Nagabala – Uses, Side Effects, Research, Medicines
Nagabala is an Ayurvedic herb, used for relieving Vata imbalance, for aphrodisiac and rejuvenative effects.
Botanical name – Sida veronicaefolia
Synonym – Sida cordata (Burm. f.) Borssum,
Sida humilis Cav.
Family – Malvaceae
There are many herbs used as this herb like – Grewia populifolia, Sida spinosa, Urena lobata, Grewia hirsuta.
Overall, it has been decided that Nagabala – is Sida veronicaefolia and Gangeruki is Grewia hirsuta.
The herb Sida veronicaefolia is distributed all over India.

Table of Contents
Morphology
Grewia hirsuta is a shrub grows up to 1 meter tall. Leaves are simple, densely covered with short hairs, lance shaped, arranged alternately, margins are toothed. Flowers are white in color, borne in axillary chymes. Fruits globose in shape, 4 lobed, hairy and red in color when ripe.
Distribution
Grewia hirsuta is found in India, Bangladesh and Sri langa. In India it is found in Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Maharastra, Odisha and Tamil Nadu.
Vernacular names
Vernacular names of Grewia hirsuta
Assamese – Hukta-pata, Huktapata, Hukta pata, Xahta
Bengali – Kukurbicha
Hindi – Kakarundah, Kukurbicha, Phrongli
Kannada – Gandaudipe, Chikkudipe, Dadachelu, Udipe
Marathi – Govli
Oriya – Kakarolim
Tamil – Kalunnu, Tavuttai, Tavadu, Tavidu
Telugu – Jibilika, Chimachipuru, Chitti Jana, Jibilike
Synonyms
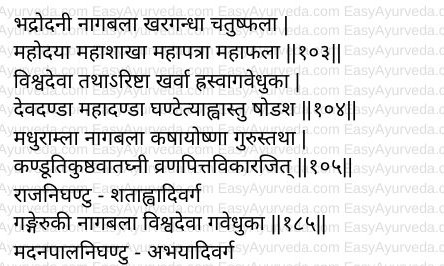
Synonyms in Sanskrit : Gangeruki, Vishvadeva, Kharagandhika, Khanda, Hrasva Gavedhuka – Similar properties of godhuma
Bhumibala – Resembles bala, but it crawls on the ground
Jhasha – Alliviate vata dosha
Kaala, Kharadhanvanika, Ghantala, Pushpagavedhuka, Bhadrodani, chatushphala,
Mahodaya, Mahashaka, Mahapatra, Mahaphala, Hrishvagavedhuka, Devadanda, mahadanda
Remedies
1. In kshatakshina (consumption), powder of nagabala is mixed with ghee and honey. This mixture is taken in the morning. (Gadanigraha 2.9.65)
2. Nagabala root powder along with Arjuna bark is consumed with milk to treat heart diseases, breathing difficulty and cough. This is also used as the best rejuvenating recipe. It is mentioned that if this is taken for 1 year the man increases his life span. (VM 31/15-16)
3. In burning micturition, nagabala fruits and flowers are used.
4. Poultice prepared with nagabala leaves is applied externally on cuts and bruises.
5. Nagabala root bark is used in vaginal white discharge and other genito urinary infections
Nagabala Rasayana
- Root of Nagabala is consumed as rasayana with milk for one month. Initial dose of 5 grams is taken and then it is gradually increased up to 40 grams. Only milk diet is followed while consuming this recipe. (Ref – Charaka Samhitha Sutra sthana 11/91 – 92)
- During chronic cough, chest injury, chronic bronchitis, tuberculosis etc conditions, 48 ml of juice of roots of Nagabala is consumed daily along with milk. The dose is increased by 6 ml, everyday. This is continued for one month. During this period, the patient should drink only milk and abstain from eating solid foods. This recipe is best to promote nourishment, lifespan, strength, skin health and immunity. (Reference: Astanga Hrudayam, Kasa Chikitsita Adhyaya, 3/118-119.)
Shloka reference:
Nagabala Rasayana
पिबेन्नागबलामूलस्यार्धकर्षाभिवर्धितम् ॥ ११८ ॥
पलं क्षीरयुतं मासं क्षीरवृत्तिरनन्नभुक् ।
एष प्रयोगः पुष्ट्यायुर्बलवर्णकरः परम् ॥ ११९ ॥
मण्डूकपर्ण्याः कल्पोऽयं यष्ट्या विश्वौषधस्य च ।
pibennāgabalāmūlasyārdhakarṣābhivardhitam || 118 ||
palaṃ kṣīrayutaṃ māsaṃ kṣīravṛttiranannabhuk |
eṣa prayogaḥ puṣṭyāyurbalavarṇakaraḥ param || 119 ||
maṇḍūkaparṇyāḥ kalpo’yaṃ yaṣṭyā viśvauṣadhasya ca |
Properties
Madhura – sweet in taste
Amla –Sour taste
Kashaya – Astringent
Ushna – Hot
Guru (heavy to digest)
Katu – Pungent
Tikta – Bitter
Vataghni – Balances Vata
Vranajit – heals wounds
Pittavikarajit – Relieves disorders of Pitta
Balya – improves strength
Raktapittaapaha – relieves bleeding disorders
Kshaayapaha – relieves tissue emaciation and weakness
Vrushya – natural aphrodisiac
Rasayani – Acts as rejuvenative.
