Indriya Pancha Panchaka: 5 Fives Of Sense Organs
By Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ay) and Dr Manasa, B.A.M.S
Indriya Pancha Panchaka are collection of 5×5 = 25 elements (terms) related to the Indriyas. They define the functional and structural components of the Indriyas in brief. Charaka has enlisted them in Charaka Sutra Sthana Chapter 8.
Table of Contents
Indriya Pancha Panchakas
इह खलु पञ्च इन्द्रियाणि, पञ्च इन्द्रिय द्रव्याणि, पञ्च इन्द्रिय अधिष्ठानानि, पञ्च इन्द्रिय अर्थाः, पञ्च इन्द्रिय बुद्धयो भवन्ति इति उक्तम् इन्द्रिय अधिकारे।(च.सू.८/३)
Table of Indriya Pancha Panchakas –
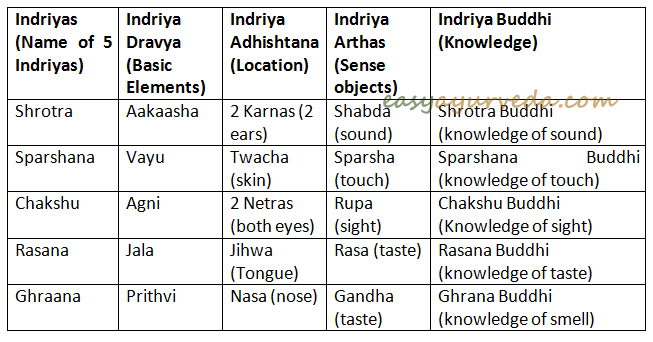
Pancha Indriyas
तत्र चक्षुः श्रोत्रं घ्राणं रसनं स्पर्शनम् इति पञ्च इन्द्रियाणि।(च.सू.८/८)
The Indriyaas are 5 in number. They are –
तत्र चक्षुः श्रोत्रं घ्राणं रसनं स्पर्शनम् इति पञ्च इन्द्रियाणि।(च.सू.८/८)
The Indriyaas are 5 in number. They are –
- Chakshu Indriya – helps in seeing and perceiving different objects which have different shapes, sizes and colors
- Shrotra Indriya – helps in hearing and perceiving different sounds
- Ghraana Indriya – helps in smelling and perceiving smells of various types
- Rasana Indriya – helps in tasting and perceiving different types of tastes
- Sparshana Indriya – helps in touching and perceiving different types of touch
- Read related: Jnana and Karma Indriyas: Organs Of Sense And Function
It is important to note that these Indriyas are different from the anatomical sense organs. Chakshu Indriya is different from the Netra or Chakshu (the eye). Chakshu or Netra i.e. the anatomical eye (indriya adhishtana) is the organ of sight which is visible to us. But the functional unit of Chakshu is Chakshu indriya which cannot be seen. Indriyas are present in minute form within their Indriya adhishtanas (anatomical organs) and help in perceiving their related senses when they come into contact with their objects. Though eyes are 2 in number, the chakshu indriya is only one, the functional component of perception of vision. Similarly this concept should be understood with respect to other Indriyas and Indriya Adhishtaanas also.
Indriya is only one. When it comes in contact with Chakshu, it helps in perception of sense objects of vision (rupa) and will be called as Chakshu Indriya. When the same Indriya comes in contact with Shrotra Indriya, it helps in perceiving sound and will be called as Shrotra Indriya. The concept should be likewise understood with other indriyaas also.
Read related: Importance Of Soul In Perception Of Knowledge: Atma Jnana
Pancha Indriya Dravyas
खं वायुः ज्योतिः आपो भूः इति।(च.सू.८/९)
Indriya Dravyas are the elements of nature which take part in the formation of Indriyas. Each Indriya is formed by all Mahabhutas or Indriya Dravyas but will be predominant in only one. The 5 Indriya Dravyas are as below mentioned –
- Aakasha Mahabhuta or Space (ether) element helps in the formation of Shrotra Indriya
- Vayu Mahabhuta or Air element helps in the formation of Sparshana Indriya
- Agni Mahabhuta or Fire element helps in the formation of Chakshu Indriya
- Jala Mahabhuta or Water element helps in the formation of Rasana Indriya
- Prithvi Mahabhuta or Earth element helps in the formation of Ghrana Indriya
Pancha Indriya Adhishtaanas
अक्षीणि कर्णौ नासिके जिह्वा त्वक् च इति।(च.सू.८/१०)
Indriya Adhishtaanas are the sites or organs where the Indriyas are located. Thus Adhishtanas are the anatomical places where their functional faculties i.e. Indriyas are embedded. The anatomical organs of sense i.e. eye, ear, nose, tongue and skin which exhibit their related senses are the Indriya Adhishtaanas.
