvedic treatment of anaemia, jaundice, inflammation etc.
- Mandura Vataka – It is a powerful Ayurvedic medicine used in treating anaemia, liver and skin conditions.
- Navayasa Churna / Navayasa loha – used in the Ayurvedic treatment of anaemia, skin and liver conditions.
- Punarnavadi Mandura – mainly used in the treatment of Anaemia, splenomegaly, piles, fever etc.
- Shiva Gutika – used for a variety of diseases like liver and spleen disorders, neuro-psychiatric conditions etc.
- Manikya Bhasma, Mukta Vati
- Mukta Pishti – used in Ayurvedic treatment of diarrhoea with bleeding, Mania, Psychosis etc.
- Prabhakara Vati – used in Ayurvedic treatment of heart diseases
- Pravala Pishti – useful in high Pitta conditions – used in Ayurvedic treatment of cough, cold, Pitta related diseases etc.
- Suvarna Bhasma – prepared from Gold. It is used in Ayurvedic treatment of infertility, asthma, tissue wasting, poisoning etc. etc.
Blood donation
How Can Blood Donation Therapy help with hypertension?
As per Ayurveda, every healthy individual has to undergo seasonal detoxification (Panchakarma) to keep the body free from disease causing toxins.
High BP is associated with blood tissue, which in turn, is related with Pitta Dosha. Blood tissue and blood pipes are directly controlled by Pitta Dosha.
Pitta Dosha naturally increases in all of us during Autumn season (September end to November). During this season, Virechana – purgation therapy is advised to everyone, to keep Pitta under balance. Virechana expels toxic Pitta out of the body. Similarly, blood letting is also useful in expelling out Pitta Dosha from the body. Blood tissue related diseases such as hypertension, bleeding disorders, allergies such as repeated hives, chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis are immensely benefited by blood letting therapy.
Autumn Season Healthy Regimen
If you are averse to get blood-letting therapy in an Ayurveda center, you can easily donate your blood once a year, during autumn season. Though blood donation is not exactly equivalent to blood-letting therapy, it is useful to some extent for sure.
For this reason, many healthy people are advised to donate blood by their Ayurvedic doctors. For all healthy people, blood donation at least once a year is good. It improves your health and also saves someone else’s life. Then why not do it in the Autumn season?
Note: This applies only to healthy people. For patients, it is advised to go with the advice of your consulting doctors. There are several conditions such as low hemoglobin levels, viral hepatitis, etc., where blood donation is contraindicated.
FAQs
1. Can a hypertensive patient take rock salt (Saindhava Lavana)
Saindhava Lavana is rich in several minerals and micro nutrients. Hence, in Ayurveda, rock salt is preferred to common salt. But rock salt also contains sodium chloride in it.
Hence, if you are already taking salt in your diet, then you can replace that with rock salt.
But if your doctor has asked you to avoid salt completely, then it is best to avoid rock salt as well.
2. With Ayurvedic treatment, hypertension with tachycardia (increased heart beat) be treated
Sarpagandha is very useful in this regard. It decreases pulse rate and blood pressure at the same time. Hence, Sarpagandhadi vati, Pancharatna gulika etc medicines are usually prescribed in these conditions.
3. Can Ayurveda totally cure hypertension?
Initially, one has to depend on Ayurvedic medicines. Side by side, lifestyle changes (such as quitting alcohol and smoking, aerobic exercise etc) and diet changes are adopted.
The diet and lifestyle changes may take up to 4 – 6 weeks to show difference.
As the patient gradually gains control over high BP with medicines, and as and when the lifestyle changes start showing results, then the medicines dose can be decreased.
Can there come a time point where one can really quit medicines? Yes, in some cases. Depends on age (younger the better), other complications such as diabetes, heart disease etc.
4. Can a switch from Allopathic medicines to Ayurvedic medicines be made?
It needs to be done with strict medical supervision. It may take between 2 – 6 months.
During the switching period, it is best for the patient to have a BP monitor at home and measure BP from time to time to see if it is normal all the time.
