Plants And Humans: Growth And Relationship
Article by Mr AK Shyam.
Plants have had a tremendous role in the human development ever since the early civilization and perhaps continue to shoulder much greater role in the future as well. There has been a parallel between plants and humans so far as the evolutionary aspect is concerned. While plants showed increasing complexity from the earliest form – Algae to Angiosperms of today through bryophytes, lycopods, ferns and Gymnosperms; the earliest documented members of genus HOMO evolved around 2.3 million years ago. Homo erectus and Homo erg aster spread through Africa, Asia and Europe are believed to have used fire and complex tools. Modern human who evolved in Africa = Homo sapiens, forerunner of anatomically modern humans evolved between 400,000 and 250,000 years ago.
Animals including humans need plants which, brought in civilization on earth. Human settlements came up on a realization that plants sustain their lives not only in providing food but also – Oxygen (Plants convert carbon dioxide into oxygen); Housing; Materials wood being key material; medicine and above all, unbeatable aesthetics.
Only, plants have the ability to combine solar energy with air and water (combined with minerals) to create vegetative as well as nutritive products (fruits, nuts, tubers)
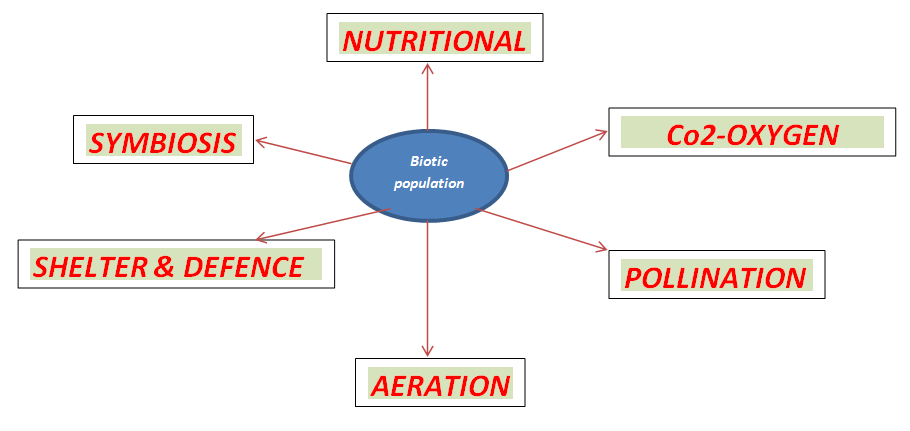
There has been a close interrelationship between plants and animals. The biotic environment (Biosphere) that they create is indeed complex and assigns a role to every single component. The delicate nutritional interdependence is quickly balanced with minor fluctuations. Biotic population of the ecosystem has various types of interdependence as it has been indicated below. Each of these interrelationship is indeed quite complex and is an education by itself IF, one wishes to observe carefully and learn.
The book is intended to guide you through some of these magnificent intricacies that nature has blessed us with which, We hardly notice when we are a part of the larger ‘Ecosystem’.
Let me start building the outline with a broad definition of ‘Ecology’ as we learnt it in our college days – The science that deals with interaction among organisms and the environment. Ecology covers both biology and earth science and delves with life processes, interactions and adaptations.
Most environmentalists consider Land (soil) Air and Water as the principal domains of the Environment. Taking the first letter of these domains, – LAW, you hear nature warranting that they have their own principles governing the surroundings. The fact the plants are anchored in the land (soil); aerial parts exposed to Air and drawing nutrients through water are ideal instruments to record changes in these domains as they have an influence on the plant morphology and anatomy.
Table of Contents
Land (Soil)
LAND (SOIL):
We, as mentioned earlier cannot distinguish biology from earth sciences. Earth science (Geology) happens to be the base for the plant populations that we see around the world. It is evident that the vegetational composition is entirely different from place to place depending upon the base geology and consequently, soil nature.
Soil consists of minerals and some organic matter which differ from their parent materials in texture, structure, & color, chemical, biological and other characteristics. Soil is the end product of parent material, climate, organisms and time. Soil is composed of broken rock particles (basic parent material) altered by physical, chemical and biological processes.

Soils, a mixture of solids, water and gases are filled with pore spaces. Igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic rocks as the base (parent material) undergo physical and chemical weathering in its transformation into soil. Quartz (SiO2); Calcite (CaCO3); Feldspar (KAISi3o8) and Mica (K(Mg,Fe)3AlSi3O10(OH)2 are the parent material for soil.
‘Residual’ materials are that have weathered in place from primary bedrock; ‘Transported’ are that have been deposited by water, wind, ice or gravity; ‘Cumulus’ is organic matter that grows and accumulates in place.
Physical disintegration begins in the earth exposed to lower pressures near the surface. Temperature fluctuations cause expansion and contraction splitting the rock along the lines of weakness. Water may then enter the cracks and freeze causing the physical splitting of material along the path toward the center of the rock. Wetting and drying cycles result in abrasion to fine size of soil particles – similar to the water, wind and gravity transportation.