The 5 Indriya Adhishtaanas are as below mentioned –
- Akshi or Netra – Anatomical eyes, adhishtaana (site) of Chakshu Indriya
- Karna – Anatomical ears, adhishtaana (site) of Shrotra Indriya
- Nasa – Anatomical nose, adhishtaana (site) of Ghraana Indriya
- Jihwa – Anatomical tongue, adhishtaana (site) of Rasana Indriya
- Twak – Anatomical skin, adhishtaana (site) of Sparsha Indriya
Pancha Indriya Arthaas
शब्द स्पर्श रूप रस गन्धाः।(च.सू.८/११)
Indriya Arthaas are the sense objects and are specific for different Indriyaas. The 5 Indriyaarthaas are as mentioned below –
- Shabda – or sound is the Indriyaartha of Shrotra indriya
- Sparsha – or touch (feel) is the Indriyaartha of Sparshana Indriya
- Roopa – or sight (vision) is the Indriyaartha of Chakshu Indriya
- Rasa – or taste is the Indriyaartha of Rasa Indriya
- Gandha – or smell is the Indriyaartha of Ghraana Indriya
Pancha Indriya Buddhis
चक्षु बुद्ध्याधिकाः ताः पुनः इन्द्रिय इन्द्रियार्थ सत्त्व आत्म सन्निकर्षजाः, क्षणिका निश्चयात्मिकाः च, इति एतत् पञ्च पञ्चकम्।(च.सू.८/१२)
Indriya Buddhis are the basic intelligence or knowledge embedded in the Indriyaas which enable them to perceive the knowledge of the related object and not others. They are responsible to generate Pancha Indriya Gnaana i.e. Knowledge related to 5 Gnana Indriyaas or sense organs. This knowledge is possible due to the inter-relation or axis of Indriya-Indriya Artha-Manas-Buddhi-Aatma. The knowledge gained due to this equation is of two types. They are:
Kshanika Indriya Gnaana – Momentary knowledge of objects, which happens immediately after the contact of Indriya and Indriyaartha. This knowledge is momentary and short lived. Example, seeing a dog and immediately understanding it as dog
Nishchayatmika Indriya Gnana – Decessive knowledge of objects, which happens after a certain time period following Indriyaartha Samyoga. Delay in gaining knowledge in this instance is due to the analytical property of Indriya Buddhi. In this instance, the buddhi needs time to analyze the input information and create an understanding of it. Example, reading a new subject and understanding it slowly
This Indriya Buddhi helps an indriya to perceive its related information. Example the Chakshu buddhi or the inborn intelligence of the Chakshu Indriya (located in the eyes) knows to perceive Rupa (form, color, shape, size etc) and not Gandha (smell) which belongs to the Ghrana Indriya (located in the nose). This should be understood on similar lines for the other Indriya Buddhis.
The 5 Indriya Buddhis are as below mentioned –
- Chakshu Indriya Buddhi – Knowledge or information of Rupa (Sight, vision, form) embedded in the Chakshu Indriya, helps to see and understand
- Shrotra Indriya Buddhi – Knowledge or information of Shabda (Sound) embedded in the Shabda or Shrotra Indriya, helps to hear and understand
- Ghraana Indriya Buddhi – Knowledge or information of Gandha (Smell) embedded in the Ghraana Indriya, helps to smell and understand
- Rasana Indriya Buddhi – Knowledge or information of Rasa (Smell) embedded in the Rasana Indriya, helps to taste and understand
- Sparshana Indriya Buddhi – Knowledge or information of Sparsha (Touch) embedded in the Sparsha Indriya, helps to feel (touch) and understand
- Click to Consult Dr Raghuram Y.S. MD (Ayu)