Note: The above said formulations shall be taken only on medical advice and under supervision
Other treatment measures
Other methods of preventing and controlling Hypertension:
- Yoga
- Taichi (Chinese art of healing)
- Acupuncture and Qi Gong – A form of traditional Chinese medicine
- Autogenic Training – Involves a series of sessions in which one learns how to control breathing, blood pressure, heart rate and body temperature. This technique reduces stress and provides relaxation.
- Meditation involving chanting, breathing and visualization
- Relaxation and Breathing exercises
- Biofeedback – It is a technique where people are taught how to gain control over internal body processes that normally occur involuntarily such as BP, Heart rate, muscle tension and skin temperature. Other than Hypertension it is also used to treat migraine, tension headache, chronic pain and urinary incontinence
- Indulging in variety of entertaining and pleasing activities to keep away from stress (Check your stress)
- Writing dairies, blogs, books etc
Takradhara for hypertension
Takradhara for hypertension treatment:
Takradhara is a traditional procedure where a stream of herb-processed buttermilk is flown over head. Among many options of treatment and medications available in Ayurveda for the management of Hypertension, Takra Dhara is the best choice.
Thus Takra Dhara is a treatment in which the medicated (processed with herbs, medicines) buttermilk is poured in stream over the target area. forehead and scalp of the patient suffering from Hypertension for a fixed duration of time while the patient lies on his or her back over a specially designed table meant for the treatment.
In hypertension the rakta dhatu or blood element is abruptly handled by the disturbed Vayu. The blood and Pitta have an inseparable relationship as Pitta resides in the blood. When the pitta gets disturbed, the rakta too gets disturbed and vice versa. Takra dhara by the virtue of its coolant effect pacifies the hot, intense and penetrating nature of both pitta and rakta. It also controls Vayu by the virtue of its combination.
Takra Dhara relaxes & revitalizes the central nervous system, balances the brain and hormonal functions and thus regularises and relaxes all the functions of the body. The stress in each and every cell and passage of the body is removed. It has a soothing effect on the endocrine system.
Takra Dhara improves the supply of blood and nutrition to the brain
The pressure and temperature effect of the medicament cannot be ruled out
With an Ayurveda perspective Takra Dhara might communicate with the deepest recesses of the brain by soothing the Marmas (vital points of convergence of bones, muscles, blood vessels, soft tissues and joints) located in the head viz Apanga, Avarta, Shanka, Utkshepa, Seemantha and Sthapani Marma’s with which the dhara liquid comes into contact with.
Most of these Marma’s are related to the eye and blood circulation to the brain. By activating the Marma’s Takra Dhara might make a strong impact on the functioning of the central nervous system and important glands within the brain.
Alochaka Pitta (Pitta subtype) which is located in the Eye is said to be of 2 types. One is Chakshu Vaisheshika (located within the eye and maintains its well being) and the other is Buddhi Vaisheshika (the part of Alockhaka Pitta which has its connectivity with higher centres of the brain and thus monitors the higher functions like intelligence, memory etc). Apanga and Avarta marma are related to the eye. Dhara might make a soothing impact on buddhi vaisheshika alochaka pitta through these Marma’s and in return soothe the nervous system.
The injury of Seemantha Marma (joints of the skull) is said to cause Chitta Nasha (psychological abnormality) and Bhaya (fear complex). Thus when the same Marma is healed through Dhara, it may reverse the Chitta Nasha and Bhaya, i.e. it might relieve stress, anxiety and depression. With this the relaxed nervous system will take care of the heart functions and circulation patterns. This in turn will benefit in reversing the events in hypertension.
The soothing of these Marma’s and in turn soothing of Nervous system and endocrine glands as an effect of Takra Dhara will definitely relax Prana Vayu, Sadhaka Pitta and Tarpaka Kapha in the brain (head). These inturn will have a relaxing effect over the Vyana Vayu, Ranjaka Pitta, Avalambaka Kapha and Udana Vayu controlling the heart functions and circulation. The ultimate effect will be a good relief from Hypertension.
What is Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)?
When the blood flows, it exerts a force against the walls of the blood vessels (muscular tubes carrying the blood). This force is called Blood Pressure. This force depends on the Cardiac output (amount of blood ejected out of heart, each time it beats) and the resistance of the blood vessels to the flowing blood.
Hypertension is a condition wherein the blood pressure is higher than 140 over 90 mm of Hg (millimetres of mercury).