Chemical decomposition involves ‘Solution’ of salts in water; ‘Hydrolysis’ transformation of polar molecules by splitting of the intervening water; ‘Carbonation’ carbonic acid (carbon dioxide + water) transforms calcite into more soluble calcium bicarbonate; ‘Hydration’ inclusion of water in mineral structure allowing easy decomposition; ‘Oxidation’ – mineral compound swells and increases its oxidation number; ‘Reduction’ oxidation number is reduced leaving them unstable, more soluble and internally stressed and easily decomposed. ‘Hydrolysis’ and ‘Carbonation’ are the most effective.
Mineral precipitation and temperature, the primary climatic influence result in distinctive characteristic climate zones. Climate has a direct influence – Shallow accumulation of lime (caliche) In low rainfall areas; acid soils in humid areas; soil erosion on steep hills; eroded material gets deposited downstream; intense chemical weathering, leaching and erosion in warm and humid regions.
Wind & precipitation have greater impact on the soil composition as they affect movement of ions and particles through soil thus resulting in different soil profiles. Soil profiles are distinct in wet and cool climates (organic materials accumulate) than in wet and warm climates (organic materials are rapidly consumed)
Vegetation cover and biological activity further influences the soil characteristics through modification of chemical reactions.
Air
AIR ENVIRONMENT
Gases and particles that vary with spatial and time scale form the earth’s atmosphere. They have a tremendous influence on climate, air quality, stratospheric ozone and weather. Human health and ecosystem vitality depend on the interactions between these components. Efforts have been made to understand how atmospheric constituents other than carbon dioxide (CO2) affect climate. Atmospheric fine particles (Aerosols) can either have cooling or warming effect depending upon factors influencing them.
Earth’s atmosphere near the surface is composed of Nitrogen and Oxygen primarily as they together form 99% of the gases in the atmosphere.
| Nitrogen | 78.084% |
| Oxygen | 20.95% |
| Argon | 0.934% |
| Carbon Dioxide | 0.036% |
| Neon | 0.0018% |
| Helium | 0.0005% |
| Methane | 0.00017% |
| Hydrogen | 0.00005% |
| Nitrous Oxide | 0.00003% |
| Ozone | 0.000004% |
Water
WATER ENVIRONMENT:
About 70% of the earth’s surface is covered with water. Ninety-seven percent of the water on the earth is salt water. Salt water is filled with salt and other minerals, and humans cannot drink this water. Although the salt can be removed, it is a difficult and expensive process. Two percent of the water on earth is glacier ice at the North and South Poles. This ice is fresh water and could be melted; however, it is too far away from where people live to be usable.
Less than 1% of all the water on earth is fresh water that we can actually use. We use this small amount of water for drinking, transportation, heating and cooling, industry, and many other purposes.
A water molecule has three atoms: two hydrogen (H) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom. That’s why water is sometimes referred to as H2O. A single drop of water contains billions of water molecules. Pure water is tasteless, odorless, and colorless. Water can occur in three states: solid (ice), liquid, or gas (vapor).
Solid water—ice is frozen water. When water freezes, its molecules move further apart, making ice less dense than water. This means that ice will be lighter than the same volume of water, and so ice will float in water. Water freezes at 0° Celsius, 32° Fahrenheit.
Liquid water is wet and fluid. This is the form of water with which we are most familiar. We use liquid water in many ways, including washing and drinking.
Water as a gas—vapor is always present in the air around us. You cannot see it. When you boil water, the water changes from a liquid to a gas or water vapor. As some of the water vapor cools, we see it as a small cloud called steam. This cloud of steam is a mini version of the clouds we see in the sky. At sea level, steam is formed at 100° Celsius, 212° Fahrenheit.
The water vapor attaches to small bits of dust in the air. It forms raindrops in warm temperatures. In cold temperatures, it freezes and forms snow or hail. The water cycle or hydrologic is a continuous cycle where water evaporates, travels into the air and becomes part of a cloud, falls down to earth as precipitation, and then evaporates again. This repeats again and again in a never-ending cycle. Water keeps moving and changing from a solid to a liquid to a gas, over and over again.
Precipitation creates runoff that travels over the ground surface and helps to fill lakes and rivers. It also percolates or moves downward through openings in the soil to replenish aquifers under the ground. Some places receive more precipitation than others do. These areas are usually close to oceans or large bodies of water that allow more water to evaporate and form clouds. Other areas receive less precipitation. Often these areas are far from water or near mountains. As clouds move up and over mountains, the water vapor condenses to form precipitation and freezes. Snow falls on the peaks.
Water on earth today has been here for millions of years. Because of the water cycle, water moves from the earth to the air to the earth again. It changes from solid to liquid to gas, over and over again.