Part Used, Dose, Anupana
Part used – Roots
Dose – 3-5 grams
Anupana – Honey, Ghee, Milk
Chemical constituents
Quinazoline, gossypol, Sterculic acid, Linoleic acid etc.
Ayurvedic medicines
Important Ayurvedic medicines with Nagabala as ingredient:
Lakshadi Guggulu – A famous Ayurvedic tablet used to strengthen bones
Manasamitra Vatakam – A famous Ayurvedic medicine used in treating neuro-psychological disorders
Maha Vishagarbha Taila – An Ayurvedic oil, used in sciatica, stiffness etc.
Qualities of place of collection
Place of collection of Nagabala:
Reference: Charaka Samita Chikitsa 1.2/11
Roots of Nagabala should be collected from a field having the following characteristics:
It should be located in Jangala Desa (arid)
Kusha plants – Desmostachya bipinnata should have thickly grown in this field
The earth of the field should be unctuous, black and sweet or it should be golden in color
The field should be free from poisons, wild animals and the faults of wind, water and fire
It
- should not be a cultivated land;
- should not have anthills;
- should not be a crematorium;
- should not have a Chattya (sacred temple);
- should not be grown in Usara (saline) land and
- should not have residential houses
This land should have been exposed to wind, water and sun according to different seasons.
Quality of Nagabala to be collected
The plants of Nagabala should have the following characteristics:-
It should not have been injured
There should not be any big tree by their side (Adhyarudha) to afflict them
It should neither be too young, nor too old
It should be full of Veerya (potency).
Collection of herb
Collection of Nagabala:
- Nagabala is to be uprooted in the month of Tapas or Magha (January- February) and Tapasya or Phalaguna (February-March)
- By a person, who is clean, Prayata (devoted) who has offered prayer to the Gods
- Persons who are Dvijatis (Brahmanas, Kshatriyas and Vaishyas) have recited Swasti – auspicious chants namely, the Chala or Indra Muhurta.
- The roots are made to a thin paste or powder and taken with milk or honey in the morning.
Sanskrit verses
Classical categorization
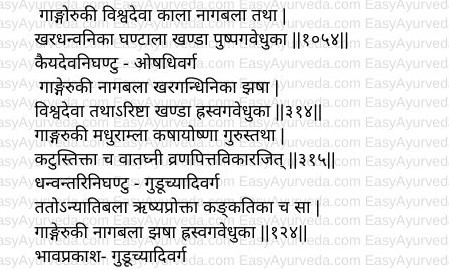
Kaiyadeva nighantu – Aushadi varga
Dhanvantari Nighantu – Guduchyadi varga
Bhavaprakasha Nighantu – Guduchyadi varga
Raja Nighantu – Shatavahadi varga
Madanapala Nighantu – Abhayadi varga
Interaction with medicines, supplements
Can this be used while taking Homeopathic medicine?
Yes. This product does not react with homeopathic medicine.
Can
this medicine be continued while taking supplements like multivitamin tablets,
Omega 3 fatty acids etc?
Yes. Generally, this product goes well with most
of the dietary supplements. However, if you are taking more than one product
per day, please consult your doctor for an opinion.
With western
medicines
Seek your
doctor’s advice if you are taking this product along with other western
(allopathic / modern) medicines. Some Ayurvedic herbs can interact with modern
medicine.
If both Ayurvedic and allopathic medicines are advised together, then it is
best to take Allopathic medicine first, wait for 30 minutes and then take the
Ayurvedic medicine.
Controversy
Chakrapani considered Gangeruki as nagabala fruit. Acharya P V Sharma considered Grewia hirsuta as Nagabala
Prof. K C Chunekar quotes that 4 species are considered as Nagabalaviz.
1. Sida veronicaefolia
2. Sida humilis
3. Sida spinosa
4. Grewia hirsuta











7 comments
Ravi
Difference between Bala, Atibala & nagabala
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)
Bala – Sida cordifolia – https://www.easyayurveda.com/2012/10/03/country-mallow-sida-cordifolia-ayurveda-details-health-benefits/
Atibala – Abutilon indicum – https://www.easyayurveda.com/2012/10/03/abutilon-indicum-atibala-ayurveda-details-usage-health-benefits/
Dipak Fulzlele
Collection of the herb – Nagabala:Persons who are Dvijatis (Brahmanas, Kshatriyas and Vaishyas)
– Does this herb will loose its medicinal value if it is collected by the person other than “Dvijatis”.
– Does the herbs/medicines also follow casteism?
Dr J V Hebbar MD(Ayu)
There is mistake in understanding the concept.
In ancient times, people were labelled with caste, based on their work and not on by-birth basis.
After the basic education from Gurukula, the Guru used to assign a person who is good in Sanskrit and studies, to continue as Brahamana, who is good in commerce, finance, as Vaishya, who was physically fit, as Kshatriya and so on.
So, casteism is nothing to do with Ayurveda or any form of science.
Science is pure, and it does not differentiate people.
Anyone who is good at mind and clean in body (physical health), is good to collect any Ayurvedic herbs.
Krishna Prasad
Quite informative ????
Krishna Prasad
Any Ayurvedic remedy for diabetic neuropathy
Pramod Hanumansingh Parihar
Nice information. How the creatinine levels can be lowered?