High Blood Pressure is seen to be an ominous sign for cardiovascular health. The more the pressure, the more is the risk to the heart. High blood pressure also puts pressure on kidneys. Hence, it is often seen that the patients who are prone for kidney disorders are monitored for their BP very regularly.
Panchakarma for obesity with high BP
Definition of hypertension
In Hypertension, we can find that the blood pressure is persistently high in the arteries. The higher the pressure and resistance, the harder the heart has to pump.
Hypertension is the name given for a condition where the readings of High Blood Pressure remain high and above normal all the time. That means, in Hypertension, the blood pressure of the person is high each and every time it is measured (consistently elevated).
This also means that having a High Blood Pressure for a short amount of time and or occasionally is just normal.
How to understand Blood Pressure reading?
The blood pressure record has two components –
Systole – the first reading
Diastole – the second reading
Systole, diastole
Meaning of systole and diastole:
Systole – Meaning – A drawing together or contraction in Greek: It is the time period when the heart is contracting (specifically when the left ventricle of the heart contracts). The systolic pressure is the maximum arterial pressure during the contraction of the left ventricle of the heart. In a blood pressure reading it is usually the first number recorded.
Example: In a blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg, 120 is the systolic pressure. It is measured in terms of millimetres of Mercury. In this the blood from the heart chamber is ejected into the adjacent chamber or a blood vessel. Electrical systole can be recorded on Electrocardiogram (ECG) and precedes mechanical systole (actual contraction of heart).
Diastole – Meaning: Drawing apart in Greek: It is a time period when the heart is in the state of relaxation and dilatation (expansion). It is the minimal arterial pressure during relaxation and dilatation of the ventricle of the heart. Diastole is the time when the heart fills with the blood. In a blood pressure reading it is usually the second number recorded. It is measured in terms of millimetres of Mercury.
Ex. In a blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg, 80 is the diastolic pressure.
Thus Diastole is a part of cardiac cycle when the heart refills with blood following systole (contraction).
Ventricular diastole is a period when ventricles (2 lower chambers of the heart) are filling and relaxing, while atrial diastole is a period during which the atria are relaxing. (Atria – 2 upper chambers of heart).
Range of blood pressure
Range of blood pressure (in mm Hg) as defined by American Heart Association:
- Normal Blood Pressure – Systolic is below 120 mm Hg and Diastolic below 80 mm Hg – 120/80
- Pre-hypertension – Systolic between 120-139 mm Hg or Diastolic between 80-89 mm Hg – 120-139/80-89
- Stage 1 Blood Pressure (Hypertension) – Systolic between 140-159 mm Hg or Diastolic between 90-99 mm Hg 140-159/90-99
- Stage 2 Blood Pressure (Hypertension) – Systolic values 160 mm Hg or higher or Diastolic values 100 mm Hg or higher – 160/100
- Hypertensive Crisis (Medical Emergency) – Blood Pressure is above 180 Systolic or above 100 mm Hg Diastolic. 180/100
Reference – Medical news today website
Natural Variations of Blood Pressure
- Blood Pressure lowers at sleep and rises on awakening
Blood Pressure naturally rises during anxiety, excitement and following physical activity
Types of high BP:
Primary (Essential) Hypertension –
• Defined as Hypertension without any obvious underlying cause
• Constitutes about 90-95% of all cases of Hypertension
Secondary Hypertension –
It is due to causes that can be very well identified – such as chronic kidney disease, narrowing of the aorta or kidney arteries or an endocrine disorder such as excess aldosterone, cortisone or catecholamines
Epidemiology
• 1 in every 4 adults in the world suffers from hypertension
• It contributes to 49 % of ischaemic heart disease and 62% of stroke worldwide
• Inadequately controlled hypertension is the current number 1 attributable risk for death across the globe
Causes of Hypertension
Primary (Essential) Hypertension:Essential Hypertension is a complex process. It results from a complex interaction of genes and environmental factors.
Genetic basis of Hypertension is still not completely understood.
Numerous common genetic variants which have small effects on Blood Pressure have been identified. Likewise some rare genetic variants which have large effects on blood pressure have also been identified.
With ageing the Blood Pressure rises and the risk of becoming hypertensive in the later part of life also proportionally increases.