Land and Plants
LAND AND PLANTS
There is a strong relationship between land and plants that has been brought out earlier, plants are anchored in soil (derived from different geological formations) and exposed to air environment.
- Parent Material – What was there before soil formation began? (Possibilities include mud deposited by a river, sand deposited by ocean, rock that weathers and breaks down, etc.);
- Organisms – usually refers to vegetation and microorganisms, but includes the complete biological community;
- Climate- on both large and small scales; determines the rate at which chemical reactions can take place. Soils in low-lying areas are saturated closer to the surface for longer periods of time than soils on higher ground. Living organisms must have ways to adapt to limited air and water availability. Conversely, organisms on the topographic high have to adapt to xeric conditions.
- Relief – or landscape position;
- Time – Young soils show minimal profile and as they mature, additional subsurface horizons are added.
Alluvial soil in India: By far the largest and most important soil group composed of sediments deposited by rivers and waves. Usually, they are deficient in nitrogen and humus – requires fertilizers.
Black soil in India: Formed due to solidification of lava spread over a large areas during volcanic activities; black due to iron and aluminum fit for cotton cultivation, cereals, oil seeds, citrus fruits, tobacco and sugarcane. Although they lack phosphorous, nitrogen and organic matter have high moisture retention quality.
Red soil in India: formed due to decomposition of ancient crystalline rocks (Granite & gneisses) rich in minerals (iron and magnesium). Although Deficient in nitrogen, humus and phosphorous but, rich in potash.
Laterite soil in India: Formed under conditions of high temperature and heavy rainfall with alternate wet and dry periods which leads to leaching away of siliceous matter and lime. Soil is rich in oxides of iron and aluminium and is best for tea, coffee, rubber, cinchona, coconut, rice and millet cultivation.
Forest and Mountain soils: Formation is governed by organic matter characteristic derived from forest growth accordingly, rich is humus but, deficient in potash, phosphorous and lime.
Arid and desert soils: The mantle of sand inhibits soil growth – phosphorous is high however, phosphates and nitrates make it rich wherever moisture is available.
Saline and alkaline soils: Some of the salts are transported in solution by rivers and canals and this makes it unfit for agriculture.
Peaty and Marshy soils: Originate in humid regions due to accumulation of organic matter and accounts for soluble salts and 10-40% organic matter.
Generally, ideal soils are categorized into – minerals (45%), organic matter (5%), air (25%) and water (25%) which means that plants derive most of its nutrients for its growth and development from soil. The fine earth fraction of soil Sand (2 mm – 0.05 mm), Silt (0.05 -0.002 mm) and clay (<0.002 mm) are the mineral portion of the soil.Being a derivative of parent material (ROCK), they (sand and silt) are inert and determine the water holding potential. Clay minerals form at / near earth’s surface and most of them belong to Phyllosilicates and carry a net negative charge. This is what makes clay responsible for Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC).
CEC is significant in that cations moving through a soil in solution may be held by the soil – these cations (usually metals) are plant nutrients, like potassium, calcium, and magnesium. The loosely held nutrients can then be taken up by plant roots or by other soil organisms. This is one of the ways that soils store nutrients for future biological use.
The cation exchange property is also responsible for the soil’s ability to filter some environmental contaminants from water.
Soil texture determines nutrient/water holding capacity, and the air movement and consequently healthy plant growth and other organisms. Soil Organic Matter (SOM) is another important component of soil and the nature depends on the type of SOM – Fresh or residual. Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorous and sulfur are typical composition of SOM BUT, may also include others as well.
A typical profile of a mature soil includes the following horizons:
- O horizon(O stands for organic) includes litter layer, duff, and sometimes a humus layer and are differentiated by the degree of decomposition of the organic matter. This horizon is often missing in cultivated soils, manicured lawns, and severely eroded soils.
- A horizon contains a mixture of organic and mineral components. This layer most closely resembles the ideal soil; commonly referred to as topsoil.
- E horizon (E stands for elluvial) is stripped of much of its clay and sometimes staining agents, and is thus often lighter in color than the others. It is lower in organic matter than the A horizon.
- B horizon is a zone of illuviation (accumulated substances—clays, organic matter, iron and aluminum compounds) that have been leached from overlying horizons.
- C horizon is lightly weathered parent material.
Plant distribution
PLANT DISTRIBUTION:
We do not find monotonous spread of same variety throughout the world but, different types. You will find three major types and seven sub-types of vegetation in the world. Forests, Grasslands and Deserts are the three major types of natural vegetation with sub-type under each of them. Natural vegetation is entirely different from those planted by humans.
