Madanaphala – Randia dumetorum – Benefits, Qualities, Side Effects
Madanaphala is one of the most commonly used Ayurveda herbs. Its botanical name is Randia dumetorum. It is used in the famous Ayurveda Panchakarma procedure called Vamana (vomiting therapy). Apart from this, the herb has many health benefits and usage.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Madanaphala is a well known Ayurvedic herb, used for Vamana Panchakarma therapy. Here, vomiting is induced to expel out toxins of aggravated Kapha Dosha. It is known as an emetic nut in English due to its action. Its botanical name is Randia dumetorum Lam. and it belongs to the Rubiaceae family.
Even though the fruits are specifically used for treatment, its flowers, leaves and roots are also used for various medicinal purposes.
It is found abundantly in the foothills of Himalaya. Also it is available in Sikkim, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Jammu etc.
Botanical Name:- Randia dumetorum Lam. (Randia spinosa Pior; R . brandisi Gamble; R. Longispina W& A; R. Tomentosa W &A; Xeromphis spinosa Keay)
Family – Rubiaceae (Manjishta kula)
Ayurvedic remedies
Some of the simple remedies and their health benefits are explained here below-
To induce vomiting
1. Hot infusion of Madanaphala seeds for inducing vomiting:
In 200 ml of hot water 12 grams of Madanaphala seed powder is added and kept for 5-8 minutes. This is given to drink as such by the traditional people. If the vomiting is not induced properly, slight mustard powder or rock salt are also added. By this vomiting takes place and the person will free from bulkiness, distension of abdomen, headache, nausea, lethargy etc.
Eczema
2. Madanaphal root paste application in eczema:
Fresh root of Madanaphala is taken and rubbed well in a stone by adding lemon juice .This is applied over the lesions of eczema and other skin diseases. In cases of Herpes also this is applied by the traditional and folk healers.

Headache
3. Flower paste with mustard seed for headache:
In case of chronic headache this formulation is very effective; especially in vascular headaches. A fist full of emetic nut flowers is collected and rubbed well with mustard seeds. This is applied over the forehead during the sufferings of headache.
Abdominal colic
4. In abdominal colic pain of children:
Mature fruit of emetic nut is taken and rubbed well with warm water and salt in a mortar. This fine paste is applied around the naval portion in cases of abdominal colic of the children. This is effective in abdominal pain and dysuria.
Wounds, ulcers
5. Leaf decoction for washing the wounds and ulcers:
In folklore practices the leaf decoction is used to wash the chronic wounds and ulcers.
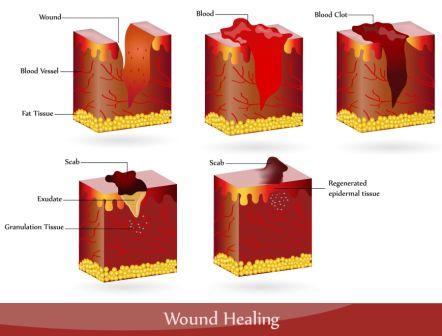
General method of decoction preparation is –
1 tablespoon (10 grams) of coarse powder of the herb is added with 2 cups of water. Boiled in open air till the total content is reduced to 1 cup. This is filtered and used.
Classical literature is developed or enriched by folklore practices and traditional knowledge only. Till today several traditional practices are still waiting for codification in classical literature. Such a time to time codification and inclusion in classical literature will enrich the herbal knowledge or otherwise it is captured by the multi -national companies and the true nature and credit of the drug is taken by the other authorities.
Click to Consult Dr MS Krishnamurthy
Vernacular names
Hindi Name – Mainaphal;
Telugu Name– Mranga Kaya;
English Name – Emetic nut
Bengali Name-Mayanaphal
Marathi Name – Golaphal
Gujarati Name – Mindhala
Tamil Name – Maruk Kalam
Kannada Name _ Madakari
Malayalam Name– Kara
Sanskrit synonyms
Synonyms –
Madana – it causes Mada – intoxication
Chardana – helps induce vomiting
Pindi, Pindeetaka – the fruit is spherical in shape
Shalyaka – has spines. (Shalya means sharp surgical instrument)
Vishapushpaka – having toxic flowers
Karahata, Ratha
Mrubhaka – Grows in dry region
Dharaphala – Fruits have streaks on its surface
Phala – Fruits are best used as medicine
Gala -It eliminate kapha
Vamana – best vamaka dravya
Golaphala – Fruits are round in shape
Vishanasaka – Madanaphala alleviates poison from the body
Vastishodhana – Useful drug for vasti karma
Rada – Best vamaka dravya
Classical categorization
Charaka–
Asthapanopaga – group of herbs used in Asthapana type of Basti (decoction enema treatment).