Environmental Factors:
These are most of the times held culprit for the causation of Essential Hypertension. They are said to influence blood pressure either singly or in combination.
The below mentioned are some of the environmental factors which have been identified as influencing Blood Pressure.
• High Salt intake, Salt rich diet through processed and fatty foods
• Lack of exercise
• Obesity
• Stress
• Depression
Other possible factors:
• Caffeine consumption
• Insulin resistance
• Early life events such as low birth weight, maternal smoking, lack of breast feeding etc
Secondary Hypertension:
• Kidney disease (most common)
• Obesity
• Sleep apnoea
• Pregnancy
• Coarctation of the Aorta
• Excessive liquorice consumption
• Illegal drugs (some)
• Arsenic exposure through drinking water
• Endocrine conditions such as Cushing’s Syndrome, Hyperthyroidism, Hypothyroidism, Acromegaly, Conn’s Syndrome (Hyperaldosteronism), Hyperparahyroidism, Pheochromocytoma, Congenital adrenal hyperplasia etc
• Excess Alcohol (Reversible). Stop alcohol and the blood pressure will start returning to normalcy.
• Excess Tobacco (Reversible)
• Use of oral contraceptives (Reversible)
• Hormonal therapy for menopause (Reversible)
Note: In secondary Hypertension the symptoms of the disease on the backdrop too would be manifested along with hypertension.
Source.
Common Risk Factors:
• Race – African-American adults are at higher risk
• Size – Being overweight or obese
• Sex – Men are more prone at younger ages. Women are more prone at older ages. (Both have same lifetime risks)
• Lifestyle – Greater uptakes of dietary salt, excessive alcohol, low dietary potassium and physical inactivity
Allopathic and Ayurvedic medicines together?
Signs and Symptoms of high BP
Any set of symptoms do not precisely describe the existence of Hypertension. Hypertension is usually identified through screening or when being checked for some unrelated problems. We should note that Hypertension itself does not cause symptoms but in the long-term leads to complications caused by narrowing of blood vessels.
Commonly complained symptoms:
• Headaches (especially in the morning, at the back of the head)
• Light headedness
• Vertigo
• Tinnitus (buzzing or hissing noises in the ear). Related: Tinnitus treatment as per Ayurveda
• Altered vision
• Fainting episodes
Note: These symptoms may be related to associated anxiety rather than the high blood pressure
On physical examination – Hypertension may be associated with changes in the optic fundus seen by opthalmoscopy (hypertensive retinopathy). The severity of retinopathy is proportionate with duration and / or severity of hypertension
Symptoms in secondary Hypertension:
Secondary Hypertension may be suspected when Hypertension is manifested with certain specific signs and symptoms related to the diseases on the backdrop
Example:
• Cushing’s Syndrome – frequently causes truncal obesity, glucose intolerance, moon face, fat humps at the back of neck or shoulder, purple abdominal stretch marks along with Hypertension
• Hyperthyroidism – Presents with weight loss, increased appetite, bulging eyes, tremors, fast heart rate etc. along with increased blood pressure
• Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) – Presents as a localised abdominal bruit to the left or right of the midline or in both directions
• Coarctation of the Aorta – Presents with decreased blood pressure in the lower extremities relative to the arms and / or delayed or absent femoral arterial pulses
• Pheochromocytoma – May cause abrupt episodes of Hypertension with headache, palpitations, pale appearance and excessive sweating
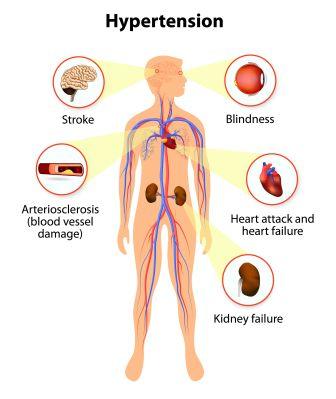
Hypertension leading to problems in different organs:
Hypertension over a period of time causes organ damages. Chronic hypertension can lead to the below said complications
Arteriosclerosis – narrowing of blood vessels by forming plaques. Continuous high pressure of blood leads to damage of artery walls, leading to plaque formation
• Enlarged or weakened heart (heart failure)
• Aneurysm – An abnormal bulge in the wall of an artery
• Blood vessel narrowing – In kidneys (leading to kidney failure), heart (leading to heart attack), brain (leading to stroke) and legs (leading to amputation)
• Rupture or bleeding from the blood vessels of the eyes – leading to vision problems or blindness
Pathophysiology
• In established Essential Hypertension – Cardiac output is normal. High pressure is due to total peripheral resistance (increased resistance to the blood flow). Peripheral resistance is the resistance to the flow of blood due to narrowing of small arteries and arterioles at the periphery. Reduction in the number of capillaries or density of capillaries may also contribute to peripheral resistance.