It is essential to make a difference between ‘Primary’ and ‘Secondary’ vegetation – the former being unspoiled forest in its original condition while the latter is in some way disturbed naturally or unnaturally and understandably, secondary vegetation have fewer variety of plants.
| NATURAL VEGETATION | ||
| FORESTS | GRASSLANDS | DESERTS |
| Tropical Rain forests
(Mainly along the equator between 23.50N and 23.50S of Equator) | Tropical Savannahs | Hot Desert Vegetation |
| Temperate Deciduous Forests
(Farther away from Equator – 23.50N & 66.50N AND 23.50S & 66.50S) | Temperate Grasslands | Cold Tundra Vegetation |
| Temperate Coniferous Forests
(Far from the Equator – Northern Hemisphere – between 600N & 700N of the equator) |
In fact, the temperature difference (less than 60C) and (above 200C) is what renders different types of natural vegetation. Similarly, rainfall, responsible for water requirements of plants is another factor that determines the forest type along with temperature. Very broadly, we could say, more than 1000 mm rainfall allows forest growth; rainfall between 200 to 1000 mm annually, facilitates grasslands and deserts receive less than 200 mm rain annually. It is here that one realizes the strong connection between vegetation and climate.
The third factor, soil is an equally important factor as an anchorage for plants. In addition to these three principle factors, altitude affects plant distribution as well.
Environmentalists, talk about the three principle domains – Land (soil), Air & Water – taking the first letter of these domains, we get a word ‘LAW’ as if nature proclaiming that it operates on its own principles and any intervention would disturb the balance to a great extent. I am afraid; we have ignored this powerful signal from nature
Natural vegetation is different at different altitudes – undergrowth restricted to the ground to about 5 meters; shrubs, climbers and epiphytes between 10 and 30 meters and canopy of large trees between 35-45 meters and beyond. Crowns of trees interlock to form continuous foliage cover so much so that light fails to penetrate through.
Plants benefits
BENEFITS OF PLANTS
In fact, human survival could not have been possible but for the vegetation cover as vegetation has a direct relationship with climate. Plants play a role in maintaining ‘Oxygen’ in the air so vital for survival of all living beings on earth; transpiring plants add water vapor in the air resulting in rainfall; wood of plants are used in furniture and they are known for their medicinal properties as well.
Plants have provided solutions to many a problem in the past and no wonder humans keep looking into plants for their solutions as the recent example demonstrates:
Quote..
“Taking a cue from fireflies, scientists have created the world’s first light producing plant, and you can have one for your very self. Bio glow’s autoluminscent plant the Starlight Avatar™, glows in the dark and could usher in a new era of living lights. The little plant has been engineered to produce its own light and will soon be up for auction.
Missouri-based Bio glow has been working on light-producing plants for a number of years and finally has one that they can sell. Starlight Avatar is an auto luminescent plant that generates light through its own pathways and does not require UV light or chemical additives. The light producing plant was made by taking an ornamental Nicotiana alata plant and introducing the light-emitting pathway from marine bacteria into its chloroplast genome. The genetically modified plant then glows a soft blue-green in the dark and could be used for decorative purposes, but is hardly bright enough to read with.
Bio glow hopes to improve their techniques and strengthen the light production capabilities. They foresee a time when the plants are used as decorative landscaping that could eliminate the need for night time lighting and decrease emissions from electricity use. Bio glow also hopes to create plants the emit red or other colored lights and maybe even use the plants to serve pollution or stress sensors.
Want your very own light producing plant? At the end of January, Bio glow will be auctioning off 20 Starlight Avatar plants with a starting bid of $1. The plants will come in their own cultivation boxes and are expected to produce light through their lifespan, which lasts about 2-3 months.”Unquote
Environment around plants
ENVIRONMENT AROUND PLANTS – MICRO AND MACRO ENVIRONMENT
While some of the plants of 260,000 plant species are so small that they can barely be seen, others are taller than people and animals (largest living plant is Sequoia trees of California). Some measure 88 meters tall and 9 meters wide. Cellulose enables plants to stand upright without either an internal or external skeleton.
Plants are the primary producers sustaining all forms of life on earth as animals (including humans) are incapable of making their own food. It is indeed quite common that carbon dioxide released by humans (respiration) to a good extent is utilized by plants to return ‘Oxygen’ vital for humans. Carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight are converted into sugar and starch by plants which, basically provides energy for plants to grow and produce flowers and seeds. Select plants have medicinal value as well. Most importantly, plants are beautiful.
Humans have failed to recognize the sacrifice that plants have made as the backbone of ‘life sustenance’ on earth.
Life cycle
LIFE CYCLE :
Life cycle of plants has been another way of categorizing plants into Annual (life cycle is completed inside one year). Biennial plants starts produces vegetative structures and food storage in the first year and in the second year, flowers, fruit and seed complete the life cycle. Perennials live for several years and after reaching maturity, produce flowers and seeds. Perennials include herbaceous, woody, deciduous, Evergreen, Tender and hardy plants.
Plant’s environment is made up of – sunlight, temperature and precipitation. Soil and other plants and animals that live in the same area are also part of this environment. Natural communities are never the same although many may resemble one another. We may sometimes wonder as to why tall trees are not seen in grassland or for that matter cacti not found in Arctic.