Anuvasanopaga – group of herbs used in Anuvasana basti (oil enema)
Vamana Dravya – group of emetic herbs
Phalini – Group of herbs with fruit as the used part.
Sushruta– Aragvadhadi, Muskakadi, Urdhabhagahara group of herbs.
Vagbhata– Aragvadhadi group of herbs.
Different varieties
In Kaiyadeva nighantu – two varieties – Madana- R. Dumetorum and Shweta pindeetaka – R. Uliginosa Dc. It is again of two types. Suksma Pinditaka and Maha Pinditaka (small and big sized fruits).
Ra Ni – Madana , Varaha
Distribution
Found throughout the tropical and subtropical forests in India.
Morphology
A large shrub, or small tree. Branches are horizontal, rigid
Leaves – Opposite but looks like fascicled on the suppressed branches
Inflorescence – Solitary and terminal or axillary or leaf opposed cyme
Flowers – White or yellowish, stamens are 5, ovary is two celled
Fruits – Berry, globose, two celled many seeded
Part used -Fruits and seeds
Major chemical constituents
R. Dumetorum: Fruits/ seeds- citric & tartaric acids; randianin – sandianin; Randia Acid, ursosaponin, dumetoronins A,B,C,D,E&F; randoside A; Arachidic, Lignoceric, Linoleic, Oleic, Palmitic & stearic acids etc.
(Reference: Illustrated Dravyaguna VIjnana, Vol. II, by Dr JLN Shastry)
Chemical constituents
The fruits are rich in saponin content. Valerenic acid is the other dominant principle of this drug. Some other significant chemical constituents are citric acid , tartaric acids, randianin – sandianin, Randia acid, Arachidic, Lignoceric, Linoleic, Oleic, Palmitic and Stearic acids etc.
The herb is hot in potency and it undergoes Pungent kind of bio transformation (vipaka).
The herb is appreciated as kaphavata shamaka and Pittanissaraka (cholagogue).
Chemical composition:
Root bark – triterpene, -1-keto-3-hydroxyoleanane,
Bark – mannitol, saponins, coumarin glycosides,
Leaves – contain an iridoid-10- methylixoside, an iridoid glycoside,
Ripe fruit – glycosides, randioside A, mollisidial triterpenoid glycosides and randianin, six saponins-dumetoronins A to F. Source
Side effects: If used in excess, it may cause excess vomiting, indigestion and anorexia
Properties
Rasa (taste)– Madhura (sweet), Tikta (Bitter)
Guna (qualities)– Laghu (light to digest), Rooksha (dry)
Vipaka (taste conversion after digestion) – Katu (pungent)
Veerya (potency) -Ushna (hot)
Karma– Balances kapha-vata
Chardana (induces vomiting),
Lekhana (scrapes inner lining of blood pipes, reduces cholesterol)
Randia dumetorum qualities and uses –
Vranapaha – helps in quick wound healing
Useful in the treatment of
Shleshma Jwara – fever of Kapha origin
Pratishyaya – running nose, rhinitis
Gulma – abdominal tumor,
Vidradhi – abscess
Shopha – inflammation
Part used, Dosage
Part Used– Fruit, seeds
Dosage– therapeutic – 1 grams
For vomiting therapy – 3 – 6 g
Method of collection
Between Spring (Vasanta) and Summer (Greeshma), in Pushya, Ashvini or Mrigashira star day, ripened yellow, moderate sized fruits of Madanaphala, which is free of worm infestation, should be collected.The fruits are wrapped in hay and cow dung paste and dried. It is kept immersed for 8 days in a heap of hay, black gram, green gram, horse gram etc.
After 8 days, when it becomes soft and starts emitting a honey-like smell, it is taken out, dried. Then the seeds are removed. It is ground with ghee, butter, honey and sesame paste and dried.
Thus obtained powder is preserved in a clean container and used for therapeutic purposes. (Charaka Samhita Kalpa Sthana 1/13)
Madanaphala for Vamana
How to use Madanaphala for Vamana?
For the patient who is fit for Vamana procedure, he should first be made to undergo Snehana (oil treatment) and Swedana (sweating treatment).
On the previous night he should be administered with Kapha increasing food like meat soup, milk, curds, black gram etc.
Next day, yavagu is given first. Then Madanaphala is given along with a little ghee. For this, the previous day, Madanaphala should be soaked in the decoction (Kashaya) of Yashtimadhu, Kovidara, Kadamba, Samudraphala, Bimbi, Shanapushpi, Arka, Apamarga.