• Pre-hypertension (Borderline Hypertension) – Younger people have high cardiac output, elevated heart rate and normal peripheral resistance. In these people the cardiac output falls and peripheral resistance rises with age. Therefore in the later life they develop features of established Essential hypertension.
• Decreased peripheral venous compliance – Veins draw blood from different parts of the body to heart. If veins are drawing the blood in excess into the heart, it increases venous return, increases cardiac pre-load and cause diastolic dysfunction.
• Isolated systolic hypertension – The pulse pressure (difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure) is frequently increased in these conditions, especially in older people with hypertension. The systolic pressure is abnormally high and diastolic pressure is normal or low at times. This may be due to increased arterial stiffness associated with ageing.
• Abnormalities of rennin-angiotensin system and sympathetic nervous system leading to disturbances in the kidney’s salt and water handling mechanisms which further lead to a rise in peripheral resistance contribute to most cases of essential hypertension.
• Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in blood vessels (vascular inflammation) may contribute to increased peripheral resistance and vascular damages occurring in hypertension
• Interleukin 17 increases the production of several immune system chemical signals like tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8 which take part in the causation of hypertension
Diagnosis
How is Hypertension diagnosed?
Sphygmomanometer is an instrument used to measure the blood pressure. It is commonly known as BP apparatus. The diagnosis is not usually done after recording a single high reading. If your doctor records three high BP readings on three separate days, then only the diagnosis is made.
Blood pressure is measured in both seated and standing postures to rule out orthostatic or postural hypotension. (posture based high BP).
White Coat Hypertension:
Many times patient may get nervous at clinic leading to erratic high BP reading. Fear of white coat of doctor, leading to high BP reading.
Self measurement of BP readings at home using BP devices may make the reading more realistic, as patient may be relaxed at home.
Masked Hypertension is opposite of White Coat Hypertension. Here the patient’s BP is above normal during daily activities but when the patient is in a clinic setting it is in a normal range
• Pseudo-hypertension in the elderly (Non compressible artery syndrome) – Caused due to calcification of arteries resulting in high readings (cuff readings) while intra-arterial measurements of BP are normal
• Orthostatic hypertension – BP increases upon standing
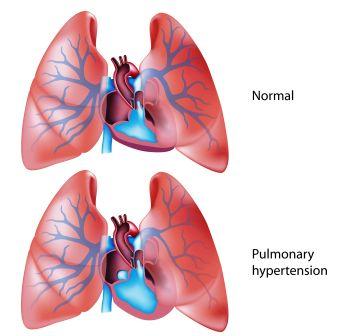
Pulmonary hypertension:
It is a rare lung disorder. Here the pipes carrying blood from heart to lungs is narrowed, making it difficult for blood to flow through the vessels. As a result, the blood pressure in these arteries, called pulmonary arteries — rises far above normal levels.
How many times BP should be checked for diagnosis of hypertension?
The National Institute of Clinical Excellence recommends 3 separate sphygmomanometer measurements at an interval of 1 month each.
The American Heart Association recommends at least 2 separate health care visits. Ambulatory BP monitoring over 12-24 hours is the most accurate method to confirm the diagnosis.
Apart from recording the blood pressure readings, the doctors would like to record a detailed case history of the patient and also of family history. Detailed physical examination of the patient with special interest towards cardiovascular health will be done.
Tests to identify possible causes of secondary hypertension:
These tests also determine the extent of damage to heart, eyes and kidneys if any.