The natural unit comprises of plants, animals and microorganisms in an area functioning together with all non-living factors of environment. Climate of a larger area such as region or country is referred to as ‘Macro-environment’ while variations in the localized climate are referred to as ‘Micro-environment’.
When we look at the microenvironment around a unit area, we find plants at the ground level, middle level and top level. The nature of these plants is entirely different as are their physiology dependent on what they absorb into them. The lesson that such a group of plants teach us is ‘Harmonious existence’ without any complaints.
Small and a specific area distinguish itself from its immediate surroundings by the amount of incident light, degree of moisture and range of temperature. The ground cover comprises of annuals and biennials whereas the middle and top levels comprise of perennials. The variety of species (Natural) packed in a unit area co-exist without any complaint – the beauty is that the character of each species is distinct although the resources (water, air and soil nutrients) in the specified area is the same. The selective preference to resources is something unique which get converted to different products among the ground, middle and top level plants – signifying physiological differences transforming them (resources) into chemicals of difference.
“Compare this to a classroom where teachers and infrastructure are the same like resources available for plants in a unit area. We do find students of different degree of understandings. Similar to plants of different category, students excel in different professions with the same education imparted to them. Institutional environment could be different similar to the different vegetational patterns.
Plant communities present a variety of not only the micro but, even macro environmental factors responsible for a combination of species in a particular area. Consequently, the character and composition of species are an indirect measure of resources that are different from one another. This is reflected in the usage of right key of requirement namely – chemistry, medicine, economic importance and also applied aspects like, geo-botany.
Geo-botanical exploration is based on the affinity of select plants to a particular element which, they absorb in higher concentrations than normal plants. This high concentration has been noticed to bring out recognizable morphological changes, leading to locating mineral deposits.
This special affinity was pretty useful in building up green cover over ‘Fly ash’ of Coal based thermal power plant where ash ponds are considered a nuisance.
The different parts of a plant – Roots, Stem, and leaves perform distinct functions in the healthy performance of the plant. For lovers of nature, ‘Flowers’ are a special attraction as we cannot imitate the structure, color and the fragrance.
| SIMILARITIES | DIFFERENCES | ||
| PLANTS | ANIMALS | PLANTS | ANIMALS |
| Tube structure for nutrient and water movement to different parts of the organism | Circulatory system are operated by gravity / water surface tension | Circulatory system is pump operated | |
| Xylem and phloem | Arteries and veins | Only water solutions flow | Have cells moving as well |
We, humans are plant-like – when we are babies’ complex processes of development take place in us and we hardly realize that we exist. Like plants, we respond to environment around us in ways that are largely pre-determined by our nature. The process of becoming conscious of our situation begins only later, when as toddlers we begin to isolate specific features in our surroundings that are of interest to us and we learn to name and relate to them in various ways. But, there are even more subtle ways in which plants and we are alike. Classical experiments performed by Jagadish Chandra Bose (1907-1927) have shown that plants respond quite distinctly to love and anger; to a peaceful atmosphere or one filled with threats of violence; to beautiful or jagged noise; their growth, their state of health, their life span are all affected by the subtle influences in their surroundings, much as people are.
Sathya, Dharma, Shanthi, Prema and Ahimsa are virtues that determine an orderly, prosperous and purposeful life for human beings. In fact, these five virtues are as important to human beings as the environmental factors to plants. The environmental factors influence characteristic responses (adaptations as they could be referred to) which shape their life processes. These visible characteristics (Morphology – external appearance) are manifestations of hundreds of subtle internal adjustments by different parts of the plant to attain homeostatic balance following disturbance in the environment around them. Human beings provide behavioral responses in shaping their personality under various situations against the five virtues mentioned above.