Ayurvedic medicines
Ayurvedic medicines with Madanaphal ingredient –
Aragwadhadi Kashayam, Aragwadhadi Ghrita – useful in skin diseases including psoriasis.
Arimedadi Thailam – used for oil pulling in teeth and gum disorders
Bala Tel – useful in cough, cold, asthma etc.
Madanaphala choorna, Madanaphaladi taila, Madanaphaladi lepa, Pindeetaka yoga, Arimedadi taila, Ashwagandhadi taila, Phalavarti etc are its formulations.
Why is Madanphal not directly available in the open market? How to get it?
Because it can induce vomiting and related complications, it is not sold openly. If you are a common man, you do not need it unless prescribed by an Ayurveda doctor. If the Ayurveda practitioner has prescribed it to you, he himself will provide it. It is usually available in Ayurveda Panchakarma centers locally.
Research
Scientists have evaluated its anti inflammatory, anti histamine activity, broncho dilating properties, anti bacterial action, immuno-modulatory activity etc .
Interaction with medicines, supplements
Can this be used while taking Homeopathic medicine?
Yes. This product does not react with homeopathic medicine.
Can this medicine be continued while taking supplements like multivitamin tablets, Omega 3 fatty acids etc?
Yes. Generally, this product goes well with most dietary supplements. However, if you are taking more than one product per day, please consult your doctor for an opinion.
With western
medicines
Seek your
doctor’s advice if you are taking this product along with other western
(allopathic / modern) medicines. Some Ayurvedic herbs can interact with modern
medicine.
If both Ayurvedic and allopathic medicines are advised together, then it is
best to take Allopathic medicine first, wait for 30 minutes and then take the
Ayurvedic medicine.
Sthanika Karma (Systemic Action)
External – Its bark has Anti inflammatory, Analgesic, and wound cleansing properties. External application of its paste is indicated in Arthritic pain (Amavata) , joint inflammation. In boils its paste can be applied. Decoction can be used for wound cleansing. Fruit powder is beneficial for abdominal colic pain (External application on Navel region).
Nervous System – Decoction of its bark is indicated in various types of vata rogas. (Diseases due to vata dosha imbalance)
Digestive System – It is considered as the best vamana medicine (Herbs which induce vomiting) . Its bark, fruit and seed can be used for this purpose. Fruit has Anthelmintic property and facilitates the movement of vata dosha in normal direction. Bark is Absorbent. It can be used as a vamana dravya in conditions like constipation, Helminthiasis, Phantom tumor etc.
Circulatory System – Purifies the blood. Indicated in inflammatory conditions.
Respiratory System – Eliminates vitiated kapha dosha. Indicated in Cough, Breathing disorders, Rhinitis.
Skin – Indicated for skin disorders.
Tapakrama – Jvaraghna
Satmikarana – Act as Aphrodisiac, rejuvenative, Anti poisonous, Promote body strength, Its leaf bud decoction is indicated in snake bite poisoning, that induce vomiting and purgation, which helps to remove toxins from the body. Its paste can be used to apply externally over skin. Also indicated in Aconitum and opium poisonings.
Reproductive System – Indicated in dysmenorrhea and in conditions like delayed labor etc.
Skin – Indicated in various r skin disorders
Tapakrama – Indicated in Fever as it stimulate sweat production
Satmikarana – Beneficial in obesity and in poisonous conditions.











6 comments
Dr Megha
May I know the chemical composition of Madanphal draya ,also may I know details about putoyavanyadi kalka plz. Thanks
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)
Puto Yavanyadi Kalka is told in the context of A.Hrudaya Kalpasthana 4/2.
पूतो यवानीफलबिल्वकुष्ठवचाशताह्वाघ पिप्पलीनाम् ।
कल्कैर्गुडक्षौद्रघृतैः सतैलैर्युक्तः सुखोष्णो लवणान्वितश्च ॥ २ ॥
Ghana = Musta
Chemical composition of Madanaphala
Root bark – triterpene, -1-keto-3-hydroxyoleanane,
Bark – mannitol, saponins, coumarin glycosides,
Leaves – contain an iridoid-10- methylixoside, an iridoid glycoside,
Ripe fruit – glycosides, randioside A, mollisidial triterpenoid glycosides and randianin, six saponins-dumetoronins A to F.
Yatender Sharma
How to do shodhan of madanphala
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)
Collection method is explained in the article above. It is the method of Shodhana.
Meera
Where to buy madanaphal choornam in Kerala
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)
Hi, because it can induce vomiting, it is not sold directly in the open market. I suggest you to contact any Ayurveda Panchakarma center locally. They will be having it.