• Tests for Diabetes and Diabetes control
• Tests for High cholesterol
• Serum creatinine – for presence of kidney disease
• Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula to estimate glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). eGFR further provides baseline measurement of kidney functions. This can be used to monitor side effects of certain anti-hypertensive drugs on kidney function
• Urine samples for proteins – secondary indicator of kidney disease
• Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) – To confirm if heart is under trouble from hypertension, to know about left ventricular hypertrophy (bulging of left lower chamber of heart) or to detect silent heart attacks
• Chest X-Ray or an Echocardiogram – To look for signs of heart enlargement or heart damage
Note: Effective lifestyle modification may lower BP as much as an individual antihypertensive drug. Combinations of 2 or more lifestyle modifications can achieve even better results.
Benefits of high BP Management:
Reduction of blood pressure by 5mm Hg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21 % and reduce likelihood of dementia, heart failure and mortality from cardiovascular disease
Target Blood Pressure (According to various expert groups):
While treating for hypertension the target blood pressure should be
• For General Population – Below the range of 140-160 / 90-100 mm Hg
• For those over 60 years of age (According to JNC-8) – 150/90 mm Hg
• For those over 80 years of age – 150/90 mm Hg
Medications:
- The classes of medications used to treat hypertension are called antihypertensive medications.
- The first line for medications are – Thiazide-diuretics, Calcium channel blockers, Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and Angiotensin receptor blockers. These can be used alone or in combination.
Resistant Hypertension:
- It is defined as hypertension that remains above goal blood pressure in spite of using at once, 3 anti-hypertensive medications belonging to different drug classes.
- Low adherence to treatment may be the chief cause.
- It may also represent the result of high activity of autonomous nervous system and is called ‘Neurogenic Hypertension’
Complications of Hypertension
Increased risk of ischaemic heart disease, stroke, peripheral vascular disease, cardiovascular diseases (heart failures) aortic aneurysm, diffuse atherosclerosis, chronic kidney disease, pulmonary embolism
Cognitive impairment
Dementia
Hypertensive retinopathy
Hypertensive nephropathy
Research
Research works and other useful data
- By the year 2025, the number of people living with hypertension (High Blood Pressure) is predicted to be approximately 1.56 billion worldwide
- About 1/3 of all the people over 20 years of age have hypertension in USA alone. Thus, in the ‘Million Hearts’ initiative, the Department of Health and Human Services, USA, has given ‘Control of Hypertension’ a key national priority.
This initiative aims to prevent at least 1 million heart attacks and strokes in the US by 2017. Lifestyle factors like physical inactivity, consumption of salt-rich diet created by processed and fatty foods, alcohol and tobacco use etc are said to be responsible for an increasing prevalence of the condition.
- One in every 3 Indians suffer from hypertension and heart ailments responsible for 30 percent of deaths in the country. Cardiovascular diseases are acquiring epidemic proportions in India and are calling for serious actions.
- Reduction of blood pressure by 5mm Hg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21 % and reduce likelihood of dementia, heart failure and mortality from cardiovascular disease
- Data from the Framingham Heart Study predict that 90% of people who are normotensive at age 55 years will go on to develop hypertension in their lifetime
- Global obesity is said to be the chief cause for an increasing level of blood pressure in children and adolescents
- Autopsy studies such as Bogalusa Heart Study and the Pathobiological Determinates of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY) has demonstrated increased atherosclerosis at higher BP levels in youth. Therefore accurate assessment and management of BP is essential to prevent target organ damage
- Ambulatory BP Monitoring (ABPM) which can detect precise changes in BP throughout daily activities is found to be superior to Clinical BP (CBP) monitoring in predicting cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Thus ABPM has widespread use in evaluation for Hypertension and risk of end-organ damage in adults.
- Uric Acid and Hypertension – Approximately 25-45% of untreated hypertensive patients have concomitant hyperuricemia. An association between elevated Serum Uric Acid (SUA) and Hypertension has been described in adults in several large epidemiological studies. Although hyperuricemia is known for its association with cardiovascular events in hypertension, it remains unknown if uric acid is an independent risk factor, a mediator or merely a marker for the development of HTN. Experimental data suggests that uric acid may induce endothelial damage, vascular inflammation and rennin-angiotensin system activation. BP control is the most established practice for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease.