Forest development
FOREST DEVELOPMENT – ONE SQUARE KILO METER (100 HECTARE)
| Sl. No. | Item | Unit | Quantity | Rate(Rs.) | Cost (in Rs.) | ||
| 1. | Barbed wire fencing – 4 m height with angle at a distance of 3 m center to center | meter | 5000 | 30 | 150,000 | ||
| 2. | Pit making – 1 m x 1 m | Nos. | 100,000 | 7 | 700,000 | ||
| 3. | Saplings | Nos. | 100,000 | 6 | 600,000 | ||
| 4. | Manuring and soil treatment of pits | Nos. | 100,000 | 7 | 700,000 | ||
| 5. | Plantings | Nos. | 100,000 | 1 | 100,000 | ||
| 6. | Watering (Tube well) | Nos. | 2 | 100,000 | 200,000 | ||
| 7. | Garden Maintenance | ||||||
| a. I Year 250 plants per person (assuming 80% plant survival per sq.km.) | 80,000 | 22 | 1,760,000 | ||||
| b. II Year – 500 plants | 40,000 | 22 | 880,000 | ||||
| c. III Year | 40,000 | 22 | 880,000 | ||||
| SUB TOTAL | 5,970,000 | ||||||
| 8. | Other miscellaneous items – 10% of the above | 597,000 | |||||
| GRAND TOTAL | 6,567,000 | ||||||
| Standard practice of Forest Department : 1000 plants per Hectare | |||||||
| Normal planting at NTPC:
Normal spacing between plants Total number of plants over 81 Sq. M Total Number of plants per Acre (4047 Sq.M) Total Number of plants per Hectare ( 2.47 Acres OR 10000 SQ.M. |
3 M 16 799.4 1,97,453 | ||||||
| COST PER SQ.KM | Rs. 65,67,000 | (1989) | |||||
| COST PER SQ.KM. | Rs. 65,67,000 | +Rs.13,13,000 (20% Escalation) | |||||
| COST PER PLANT | Rs. 41.65 | ||||||
| 1 m3 of biomass | Sequesters 0.26 tons of Carbon |
| 24 m3 of biomass ( one Hectare) | Sequesters 6.24 tons of Carbon |
| 465 million hectare
(11.16 billion m3 biomass) | Sequesters 2.9 billion tons of carbon |
| 9 X 9 m = 81 Sq. M | Acre 4047 Sq. m | Number of plants | Cost per plant (in Rupees) | ||
| Hectare | Sq. Km. | 1989 | 1990 | ||
| 8 | 404 | 10,000 Sq.m
Rectangular, 2.5 x 4 m | 10,00,000 | 65.67 | 78.80 |
| 9 | 448 | 1,111
Square 3 x 3 m | 11,11,000 | 59.1 | 70.93 |
| 10 | 505 | 1250
Line planting 2 x 4 m | 12,50,000 | 52.53 | 83.04 |
| 15 | 747 | 1848
Triangular 2,5 m | 18,40,000 | 35.53 | 42.64 |
| 26 | 1293 | 32000
Quincunx planting | 32,00,000 | 29.53 | 24.6 |
Plants and humans
PLANTS AND HUMANS:
There are genetic and biological reasons for us to be more closely related to nearly everything than we previously thought. It was originally thought that land-based life forms came from the many different types of algae floating around the sea. Now it looks like first life happened to fresh water and the original land-based life came from only one type of algae in that fresh water. This means that we’re more closely related to anything on land than water-based algae – even the stuff that’s evolved symbiotically with us and is swimming around our guts right now.
The basic structure of DNA (i.e. Double Helix) is shared among all living organisms. The code or sequence of DNA (instructions for our cells) is different. Even so, our DNA is likely more similar to plants than different. For example, we share approximately 60% of our DNA with a banana plant.
But how do we know that that common ancestor budded out plants and fungi so far apart that the fungi are closer to us than to plants? We take a look at genetic similarity, and how that kicks over into physiology. There was a marked lack of chlorophyll in the near history of both animals and fungi. We both took a step away from photosynthesis before we started becoming what we are. Fungal cell walls are made of chitin, the same thing that makes up insect’s outer carapaces, but is found nowhere in the plant world. Fungal proteins look more like animal than plant proteins. And then there are sterols – important alcohol groups that play a part in everything from biological messenger systems to cell walls. For a long time, these were considered the Achilles Heel of the fungi-animal connection, because while animals have cholesterol, fungi have ergesterol. How could they be alike if they differ in such a fundamental way? Then it was discovered that both animals and fungi contained a component called lanosterol, while plants had nothing like it. The weakest link turned out to be the strongest argument.
Obviously, no one’s committing cannibalism when they eat a mushroom risotto. Still, it’s clear that whatever the common ancestor between humans and mushrooms was, it was closer to us than it was to plants. The flavor we’re savoring in that risotto has more in Both Plants and Humans are living organisms
- Both Plants and Humans need things to keep them living
Plants – sunlight, Carbon Dioxide, and water
Humans – Calories, Oxygen, and water
- Both produce substances that keep the other living
- Plants produce oxygen which humans breathe in, in return humans breath out carbon dioxide for plants to create oxygen as a byproduct of Photosynthesis
- Both Humans and Plants reproduce through sexual means by fertilization, but plants are hermaphrodites
- Both Plants and Humans are multi-cell organisms, except that plants are made of plant cells, and humans are made of animal cells
Common with us than it does with the rice. Maybe that’s why we like it so much.
Plants and spirituality
PLANTS AND SPIRITUALITY
In other words, by examining the type of vegetation, we can deduce the climatic factors. Similarly, by watching human behavior we can deduce the character development and also assess the degree of value development.