- Hypertension is one of the common diseases in the elderly. The prevalence of hypertension markedly increases with advancing ageing. Both ageing and HTN have a critical role in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications.
- Prompt treatment of Hypertension may cut off the risk of hiring Alzheimer’s disease. Related
- Sleep disorder is linked to hypertension. In people with sleep apnea and hard-to-control high blood pressure, blood pressure values drop if sleep disorder is treated. Related
- Those having high blood pressure for a certain period (more than 6 years) have a risk of developing psoriasis, especially in women. related
Switching to Ayurveda from Allopathy For Hypertension Treatment?
History and other useful information:
- William Harvey (physician) first described the circulation of blood in his book ‘De motu cordis’. This led to the modern understanding of the cardiovascular system.
- Stephen Hales (English clergyman) made the first published measurement of blood pressure in 1733
- In 1896 Scipione Riva-Rocci invented the cuff-based Sphygmomanometer. Following this hypertension as a clinical entity came into being. This allowed the measurement of blood pressure in the clinic.
- In 1905, Nikolai Korotkoff improved the technique by describing Korotkoff sounds that are heard when the artery is auscultated with a stethoscope while the sphygmomanometer is deflated
- Fullness Disease: This is a disease explained in medieval Persian medical texts. The signs and symptoms are similar to those of patients with hypertensive crisis. The symptoms include headache, heaviness in head, sluggish movements, general redness and warm touch feel of the body, prominent, distended and tense vessels, fullness of the pulse, distension of the skin, coloured urine, loss of appetite, weak eyesight, impairment of thinking, yawning, drowsiness, vascular rupture and hemorrhagic stroke.
- Descriptions of hypertension as a disease came from Thomas Young (1808) and Richard Bright (1836).
- The first report of elevated BP in a person without evidence of kidney disease was made in Frederick Akbar Mahomed (1849-1884)
- Hard Pulse Disease – A disease named ‘Hard Pulse Disease’ which resembles high blood pressure was historically treated by reducing the quantity of blood by bloodletting or application of leeches. This was advocated by Yellow Emperor of China, Cornelius Celsus, Galen and Hippocrates. The treatment approach included changes in lifestyle like staying away from anger and sexual intercourse. The dietary programme included avoiding wine, meat and pastries, reducing the volume of food in a meal, maintaining a low energy diet and use of spinach and vinegar.
- 3 treatment modality: In the 19th and 20th centuries, before effective pharmacological treatment for HTN became possible the 3 treatment modality were used – Strict sodium restriction (ex. Rice diet), sympathectomy and pyrogen therapy. They had a lot of side effects and did not get popular.
- Sodium thiocyanate – was the first chemical for hypertension which was used in 1900. It got unpopular because of many side effects.
- Post 2nd World War – Tetramethylammonium chloride, Hexamethonium, Hydralazine and Reserpine 9derived from the medicinal plant Rauwolfia serpentine were brought into practise
- Major Breakthrough – The discovery of well tolerated oral agents made a major breakthrough in the treatment and management of HTN. The first was Chlorthiazide, the first thiazide diuretic which came available in 1958. Subsequently the beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors), angiotensin receptor blockers and rennin inhibitors were developed as antihypertensive agents
You have the best remedies for Hypertension in Ayurveda but don’t forget to consult an Expert Ayurveda Doctor for an opinion before starting on with anything
Article By Dr Raghuram
Click to consult Dr Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)
Best salt for high BP
Which is the best salt to use for patients with high blood pressure?
Dr JV Hebbar:
To understand high blood pressure in Ayurvedic terms, it is a disease caused by vitiation of blood and blood vessels. Pitta and Vata dosha vitiation are directly related to disorders of blood and blood vessels (pipe).
Hence, primarily Pitta and secondarily Vata calming substances are ideally used in such disorders.
Keep in mind, salt, sour and pungent tastes increase Pitta and sweet, bitter and astringent tastes decrease Pitta dosha.