- The very existence of life in Nature can be spoken of as ‘Sathya’ or ‘Truth’
- Abiding strictly to the natural laws that are appropriate to their own kind Is their adherence to ‘Dharma’ or ‘Righteousness’
- Natural vegetation with its greenery has always been considered a universal Symbol of ‘Shanthi’ or ‘Peace’
- In its flowering and fruition, plants reflect abodes of ‘Prema’ or ‘Love’
- In their silent and patient endurance and harmlessness, plants are true essence Of ‘Ahimsa’ or ‘Non-violence’
Flowers have been cultivated for their beauty and aroma from earliest times. They are veritable treasure houses filled with symbolic associations that have been preserved in the legends of most cultures. Large trees are principally identified on the basis of their flowers (reproductive organs and produce seed bearing fruits)

Every flower is a terminal branch consisting of a modified stem – the floral axis or ‘Receptacle’ which bears specialized appendages (modified leaves) arranged in whorls. In a typical flower, the outermost whorl CALYX consists of sepals which protect the flower bud before blooming; the next whorl COROLLA consists of petals often bearing nectar producing glands that aid in attracting pollinators; ANDROECIUM, the third whorl consists of stamens which produce pollen in anthers necessary for reproduction; The innermost or higher whorl GYNOECIUM consists of several carpels each of which contains placenta to which the ovules (immature seeds) are attached. Flowers with all four appendages mentioned above are considered ‘COMPLETE.
In complete flowers of di-cotyledons, the basic number of each of the floral organ (Sepal, Petal, Stamen & Carpel) is five or multiples of five (PENTAMEROUS)
This number is significant in many ways. Soul of humans has been viewed in the spiritual teachings as the conscious witness (PURUSHA) embodied in a blended complex of FIVE ELEMENTS – space (Ether), Air, Fire, Water and Earth and set in motion by the action of five vital airs – PANCHAPRANAS (pancha is five, Prana is life). Similarly, PANCHENDRIYAS (Ear, Eye, Nose, Tongue and Skin) are five sheaths in which the SOUL is encased. There are innumerable examples of this basic number – FIVE.
Considering the PENTAMEROUS flowers, one is always reminded of these five values / virtues:
Thalamus or RECEPTACLE along with the other floral appendages makes a unit of FIVE. Since each of the floral appendages has a specific role in the ultimate objective of perpetuation and propagation through seeds, we could equate them to values:
- RECEPTACLE, the seat of all the four appendages is the truth or SATHYA
- Sepals meant to protect floral bud before blooming, as DHARMA
- Petals in varied colors and filled with nectar attracting and rewarding pollinators as PREMA
- Stamens, pollen transfer from anthers to stigmatic surface gently and harmlessly as AHIMSA
- When the act of fertilization culminates in the fructification, Carpel, centrally placed floral organ can be considered as Shanthi.
In a way, FLOWER is an embodiment of all the five cardinal values / virtues.
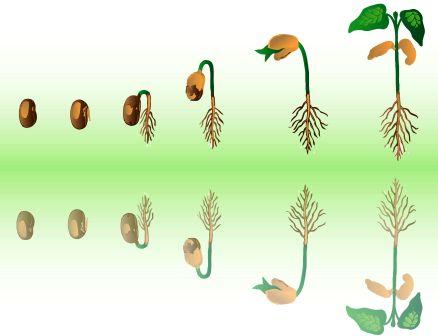
The initial life process between plants and animals indeed are so strikingly similar that one would be surprised – the fertilized egg, result of an union between male and female reproductive organs, makes the mark of a ‘NEW LIFE’ on earth. Biology / Medical professionals interpret this beginning as a combination of ‘Typical Characters’ of both the contributors.
While there is a subtle change in the ‘Seed Formation’ in plants, the resultant product – Egg – in humans derives nutrition from the Mother right from day one. A SEED is a ripened ovule containing an embryo. A fruit, in terms of origin, is a ripened ovary containing the seeds. Both ovule and ovary are in the pistil of the flower. To identify seeds and fruits correctly, one has to follow the development of these parts to maturity.
Growth of the fertilized egg and its differentiation into an embryo plus a surrounding coat—the seed; and maturing of the seed, usually with an accumulation of stored food marks the beginning of a new life among plants. The differentiation into Dicot and monocot is based on the number of cotyledons (1 or 2) which facilitate initial nutrition to the embryo in transforming into distinct – ground (Root) and aerial(Leaf) portions. The sapling as this is referred to, from this stage onwards does not lean on anything else for nutritive requirement and thus they are called – Autotrophs (Synthesize their own food in the presence of light and carbon dioxide.
‘Zygote’, the single cell is a capsule that stores tremendous information of the form that is attained over a period of time – both in plants and animals. The repeated multiplication of this single cell evolves into different forms and functions depending upon their positions.
When we consider the mature plant, we realize that it rooted firmly in the soil, the trunk supports innumerable branches carrying foliage (leaves). The tree starts fruiting and seeding every year depending upon the nature of the plant.
The xylem vessel is specialized to transport water and dissolved minerals from the root up to all the other parts of the plant, and also to helps supporting the stem and strengthening it.
This is a long tube that runs alongside the xylem tissue. They are made of long narrow tubes with perforated sieve plates along the thin length.
The function of the phloem tissue is to transport food nutrients such as glucose and amino acids from the leaves and to all other cells of the plant, this is called translocation.
Unlike the xylem, the phloem tissue is made of columns of living cells, which contains a cytoplasm but no nucleus, and its activities are controlled by a companion cell next to it which has a nucleus, but companion cells have no function in translocation.
In addition to these main transporting systems in plants, there is another striking network – Venation – in the foliage (leaves). Understandably, the pattern varies according to the leaf shape as indicated in the figure below.
The venation pattern facilitates material transportation to every inch of the plant. Leaves are also provided with openings called ‘Stomata’ through which it respires taking carbon dioxide into them and releasing the most vital element of survival – Oxygen – to humans. Water molecules combined with carbon dioxide and sunlight make plants – Autotrophs (synthesize their own food) – perhaps the only organism on earth to do so.
It is this special character of plants that support innumerable living organisms on earth including HUMANS. Plants as mentioned above, has in addition, the ability to synthesize (similar to the process in a chemistry laboratory) vital chemicals of utmost value and importance to humans – vegetables and fruits do provide ingredients pretty vital to the human body in many ways. The exceptional plants with curative properties generally are referred to as ‘Medicinal Plants’.
Plants, which provide vital Oxygen for human survival cries at the roof top that it has manufactured vital ingredients in its factory (physiology) and urges you to consume them in the form vegetables and fruits. DO WE LISTEN TO THE CRY? BIG NO as we listen to the doctor and take shelter in tablets without even questioning once. If only we realize the potential of plants (Vegetables/Fruits/Medicinal), we could keep the hospitals and the doctors away forever
- Vegetables, are low in calories and fats but, contain good amounts of vitamins and minerals. All the Green-Yellow-Orange vegetables are rich sources of calcium, magnesium, potassium, iron, beta-carotene, vitamin B-complex, vitamin-C, vitamin-A, and vitamin K.
- Vegetables too are home for many These health benefiting phyto-chemical compounds firstly; help protect the human body from oxidant stress, diseases, and cancers, and secondly; help the body develop the capacity to fight against these by boosting immunity.
- Vegetables are packed with soluble as well as insoluble dietary fiber known as non-starch polysaccharides (NSP)such as cellulose, mucilage, hemi-cellulose, gums, pectin…etc. These substances absorb excess water in the colon, retain a good amount of moisture in the fecal matter, and help its smooth passage out of the body. Thus, sufficient fiber offers protection from conditions like chronic constipation, hemorrhoids, colon cancer, irritable bowel syndrome, and rectal fissures.
…Go for greens today to help you stay fit and healthy!
Human embryo development
HUMAN EMBRYO AND ITS DEVELOPMENT
Human fertilization is the union of a egg and sperm, usually occurring in the ampulla of the uterine tube. The result of this union is the production of a zygote cell, or fertilized egg, initiating prenatal development. Scientists discovered the dynamics of human fertilization in the nineteenth century.
The process of fertilization involves a sperm fusing with an ovum. The most common sequence begins with ejaculation during copulation, follows with ovulation, and finishes with fertilization. Various exceptions to this sequence are possible, including artificial insemination, In vitro fertilization, external ejaculation without copulation, or copulation shortly after ovulation. Upon encountering the secondary oocyte, the acrosome of the sperm produces enzymes which allow it to burrow through the outer jelly coat of the egg. The sperm plasma then fuses with the egg’s plasma membrane, the sperm head disconnects from its flagellum and the egg travels down the Fallopian tube to reach the uterus.
This single cell – Zygote – carries the transcript of the physical form that evolves over a period of time. The uncountable multiplication of this single cell results in various parts of the human body – alimentary system, circulatory system, nervous system and so on for an effective and successful functioning of the body through the life. The co-ordination among these systems are simply marvelous.
Humans also seem an exception apart from being intelligent the only living organism to lean on the medical fraternity for help and allow them to control the body. There are many animals (mammals) who are at the mercy of rigorous nature who are least cared by the doctors unless of course, the owners of the pets afford treatment. If we look at the domestic insect populations, they breed happily and live happily without any medical attention.
We fail to recognize the intricacies of a wonderful co-ordination among the various organs of this amazing human body that develops from a single cell – the Zygote (simply a genetic mix of male and female partners and which carries the entire transcription of all the features of male or female child).
We are slaves of our own misthoughts and misgivings which ultimately leads to succumbing to the medical revelations pretty seriously and losing our mental balance. I believe strongly that these are our own mental misgivings which at best could be evaluated through daily body response. I have always maintained a steady health through regular walk and a few yogic exercises. I have always wondered how this human body which is simply a manifestation of single cell – Zygote- that multiplies several times and carves out every organ of the body with specific function and the coordination among the major organs like, Brain, Lungs, and Heart and Alimentary systems is extremely fascinating.
In fact, it is said that “You are what you eat”. Whether you are a vegetarian or non-vegetarian, the energy intake into the system manifests itself into good, bad and the ugly.