As per Acharya Sushruta, qualities of rock salt (Saindhava lavana) are:
चक्षुष्यं सैन्धवं हृद्यं रुच्यं लघ्वग्निदीपनम् | स्निग्धं समधुरं वृष्यं शीतं दोषघ्नमुत्तमम् ||३१४|||
cakṣuṣyaṃ saindhavaṃ hṛdyaṃ rucyaṃ laghvagnidīpanam | snigdhaṃ samadhuraṃ vṛṣyaṃ śītaṃ doṣaghnamuttamam ||314|||
Reference:
Sushruta Samhita, Sutrasthana 46th chapter, Shloka number 314
Saindhavaṃ – Rock salt is
cakṣuṣyaṃ – good for eyes
hṛdyaṃ – cardiac tonic, good for heart
rucyaṃ – improves taste of food
laghu – light to digest, quick to undergo digestion
agni dīpanam – kindles digestive fire
snigdhaṃ – unctuous
samadhuraṃ – slightly sweet
vṛṣyaṃ – aphrodisiac
śītaṃ – coolant
doṣaghnamuttamam – balances all three doshas.
Read in detail: Rock salt (Saindhava Lavana) Uses, Side Effects
Usually pitta aggravating foods are not good for eyes and heart, but rock salt is healthy for eyes and heart.
Acharya Sushruta has explained it as a coolant and wholesome.
It is explained by Acharya Charaka as one of the food ingredients that is good to have daily.
Considering all these factors, if a person with hypertension wants to use any salt, out of all types, rock salt is the best.
Keep in mind, there is another principle in Ayurveda, called ati sarvatra varjayet – avoid all things in excess. So, just half to one gram of rock salt per day is well tolerated, as with all things, rock salt, if used excessively, is not good for blood pressure.









15 comments
drsranganathan
Dear Dr Hebber, I find most your write ups quite meaningful and relevant. Unlike some, you are quite clear in your statement that direct correlation for hypertension is not there in Ayurveda. You are very honest and scientific in your assertions.
The question I could not understand is why when Ayurveda has so much, many of your fellow colleagues engage in cross pathy?
Dr S Ranganathan
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Dear Dr Ranganathan, thanks for your kind words of appreciation.
Need for basic allopathic healthcare in rural areas, where allopathic doctors do not practice, is the main reason that I have found that makes a few of my colleagues to engage in cross pathy.
Ashwani Kapur
Probably,the best single and composite article on the subject
Sujata Ingle
Very good information.Thank you sir
B S MURTHY
Very useful to every educated / employees. They should be conscious of their health in their own interest and of their family.
Lokesh Mitter
Thank you Dr. Sir, you have definitely done hard work to gather all the relevant information, I sincerely, want to congratulate you.. Sir, my BP reading is 90/150 what should i do to reduce this. I am vegetarian, non-smoker, non-drinker, and also do walking and exercise, but due to my mothers health i have this problem. pl guide me. Thank you,
lokesh mitter
Ravi (@Ravi_in_)
Practice yoga and breathing exercise daily morning and evening. Your problem is due to stress hence not controlled by walking and other exercise. Need some good breath exercise and yoga daily. Initially that 90 will become 80 in a month which is more important than higher. later the other part also will become normal. Don’t worry stay happy.
Dr shabna
Thanks u sir very useful information.
Ravi (@Ravi_in_)
Hypertension or High BP can be easily controlled through simple yoga and breathing exercise. Yoga also helps one to pacify extra grated nadies in body. Mind related issues like Anxiety, depression, fear are also slowly overcome. I think mind plays a major role in High or Low BP in major cases. All can do simple yoga exercise irrespective of age daily 1 hour and stay healthy instead of running after doctors and medicines.
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Hi, you should not quit medicines without consulting the doctor.
Khalid Hamza
Hello Sir,
Today my daughter aged 18 years is diagnosed with
Mild Tricuspid Regurgitation and
Mild Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Is there a complete treatment plan in Ayurved for her condition?
Please suggest.
Ishwar
How should we make the Hibiscus tea mentioned above?
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
1 tablespoon of dry hibiscus flower powder + 1 cup of water, boil and reduce to half a cup. Filter and add sugar if needed.
Rajesh Bhatgare
Sir, Currently I have taking stamlobeta 1 tab daily….I have just started Cardistab tab…..2 morning and 2 tab evening…. ShoySh I stop taking allopathy medicine now
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)Author
Please consult an Ayurveda doctor for the dose fixing.